处理放射性气态碘的方法,有液体吸收法和固体吸附法[6]。液体吸收法,是使放射性碘气体通过吸附液发生化学反应以使其除去,此法产生大量的放射性液体废物且捕集效率较低。固体吸附,是用较大比表面积的吸附材料对放射性气体进行物理和化学吸附[7]。常见的固体吸附材料,有活性炭(煤基活性炭、活性炭纤维等)[8]、金属有机框架材料(ZIF-8)[9]、气凝胶材料(二氧化硅气凝胶、金属硫化物气凝胶)[10]、金属改性陶瓷(Al2O3)[11]以及金属材料(Ag、Cu等)[12]。活性炭纤维(ACF)的比表面积大和孔道结构发达,吸附活性位点较多。上海纺织科学院研制的核级活性炭纤维,对放射性单质碘的吸附效率为99.7%,对放射性甲基碘的吸附效率为99.6%[13]。研究表明,粘胶基活性炭纤维对单质碘、甲基碘的吸附容量分别为1.36 g/g和0.2 g/g。对活性炭纤维进行改性,可提高其对气态碘的吸附性能[14]。Ampelogova等[15]的研究表明,busofite型炭纤维对甲基碘的吸附容量可达0.25 g/g。Matyáš和Engler[16]研发的二氧化硅高附银量的复合材料对放射性碘分子吸附可达0.44 g/g,吸附后其结构稳定。叶明吕等[17]发现,附银丝光沸石对气态碘的吸附性能稳定,水蒸气和氮氧化物不影响吸附性能。附银吸附材料,是通过浸渍将银离子负载到多孔材料中,银离子与气态碘发生反应实现对气体的捕集,捕集后生成的碘化银产物的稳定性较高[18];目前,附银材料对碘的吸附容量小、吸附效率和利用率较低。纳米金属材料的比表面积较大、反应活性和选择性较高,是处理放射性废气的新型材料[19]。为了提高银对碘的吸附性能,可将银离子还原成纳米银以增加吸附活性位点。但是,在纳米银材料的制备过程中出现的团聚使其对碘的吸附性能降低[20]。使用大比表面积的基体材料负载纳米金属,可将纳米金属均匀分散在基体材料中制备出高比表面积的吸附材料。本文用原位自还原制备纳米Ag0@ACF材料,研究其对气态碘的吸附性能。
1 实验方法
1.1 实验用材料和仪器设备
实验用材料和试剂:活性炭纤维(ACF)(以棉纤维为原料、ZnCl2为活化剂,用自黏结成形法制备,活化温度为600 ℃,成型压强10 MPa,有丰富的官能团,以微孔为主,比表面积为1743 m2/g,平均孔径为2.17 nm)。硝酸银(AgNO3)、单质碘(I2)、甲基碘(CH3I)。均为分析纯。
实验用仪器:电子天平;高温烘箱;升降烧结炉;场发射扫描电镜SEM(Ultra 55型),能量色散光谱仪EDS(EDX1800B型);X射线衍射分析仪XRD(BRUKER D8型);Quantachrome Autosorb-iQ全自动比表面和孔径分析仪(BET);X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)。
用SEM观测材料的表面形貌,结合EDS定性和定量分析材料的元素组成及其分布。测试XRD谱的扫描范围为10°~80°,步长为0.02°,扫描时间为0.05 s。用全自动比表面和孔径分析仪测定材料的孔径分布和N2吸附-解吸等温线;用XPS分析材料中元素的价态。
