1 实验方法
使用多弧源电弧离子镀设备(MAD-4B型)在W18Cr4V高速钢基体上沉积(CrTiAl)N硬质膜。为了保证所沉积的(CrTiAl)N硬质膜具有可对比性,均采用双阴极弧源靶[11],分别为Ti-Cr合金靶(名义成分为Ti∶Cr=60%∶40%,原子分数)和Cr-Al合金靶(名义成分为Cr∶Al=60%∶40%,原子分数)。对2个弧源靶电流进行不同组合以实现膜层成分的改变(表1)。其它沉积条件,如气体流量(压强)、沉积时间、沉积温度,则相同,各镀膜试样分别标记为1#~4#。为了与(TiCr)N硬质膜比较,使用2个Ti-Cr合金靶(名义成分为Ti∶Cr=60%∶40%),沉积弧电流均为55 A,其它沉积条件同上,制备出的试样标记为0#。为了使膜层具有较高的附着强度,在氩气(3.0×10-1 Pa)气氛中用高负偏压(-320 V~-350 V)双靶弧光预轰击高速钢基片的方式清洗12 min,弧光轰击开始初始镀膜温度为180℃。然后,依次沉积合金过渡层(持续8 min、偏压降为-200 V)、低N2流量膜层(持续15 min、偏压-180 V)、正常N2流量膜层(持续37 min、偏压-180 V),如图1所示。镀膜结束时真空室的温度为200±10℃。
表1 (CrTiAl)N和(TiCr)N硬质膜的沉积工艺参数
Table 1
| Film samples | Cathodic arc current/A | |
|---|---|---|
| TiCr | CrAl | |
| 1# | 60 | 48 |
| 2# | 55 | 50 |
| 3# | 50 | 55 |
| 4# | 48 | 60 |
| 0# | 55\55 | ~ |
图1
用S-4800Ⅱ型扫描电镜(能谱)观察(CrTiAl)N膜和(TiCr)N膜的表面形貌和断面形貌。用X’Pert PRO型X射线衍射仪分析膜层的相组成,辐射源为Cu靶(λ=0.154 nm),电流40 mA,电压40 kV,扫描范围为10°~90°,步长为0.05°。用402MVD型维氏硬度计测试高速钢基片表面膜层的硬度,同一视场分取三个位置,荷载为10 gf,保持时间为15 s。
2 结果和讨论
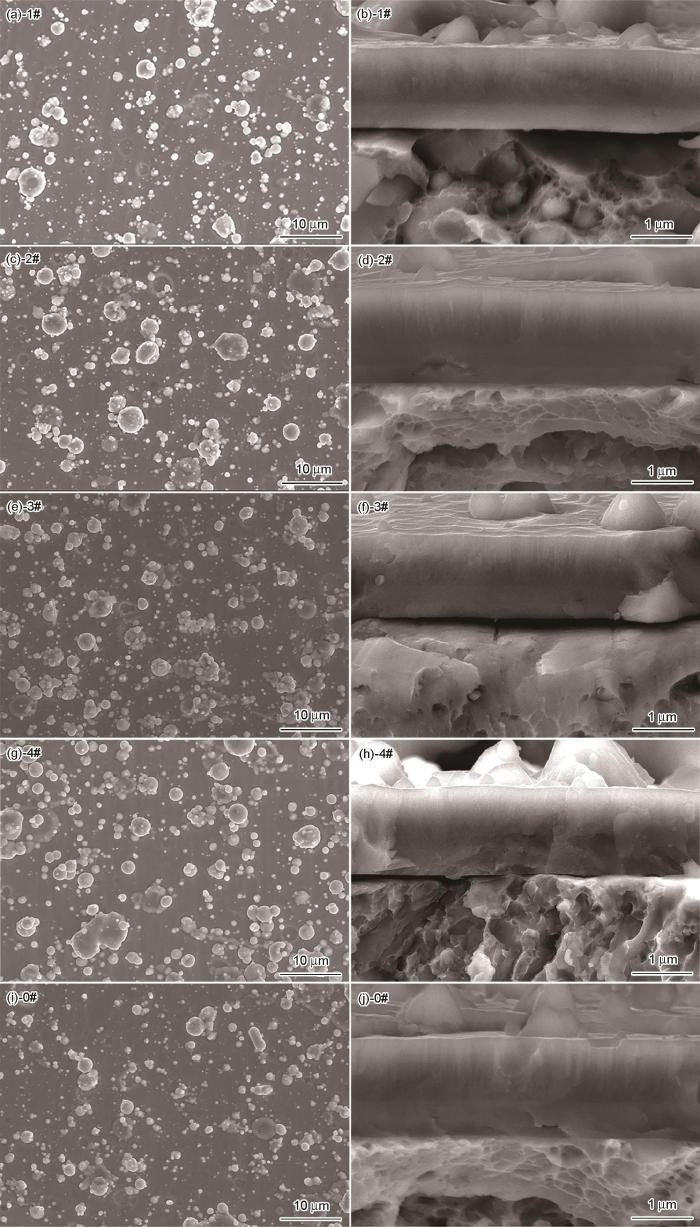
2.1 膜层表面和断面形貌
图2
图2
(CrTiAl)N膜和(TiCr)N膜的表面和断面形貌
Fig.2
Surface and fracture section morphology of the as-deposited (CrTiAl)N and (TiCr)N films
在本文的沉积实验中,设定两个阴极弧源靶的电流之和基本相同,为105~110 A,且其沉积时间均为8+15+37 min;这些条件,保证了沉积过程中氩气、氮气流量相同,使膜层沉积温度(200±10℃)、膜层N含量、膜层的微观组织形貌以及膜层厚度基本相同(试样0#膜层厚度稍微偏大)。因为膜层成分的差别主要来源于弧源靶成分的差别,膜层性能的差别主要决定于膜层元素(膜层成分)和相组成。而膜层的相组成又由膜层的成分变化所决定,以上条件保证了以膜层成分作为膜层性能变化的单一影响因素。
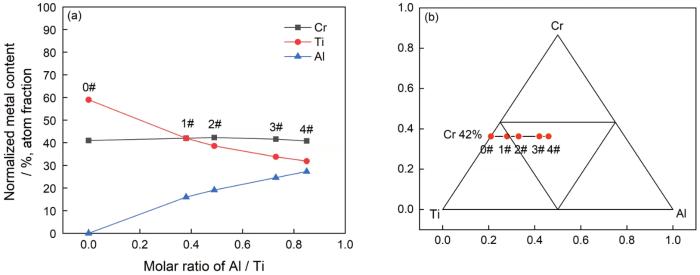
2.2 膜层表面成分分析
图3
图3
(CrTiAl)N膜的Al/Ti摩尔比以及对应的(归一化后)金属元素含量
Fig.3
Al/Ti molar ratio and the corresponding metal content of (CrTiAl)N films (normalized)
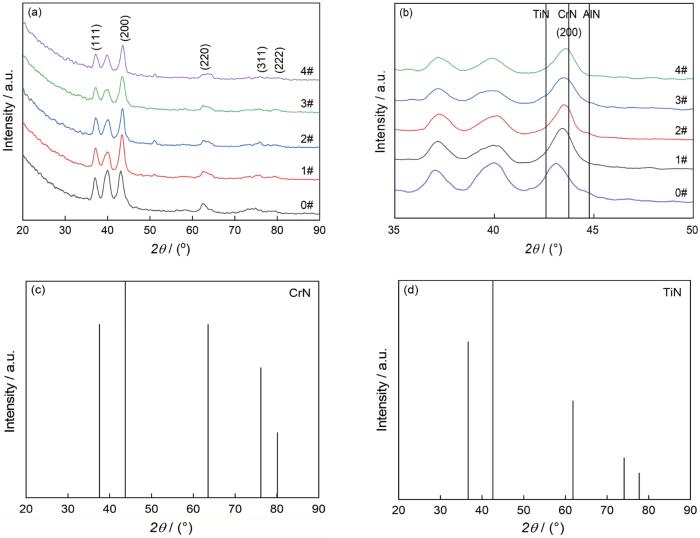
2.3 膜层的相结构
对膜层样品进行小角度XRD测试并使用JADE软件处理,得到图4a中的衍射谱。可以看出,所有膜层样品XRD衍射谱的衍射峰强度分布相似。结合CrN、TiN的标准衍射图谱(图4c和4d)确定出,(CrTiAl)N膜由有置换式固溶体型特征的面心立方(CrTiAl)N相和TiCr(Al)合金相组成,没有TiN相、CrN相以及AlN相。膜层表面的大颗粒来自于沉积过程中的阴极弧源靶表面金属熔滴,生成了由Cr、Ti(Al)元素组成的CrTi(Al)合金相[15,17]。分析各膜层的XRD图谱发现,随着Al/Ti摩尔比的增大衍射峰趋于向大角度偏移(图4b),表明Al原子部分替代Ti原子使晶格常数减小。采用织构系数计算公式计算出面心立方(CrTiAl)N相(200)、(111)晶面的衍射系数,其值均大于1,表明(CrTiAl)N膜层具有(200)、(111)晶面的双择优生长取向。