1.2 活性炭纤维负载纳米银Ag0@ACF的制备
用水热合成法和高温真空自还原法制备Ag0@ACF复合材料。将不同浓度的AgNO3溶液(1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, 5%)和活性炭纤维ACF(5 cm × 7 cm)放入容积为100 mL的反应器(PTFE)中,然后将反应器放入80 ℃烘箱中进行水热反应24 h。将浸渍好的ACF材料在80 ℃烘干5 h。将改性后的ACF置于250 ℃的高温烧结炉(GSL-1750-S)中在4 h内将银离子还原为纳米银(还原剂为ACF自生炭源),制备出Ag0@ACF复合材料。将不同改性剂浓度的Ag0@ACF命名为xAg0@ACF (1%Ag0@ACF, 2%Ag0@ACF, 3%Ag0@ACF, 4%Ag0@ACF, 5%Ag0@ACF),其中x为改性剂浓度。
1.3 对气态单质碘和甲基碘吸附性能的测定
图1
式中q为单位质量碘的吸附容量(g/g),m0为吸附剂Ag0@ACF的质量(g),m1为Ag0@ACF吸附碘后的质量(g)。实验中使用三块平行样,材料的吸附量为其结果的平均值。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 Ag0@ACF吸附材料的结构
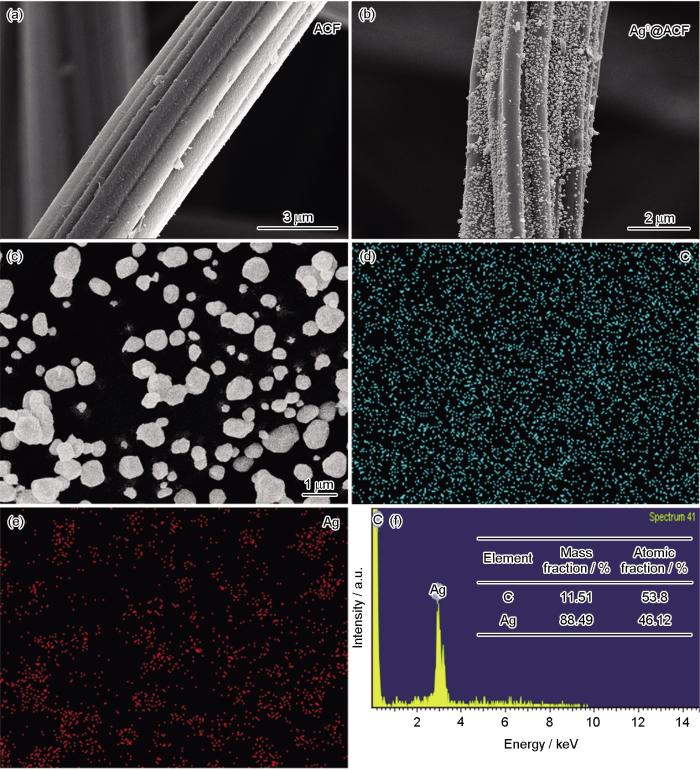
图2给出了ACF和Ag0@ACF复合材料的SEM-EDS图像。可以看出,活性炭纤维材料为束状纤维结构,表面光滑无杂质;Ag0@ACF材料的表面良好均匀地附着粒径约为百纳米的颗粒物质。为了测定颗粒物质的元素组成,对Ag0@ACF进行了EDS能谱扫描。图2a给出了ACF的SEM图像,图2b给出了Ag0@ACF的SEM图像。可以看出,ACF的纤维棒表面没有杂质。将ACF改性还原后Ag0@ACF的微观形貌发生了一些变化:许多纳米级颗粒物质均匀地分散在纤维棒表面。图2c~f给出了改性材料的能谱扫描,分析后可得到元素分布及含量。结果表明,改性材料中除了碳元素,还有银元素。元素的映射图像与SEM的图像一一对应,分布均匀。碳元素的含量最高,银元素的含量较低,因为材料的基体是ACF(碳和银的峰值信号清晰)。EDS结果表明,负载在ACF上的颗粒物质是单质银,纳米颗粒清晰可见。
图2
图2
ACF和Ag0@ACF复合材料的SEM照片以及Ag0@ACF的EDS-Mapping能谱
Fig.2
SEM images of ACF (a) and Ag0@ACF composites (b), and the corresponding EDS-Mapping spectra of Ag0@ACF (c-f)
图3
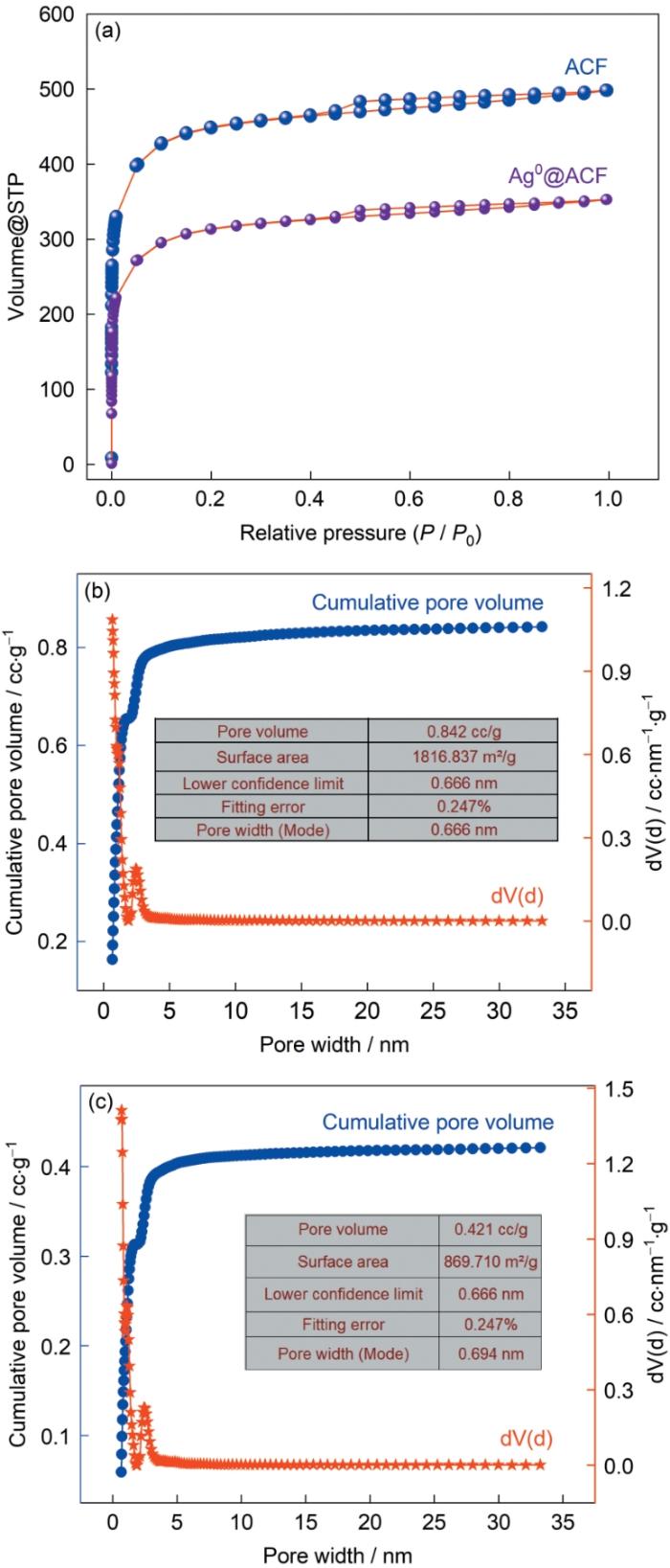
表1 Ag0@ACF的比表面积和孔容
Table 1
| Adsorbent | Specific surface area / m2·g-1 | Pore volume /cc·g-1 |