图4
图4
(CrTiAl)N膜的XRD衍射谱和CrN、TiN的标准衍射谱
Fig.4
XRD patterns of (CrTiAl)N films and the standard diffraction patterns of CrN and TiN films
同时,多弧离子镀TiAlN/TiN多层膜的研究表明,工艺参数(负偏压增大)的变化使择优取向从(200)晶面转变到(111)晶面[26];而对多弧离子镀TiAlN/CrN多层膜的研究则表明,虽然单层膜TiAlN和CrN均具有(200)晶面的择优生长取向,但是TiAlN/CrN多层膜的择优取向却是(111)晶面[27]。这些结果表明,沉积技术工艺的不同使制备出的Ti、Al、Cr多组元氮化物膜系中各个膜层的择优取向不同,却都容易形成固溶体式结构而不容易出现TiN、CrN、AlN等分离的第二相。在本文的研究中,由于前述沉积工艺基本相同,单一的成分变化并未引起相组成和晶体结构形式的变化,所有膜层均为置换式固溶体型特征的面心立方(CrTiAl)N相构成。这表明,这些膜层性能的变化源于成分变化的影响,而这种影响主要是晶格畸变引起的固溶强化。
根据(CrTiAl)N膜层XRD谱中特征衍射峰的位置,使用JADE软件可计算出面心立方固溶体型(CrTiAl)N相的晶格常数;将(CrTiAl)N膜当做TiN相、CrN相及AlN相形成的置换式固溶体处理,其各自比例以金属元素浓度归一化后的比例代替,根据VEGARD定律可计算出各组膜层试样面心立方固溶体结构的理想化晶格常数,如图5所示。可以看出,随着膜层Al/Ti摩尔比的增大晶格常数减小。其原因是,在CrN比例一定的条件下Al/Ti摩尔比的增大意味着Al含量的增大和Ti含量的降低,即点阵中的部分Ti原子被Al原子所代替,从而引起晶格收缩形变,使晶格常数减小。同时,与CrN、TixZryN、Ti1-xCrxN等氮化物膜的结果相似,实际测得的本文所有(CrTi)N、(CrTiAl)N膜层试样的晶格常数均高于根据VEGARD定律的理论计算值[22,25]。膜层的沉积过程为非平衡过程,膜层中的点缺陷和残余热应力使晶格常数增大[28]。与(CrTi)N膜层相比,(CrTiAl)N膜层的晶格畸变更为复杂,更容易使缺陷增加从而使晶格常数与VEGARD定律计算值的偏离更大。而随着Al含量的提高(Al/Ti摩尔比≤1),这个偏离随之变大。
图5
图5
(CrTiAl)N膜的实测晶格常数与根据VEGARD定律计算结果的对比
Fig.5
Comparison between the measured lattice constants of (CrTiAl)N films and the calculated from Vegard's law
2.4 膜层的显微硬度
所有膜层样品显微硬度的测试结果,如图6所示。可以看出,Ti58Cr42N膜层的硬度约为3500HV,Al原子部分替代Ti原子,生成了(CrTiAl)N固溶体相。Al/Ti摩尔比较小时,膜层的硬度没有大的提高;当Al/Ti摩尔比接近0.5时膜层硬度出现极大值,达到4200HV;而Al/Ti摩尔比进一步增大则膜层硬度降低,Al/Ti=0.85时的硬度甚至降为2600HV,明显低于Ti58Cr42N膜层的硬度。这表明,在CrN浓度不变的条件下,加入少量的Al原子并不能使(CrTi)N固溶体膜层发生进一步的固溶强化,只有当Al浓度提高到一定程度才能显著提高(CrTiAl)N固溶体相的硬度,而加入过量的Al原子反而使(CrTiAl)N固溶体相的硬度降低。
图6
图6
Al/Ti摩尔比对(CrTiAl)N膜硬度的影响
Fig.6
Effects of Al/Ti mole ratios on hardness of (CrTiAl)N films