|---|---|---|
| ACF | 1816 | 0.842 |
| 1%Ag0@ACF | 1562 | 0.68 |
| 2%Ag0@ACF | 1403 | 0.642 |
| 3%Ag0@ACF | 1287 | 0.578 |
| 4%Ag0@ACF | 1095 | 0.492 |
| 5%Ag0@ACF | 915 | 0.421 |
图4
图4
N2的吸脱附曲线、ACF的孔径分布和5%Ag0@ACF的孔径分布
Fig.4
N2 adsorption and desorption curves (a), pore size distribution of ACF (b) and 5%Ag0@ACF (c)
2.2 改性剂浓度对材料吸附气态碘性能的影响
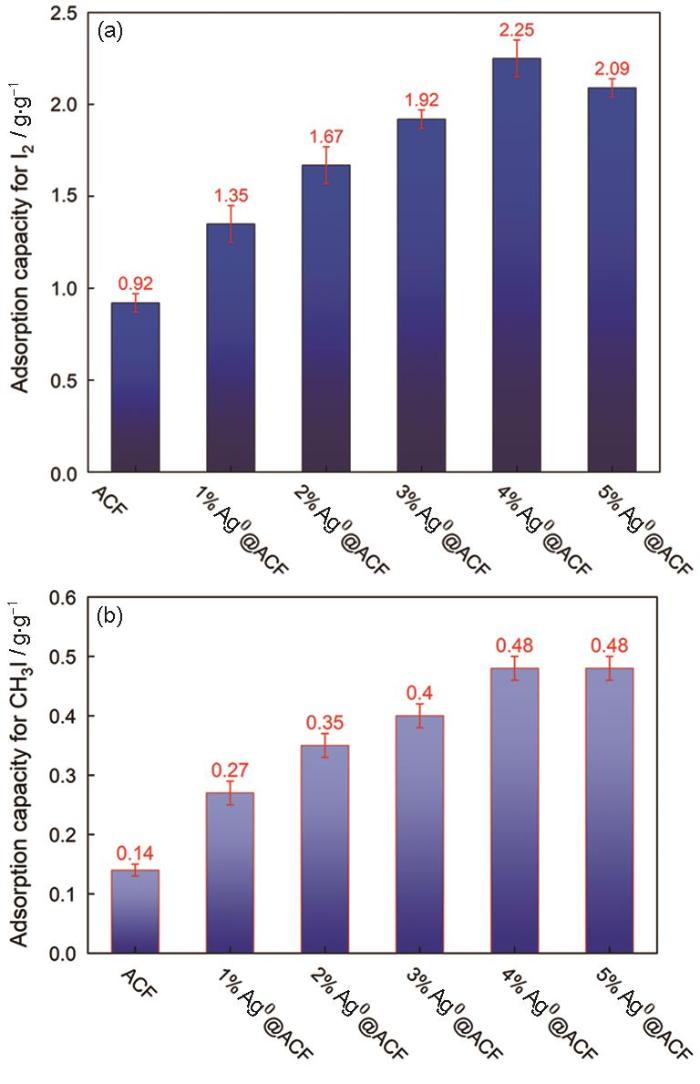
图5a,b显示了改性剂浓度对Ag0@ACF吸附碘性能的影响。改性剂的浓度分别为1%、2%、3%、4%、5%,在密闭反应釜中反应4 h。对气态单质碘和甲基碘吸附容量表明,随着改性剂浓度的提高材料对单质碘和甲基碘的吸附容量都随之提高。改性剂浓度为4%时吸附容量最大为2.25 g/g;浓度为5%时对单质碘的吸附容量明显降低,因为在ACF上负载过量纳米银团聚堵塞了孔道,使材料的比表面积减小而影响了材料的物理吸附。Ag0@ACF对甲基碘的吸附主要是化学吸附,改性剂的浓度越高吸附性能越高;浓度为4%~5%时的饱和吸附容量约为0.48 g/g。对Ag0@ACF吸附性能的分析表明,4%Ag0@ACF的吸附性能较为优异;比ACF(物理吸附)对单质碘和甲基碘吸附容量分别提高近2.5倍和3.5倍。纳米银的高反应活性,提高了材料对气态碘的化学吸附。
图5
图5
Ag0@ACF材料对单质碘及甲基碘的吸附容量
Fig.5
Adsorption capacity of Ag0@ACF materials for elemental iodine (a) and methyl iodide (b)
2.3 吸附时间对气态碘吸附性能的影响
吸附时间对4%Ag0@ACF吸附气态碘的影响,如图6所示。可以看出,ACF对气态碘的吸附可分为三个阶段。吸附时间为0~20 min效果明显,迅速达到很高的吸附容量,属于高速吸附阶段。Ag0@ACF有丰富的活性位点,在较短的时间内就能与碘结合。吸附时间为20~60 min吸附速度明显降低,属于缓慢吸附阶段。时间超过60 min,吸附逐渐趋于平衡,吸附容量不随时间变化,属于平衡吸附阶段。结果表明,Ag0@ACF对气态碘的吸附平衡时间为60 min,单质碘的最大吸附容量约为2.25 g/g,甲基碘的最大吸附容量为0.48 g/g。改性材料的吸附性能优于其他吸附材料(表2),吸附速率和饱和吸附量较高;Ag0@ACF吸附材料对气态碘的高速吸附的性能,可能取决于纳米银较高的反应活性。
图6
图6
吸附时间对单质碘及甲基碘吸附性能的影响
Fig.6
Effect of adsorption time on the performance for elemental iodine (a) and methyl iodide (b)
表2 不同吸附材料对气态碘的吸附容量
Table 2
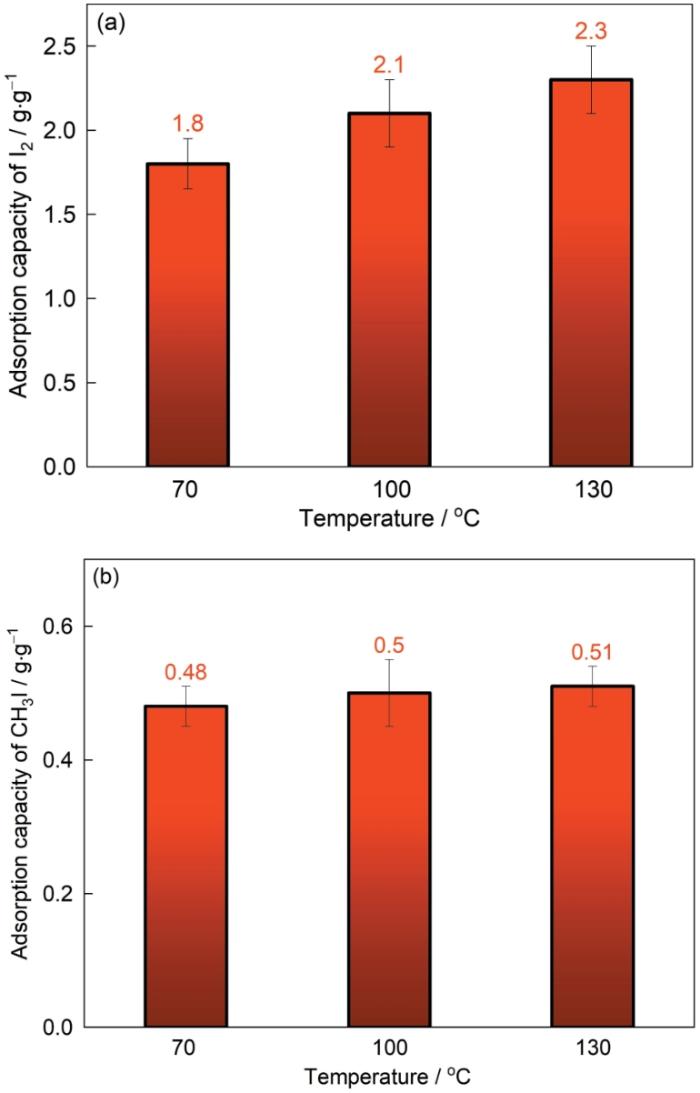
2.4 温度对吸附气态碘性能的影响
图7
图7
吸附温度对单质碘及甲基碘吸附性能的影响
Fig.7
Effect of temperatures on the adsorption performance for elemental iodine (a) and methyl iodide (b)
3 吸附机理
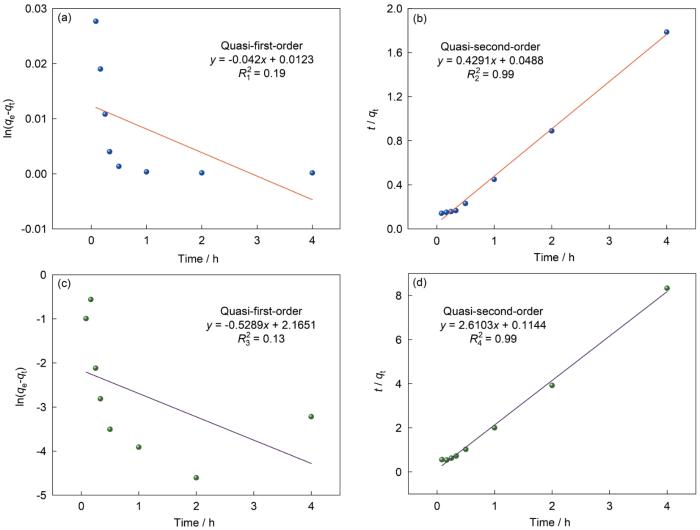
为了揭示Ag0@ACF对气态碘的吸附机理,采用准一阶和准二阶动力学模型[5]
分析了材料的吸附动力学。式中qe(mg/g)为吸附平衡时的饱和吸附容量,qt (mg/g)为吸附时间t下的吸附容量,常数k1(min-1)和k2(mg/g·min-1)分别为准一阶速率、准二阶速率。
图8给出了Ag0@ACF材料对气态碘吸附的两种模型动力学曲线。图8a、b给出了气态单质碘吸附的动力学模型曲线,图8c、d给出了气态甲基碘吸附的动力学模型曲线,表3列出了动力学参数。气态单质碘吸附的准一级动力学模型、准二级吸附动力学模型拟合的线性相关系数分别为
图8
图8
气态单质碘和气态甲基碘的吸附准一阶模型拟合曲线和准二阶模型拟合曲线
Fig.8
Quasi-first-order model fitting curves (a) and quasi-second-order model fitting curves (b) for elemental iodine adsorption, and quasi-first-order model fitting curves (c) and quasi-second-order model fitting curves (d) for methyl iodide adsorption
表3 Ag0@ACF对气态碘的吸附动力学参数
Table 3
| Adsorption kinetics of gaseous iodine on Ag0@ACF | Pseudo first-order | Pseudo second-order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe | K1 | R2 | qe | K2 | R2 | |
| I2 | 1.0123 | 0.042 | 0.19 | 2.3304 | 1.7455 | 0.99 |
| CH3I | 0.1147 | 0.5289 | 0.13 | 0.3830 | 2.3268 | 0.99 |
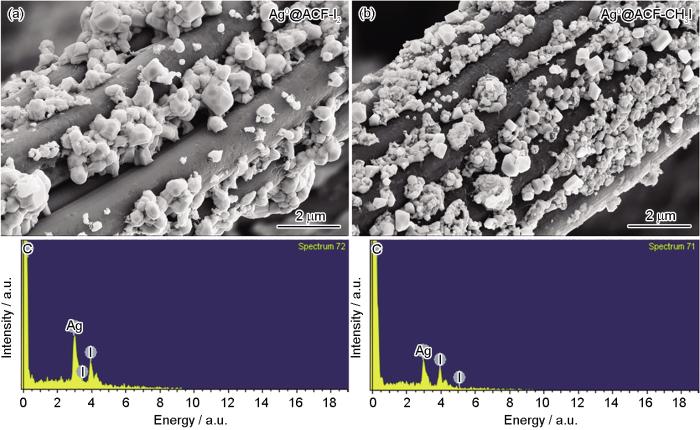
分析和表征了吸附后单质碘(Ag0@ACF-I2)、吸附后甲基碘(Ag0@ACF-CH3I)样品的微观形貌。图9给出了吸附碘样品的SEM-EDS图。分析结果表明,Ag0@ACF表面生长了较大的颗粒物,粒径尺寸为微米量级,分布均匀;与未吸附材料相比,表面的纳米级颗粒粒径明显增大。对吸附后样品的表面颗粒EDS能谱分析表明,其主要成分为Ag和I,即把气态碘较好的捕集到材料中。