在保持面心立方晶格结构的前提下,随着第二金属组元加入,两个金属组元成分趋近,Ti-Al-N、Ti-Zr-N、Ti-Nb-N、Cr-Al-N等三组元置换式固溶体氮化物硬质膜层的硬度增大,当金属组元比例约为1:1时达到极大值。其原因是,晶格畸变产生了固溶强化[7~9]。本文的研究实现了相近的沉积工艺、相同的膜层组织、厚度和相结构,各膜层的差别只是成分变化引起的固溶体中晶格畸变引起的。一方面,作为对照的面心立方固溶体Ti58Cr42N膜层,其晶格畸变有明显的强化作用,硬度接近于(TixCry)N固溶体膜层系中的硬度极大值;另一方面,Al原子的加入输出了(CrTiAl)N固溶体相,TiN、CrN、AlN晶格常数的差异使晶格畸变更为复杂。从膜层成分的角度来看,即使CrN的含量不变,Al/Ti摩尔比的增大和Al、Ti、Cr的含量趋近(图3a和b)仍然不能保证单调的晶格畸变加剧。这表明,(CrTiAl)N固溶体型膜层的硬度并不随着Al/Ti摩尔比的增大而单调变化。
3 结论
(1) 以Ti58Cr42N为基础,在确定Cr含量(在金属元素中的占比为42%)的条件下,在(CrTi)N中添加第三金属组元Al可形成(CrTiAl)N置换式固溶体膜层,不会形成CrN、TiN和AlN等杂相。
(2) 在Cr含量基本不变的条件下,单一改变Al/Ti摩尔比直接影响(CrTiAl)N膜层硬度,在硬度与Al/Ti摩尔比之间呈现非单调变化关系;与(CrTi)N膜相比,第三金属组元Al的添加并不能总是保证提高(CrTiAl)N置换式固溶体膜层的硬度。
(3) 在Cr含量基本不变的条件下,优化Al/Ti摩尔比可使(CrTiAl)N膜层的硬度明显高于(CrTi)N膜并达到超硬性。
参考文献
Mechanical properties and machining performance of Ti1-xAlxN-coated cutting tools
[J].
Investigation of the Properties of TixCr1-xN Coatings Prepared by Cathodic Arc Deposition
[J].
Mayrhofer. Influence of bias potential and layer arrangement on structure and mechanical properties of arc evaporated Al-Cr-N coatings
[J].
Interdependence between stress and texture in arc evaporated Ti-Al-N thin films
[J].
Characterization of Ti-Zr-N films deposited by cathodic vacuum arc with different substrate bias
[J].
Microstructure and nanohardness properties of Zr-Al-N and Zr-Cr-N thin films
[J]. J.
Metastable Ti1-xAlxN films with different Al content
[J].
Structure and hardness of vacuum arc deposited multi-component nitride coatings of Ti, Zr and Nb
[J].
Effects of Al contents on microstructures of Cr1-xAlxN and Zr1-xAlxN films synthesized by cathodic arc method
[J].
Deposition and characterization of TiAlZrN films produced by a combined steered arc and unbalanced magnetron sputtering technique
[J].
Mechanical properties and phase structure of (TiAlZr)N films deposited by multi arc ion plating
[J].
Properties of (Ti,Cr,Al)N coatings with high Al content deposited by new plasma enhanced arc-cathode
[J].
Microstructure and mechanical behavior of TiAlCrN multilayer thin films
[J].