图9
图9
材料吸附单质碘和甲基碘的SEM-EDS图
Fig.9
SEM-EDS plots of adsorbed elemental iodine (a) and adsorbed methyl iodine (b)
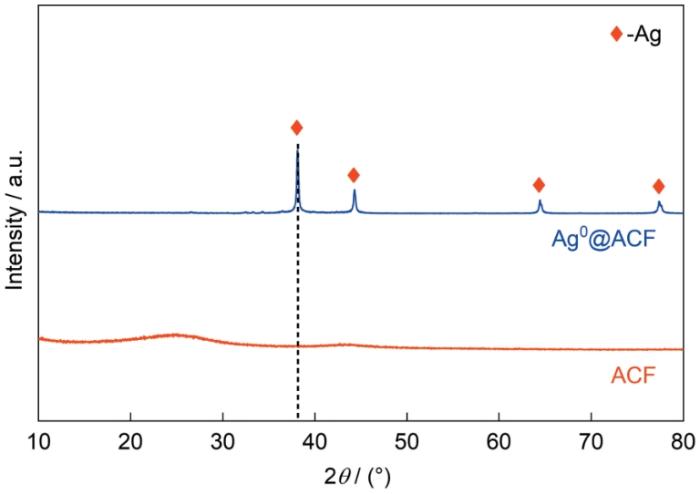
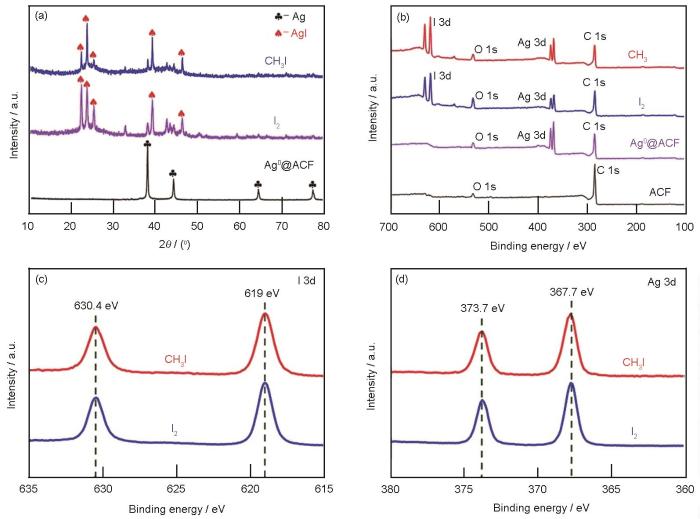
图10a给出了吸附前后材料的XRD谱。Ag0@ACF吸附气态I2和CH3I样品在谱中2θ为22.3°、23.6°、25.3°、39.2°、46.4°均出现了衍射峰,对应AgI的特征峰[29]。这种材料吸附气态单质碘和甲基碘均形成AgI,与吸附动力学分析给出的这种材料的吸附过程属于化学吸附一致。根据XPS分析了ACF、Ag0@ACF、吸附气态碘(I2、CH3I)样品的元素和价态。图谱分析数据表示在图10b中。在Ag0@ACF中检测出Ag元素,得到了Ag 3d的一组双峰谱;吸附气态碘样品不仅出现了银的双峰谱,还出现了I 3d的一组双峰谱,表明Ag0@ACF吸附了碘。图10c显示,I 3d在结合能为619、630.4 eV处出现了双峰谱,是碘离子典型的特征双峰谱(I-)[30]。在图10d过程的能谱中发现Ag 3d在结合能367.7、373.7 eV处出现了双峰谱;吸附后材料Ag的能谱明显向高能区偏移,表明吸附气态碘后样品中银价态为+1价[31]。对吸附气态碘前后物相结构表征以及价态分析表明,Ag0@ACF对气态碘的吸附是气态碘与银发生反应形成了稳定AgI的化学吸附,化学反应为
图10
图10
吸附碘样品的XRD谱和XPS能谱、吸附碘I 3d双峰谱对比、吸附碘Ag 3d双峰谱对比
Fig.10
Comparison of XRD diffraction of samples after adsorption of iodine (a), XPS energy spectrum of samples after adsorption of iodine (b), comparison of I 3d bimodal spectrum after adsorption of iodine (c) and comparison of Ag 3d bimodal spectrum after adsorption of iodine (d)
4 结论
(1) 进行水热改性可将银离子负载在高比表面积ACF材料的微孔中。利用活性炭纤维为炭源在纤维原位将银离子自还原为纳米银,可将高反应活性的纳米银负载在高比表面积活性炭纤维材料上制备纳米Ag0@ACF改性材料。活性炭纤维材料(ACF)有丰富的多孔结构,其对气态碘的吸附主要是物理吸附,吸脱附速率较高和容易解吸。
(2) 纳米Ag0@ACF对气态碘的吸附性能较高,随着改性剂浓度的提高其静态吸附性能随之提高。随着温度的提高这种材料的吸附性能随之提高。
(3) Ag0@ACF对气态碘的吸附符合化学吸附准二级动力学模型(R2 = 0.99)。Ag0@ACF对碘的吸附机制,是气态碘和银发生了化学反应生成了稳定碘化银,实现了对气态放射性碘的高效稳定吸附。
参考文献
Capture of organic iodides from nuclear waste by metal-organic framework-based molecular traps
[J].Effective capture of radioactive organic iodides from nuclear waste remains a significant challenge due to the drawbacks of current adsorbents such as low uptake capacity, high cost, and non-recyclability. We report here a general approach to overcome this challenge by creating radioactive organic iodide molecular traps through functionalization of metal-organic framework materials with tertiary amine-binding sites. The molecular trap exhibits a high CH3I saturation uptake capacity of 71 wt% at 150 degrees C, which is more than 340% higher than the industrial adsorbent Ag-0@MOR under identical conditions. These functionalized metal-organic frameworks also serve as good adsorbents at low temperatures. Furthermore, the resulting adsorbent can be recycled multiple times without loss of capacity, making recyclability a reality. In combination with its chemical and thermal stability, high capture efficiency and low cost, the adsorbent demonstrates promise for industrial radioactive organic iodides capture from nuclear waste. The capture mechanism was investigated by experimental and theoretical methods.