Reducing the macroparticle content of cathodic arc evaporated TiN coatings
[J].
Effects of bias voltage on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,Al,Cr)N hard films with N-gradient distributions
[J].
Effects of nitrogen pressure and pulse bias voltage on the properties of Cr-N coatings deposited by arc ion plating
[J].
Influence of negative bias voltage on microstructure and property of Al-Ti-N films deposited by multi-arc ion plating
[J].
Effects of bias voltage on microstructure, mechanical properties, and wear mechanism of novel quaternary (Ti, Al, Zr)N coating on the surface of silicon nitride ceramic cutting tool
[J].
The effect of deposition conditions on the properties of TiN thin films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum-arc technique
[J].
Structural and mechanical properties of ZrN films prepared by ion beam sputtering with varying N2/Ar ratio and substrate temperature
[J].
Influence of Nitrogen Content and Bias Voltage on Residual Stress and the Tribological and Mechanical Properties of CrAlN Films
[J].
Deposition and characterisation of arc-bond sputter TixZryN coatings from pure metallic and segmented targets
[J].
Mechanical properties of hard AlCrN-based coated substrates
[J].
Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCrN films deposited by CFUBMS
[J].
Structure and properties of TiCrN coatings produced by the ion-plating method
[J].
Cathodic arc evaporation of (Ti,Al)N coatings and (Ti,Al)N/TiN multilayer-coatings—correlation between lifetime of coated cutting tools, structural and mechanical film properties
[J].
Structural and mechanical properties of nanolayered TiAlN/CrN coatings synthesized by a cathodic arc deposition process
[J].
A comparative study of structure and residual stress in chromium nitride films deposited by vacuum arc evaporation, ion plating, and DC magnetron sputtering
[J].