Adsorption of volatile polonium and bismuth species on metals in various gas atmospheres: Part I – Adsorption of volatile polonium and bismuth on gold
[J].
Adsorption of iodine by ZIF materials
[J].Radioactive iodine present in nuclear waste water streams is harmful to human health and environment. Since iodine will exist in multiple states in water, accurate quantification of the total iodine content in any given sample is very difficult. The development of a method for determining the total iodine content accurately in water, and finding materials which can effectively remove the iodine are of particular importance. Here, a method was proposed for determining the concentration of iodine by cyclohexane extraction. And two kinds of zeolite imidazole skeleton materials ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 were prepared to be used as adsorbents to effectively adsorb iodine from an aqueous environment. Samples ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 were characterized by different methods. The results show that these two kinds of materials have good chemical structure and large specific surface area. The results of adsorption kinetics experiments show that the adsorption of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 materials to iodine can reach the equilibrium within 60 min. The iodine adsorption behaviors of both materials are fitted with the pseudo second-order kinetic model. Their adsorption thermodynamics indicate linear adsorption behavior for iodine in the case of both zeolites. Adsorption capacities of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 for iodine could reach as high as 2000 mg·g -1.
ZIF材料对碘的吸附特性研究
[J].
Cancer incidence and mortality following treatment of hyperthyroidism with radioactive iodine
[J].Hyperthyroidism is a commonly encountered clinical issue. Radioactive iodine is one of the treatment modalities employed over the last 80 years. Prior studies are conflicting as to whether radioactive iodine is associated with an increased risk of subsequent malignancy and associated mortality. The present article reviews recent publications on this subject.Two recent studies make meaningful contributions to the existing literature; however, data remain inconsistent. The first, conducted using the Clalit Health Services database, evaluated solid tumor incidence after radioactive iodine and found no association with increased risk of solid tumor malignancy. The second, which is an updated analysis of the Cooperative Thyrotoxicosis Therapy Follow-up Study, concluded that there is a dose-dependent increased risk of solid tumor mortality using a novel method of estimating organ-specific radiation exposure.In patients with hyperthyroidism, radioactive iodine is a popular and effective treatment option. Prior studies reach conflicting conclusions on the potential relationship between radioactive iodine and both subsequent cancer incidence and mortality. We review recent publications that add to our understanding of this important clinical question.
Preparation and adsorption properties of Cu-Zn@C with ZIF-8 template
[J].
以ZIF-8为模板的Cu-Zn@C制备与吸附性能
[J].
Reviews on methods for air-bone radioiodine capture
[J].
气态放射性碘的捕集方法综述
[J].
Materials and processes for the effective capture and immobilization of radioiodine: a review
[J].
Capture and reversible storage of volatile iodine by porous carbon with high capacity
[J].
Thermochemical evidence for strong iodine chemisorption by ZIF-8
[J].For the first time, using aqueous solution calorimetry, we clearly identify the chemisorption of an unusually strong iodine charge-transfer (CT) complex within the cages of a metal-organic framework. Specifically, we studied the sorption of iodine gas in zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8, Zn(2-methylimidazolate)2). Two iodine-loaded ZIF-8 samples were examined. The first, before thermal treatment, contained 0.17 I2/Zn on the surface and 0.59 I2/Zn inside the cage. The second sample was thermally treated, leaving only cage-confined iodine, 0.59 I2/Zn. The energetics of iodine confinement per I2 (relative to solid I2) in ZIF-8 are ΔHads = -41.47 ± 2.03 kJ/(mol I2) within the cage and ΔHads = -18.06 ± 0.62 kJ/(mol I2) for surface-bound iodine. The cage-confined iodine exhibits a 3-fold increase in binding energy over CT complexes on various organic adsorbents, which show only moderate exothermic heats of binding, from -5 to -15 kJ/(mol I2). The ZIF-8 cage geometry allows each iodine atom to form two CT complexes between opposing 2-methylimidazolate linkers, creating the ideal binding site to maximize iodine retention.
Radioactive iodine and krypton control for nuclear fuel reprocessing facilities
[J].
Iodine adsorption on silver-exchanged titania-derived adsorbents
[J].
Improved utilization of Cu0 for efficient adsorption of iodine in gas and solution by mesoporous Cu0-SBA-15 via solvothermal reduction method
[J].
Study on the adsorption and desorption performance of radioactive methyl iodine by modified activated carbon
[D].
改性活性炭对放射性甲基碘吸附与解吸性能的研究
[D].
Adsorptive removal of gaseous methyl iodide by triethylenediamine modified activated carbon fiber
[J].
三乙烯二胺改性活性炭纤维对气态甲基碘吸附研究
[J].气态甲基碘是核设施运行过程中难以处理的放射性气态产物之一。本文通过水热法制备了三乙烯二胺(TEDA)改性高比表面积粘胶基活性炭纤维材料,并开展了改性材料气态甲基碘吸附研究,通过BET、SEM-EDS、FT-IR、TGA、放射性测试方法对材料进行了表征和吸附性能分析。静态气态碘吸附结果表明,水热改性材料对单质碘吸附量提高了36%,达到1.84 g/g,甲基碘吸附量达到400 mg/g。甲基碘动态吸附实验表明,改性材料具有较高的吸附效率;随着温度和湿度的增加,吸附效率略有降低;环境湿度对气态甲基碘的吸附性能影响较大。温度30 ℃、相对湿度95%条件下的穿透测试表明,材料在12 h内未出现穿透,改性材料展现出优异的甲基碘吸附性能。放射性甲基碘吸附实验显示,水热改性材料吸附效率接近95%,超过未改性材料的3倍;TEDA改性活性炭纤维明显提高了对气态甲基碘的化学吸附能力。水热法TEDA改性粘胶基活性炭纤维材料表现出优异气态甲基碘吸附性能。
Carbon-fiber adsorbent materials for removing radioactive iodine from gases
[J].
Assessment of methods to consolidate iodine-loaded silver-functionalized silica aerogel
[R].
A study of the adsorption properties of the silver nitrate impregnated mordenite for airborne radioiodine
[J].The silver nitrate impregnated mordenite is prepared, the adsorption characteristics of this inorganic adsorbent for airborne radioiodine is examined. The effects of various operating conditions on decontamination factors (DF) of radioiodine are investigated. Results show that this adsorbent has good adsorption properties for both elemental iodine and methyl iodine, the adsorption capacity is up to 196.6mg(Ⅰ)/g(AgX), the effects of water content and NOx in feed gases on DF are very small. The adsorbent can be used to remove radioiodine from nuclear fuel reprocessing off-gases and from air cleaning systems of nuclear reactors.
附银丝光沸石对气载放射性碘的吸附特性的研究
[J].
Study on dynamic adsorption of gaseous iodine by silver loaded mordenite and alumina
[J].
载银丝光沸石和载银氧化铝对气态碘的吸附研究
[J].
Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management
[J].
Research progress in the removal of radioactive iodonucleoid from the water body
[J].
去除水体中放射性碘核素的研究进展
[J].
Pore size and surface properties of activated carbon fibres modified by high temperature treatment
[J].
高温热处理对活性炭纤维微孔及表面性能的影响
[J].
Enhanced uptake of iodide on Ag@Cu2O nanoparticles
[J].
AgII doped MIL-101 and its adsorption of iodine with high speed in solution
[J].
Cover feature: boosting the iodine adsorption and radioresistance of Th-UiO-66 MOFs via aromatic substitution (Chem. Eur. J. 4/2021)
[J].
Flexible surface-supported MOF membrane via a convenient approach for efficient iodine adsorption
[J].
Novel synthesis of NaY-NH4F-Bi2S3 composite for enhancing iodine capture
[J].
Controllable synthesis of porous Cu-BTC@polymer composite beads for iodine capture
[J].
The study of activated carbon fiber's capability of adsorbing precious metal ion
[J].
活性炭纤维对贵金属离子吸附性能的研究
[J].
Highly efficient removal of radioactive iodine anions by nano silver modified activated carbon fiber
[J].
Ag-doped silicon-based nanospheres for the efficient capture and remove of iodide anions from solutions
[J].
Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and mechanism of BiPO4 nanorods modified with AgI nanoparticles
[J].