目前,提高钕铁硼磁体高温性能的主要方法有:提高磁体的矫顽力(降低热退磁)和增大磁体的电阻率(降低涡流)。在钕铁硼磁体中添加重稀土元素(Tb和Dy),可提高其矫顽力。但是,较高的成本限制了重稀土的应用[8]。掺杂WC[9]、h-BN[10]、TiC[11]等高熔点纳米颗粒可细化Nd-Fe-B的晶粒,但是使其磁性能降低[12]。在钕铁硼磁体中引入高电阻率绝缘物质,如氧化物[13],氮化物[14]和氟化物生成连续分布的绝缘层[15],可提高其电阻率使涡流降低。采用机械搅拌/介质辅助混粉[16]、高能球磨[17]、电泳沉积[18]、液相化学合成[19]等物理或化学方法,可在热压热变形磁体中引入高电阻率绝缘物质。但是,用常规的物理方法引入的高电阻率物质极易团聚,不利于高电阻率物质的均匀分布。用化学方法引入高电阻率物质的效果较好,但是其过程较为复杂。六方氮化硼是一种高电阻率物质,具有良好的电绝缘性、优异的热稳定性和化学稳定性,在水中的分散性良好,熔点高达2973 ℃。本文用物理喷涂方法引入适量的BN制备热压热变形钕铁硼磁体,研究BN掺杂对其性能的影响。
1 实验方法
实验中使用商用钕铁硼快淬磁粉(MOU-F)(原始磁粉,主要成分为Nd30.3Fe62.88B0.92Co4.2Pr0.1Dy0.02Ga0.51)和氮化硼(BN)离型脱模剂进行喷涂掺杂。先将钕铁硼磁粉平铺在水平平面上,在磁粉表面往复喷涂氮化硼喷剂(喷涂量质量分数分别为0%,0.2%,0.4%,0.6%和0.8%),使其均匀的附着在磁粉表面。然后将喷涂后的混合粉末置于50 ℃的真空干燥箱中真空干燥2 h。对干燥后的混合粉末进行热压变形制备直径为25 mm厚度为6 mm的钕铁硼磁体,热压工艺为:在550 ℃保温1 min,压强约为370 MPa;热变形工艺为:在850 ℃变形80 s、压强约为100 MPa、变形量为70%。
用电火花线切割机将钕铁硼磁体加工成直径为10 mm厚度为6 mm的圆柱形样品,用FT-300A1型导电材料电阻率测试仪和四引线法测试其室温电阻率[20]。用NIM-6200C型磁性能测试仪测量磁体的室温磁性能和温度稳定性。用D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪(XRD)表征磁体的晶体结构(扫描范围为20°~70°,扫描速度为1(°)/min)。用Gemini Sigma 300X型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能谱分析(EDS)表征磁体的微观结构和元素分布。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 喷涂BN磁粉的表面形貌和元素分布
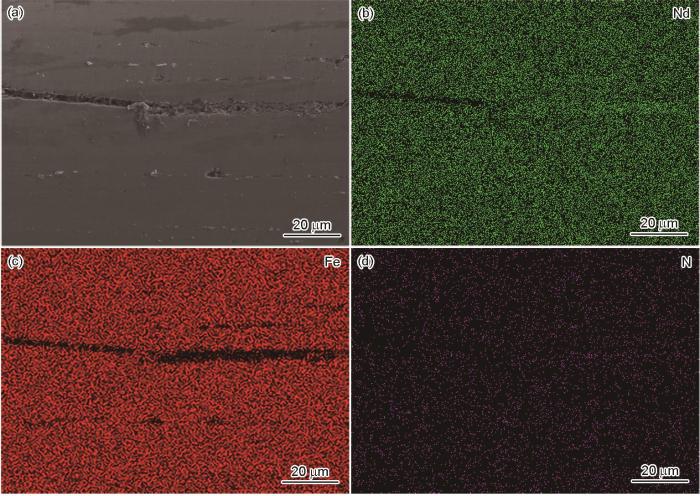
图1
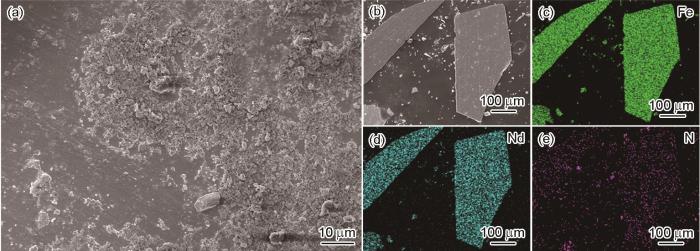
图1
喷涂0.6%BN磁粉表面的SEM、喷涂磁粉的区域以及Fe、Nd、N的EDS图
Fig.1
SEM of the surface of 0.6 % BN magnetic powder (a), Select the area of spraying magnetic powder (b~e) and the EDS diagram of Fe (c), Nd (d) and N (e)
2.2 喷涂BN的热变形钕铁硼磁体的室温电阻率
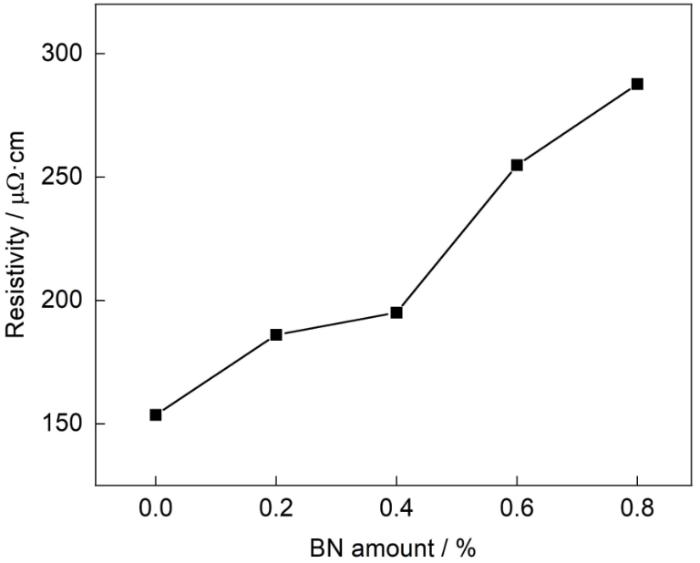
图2
图2
BN喷涂量对热变形磁体电阻率的影响
Fig.2
Effect of BN spraying amount on the resistivity of hot-deformed magnet
2.3 喷涂BN热变形钕铁硼磁体的磁性能
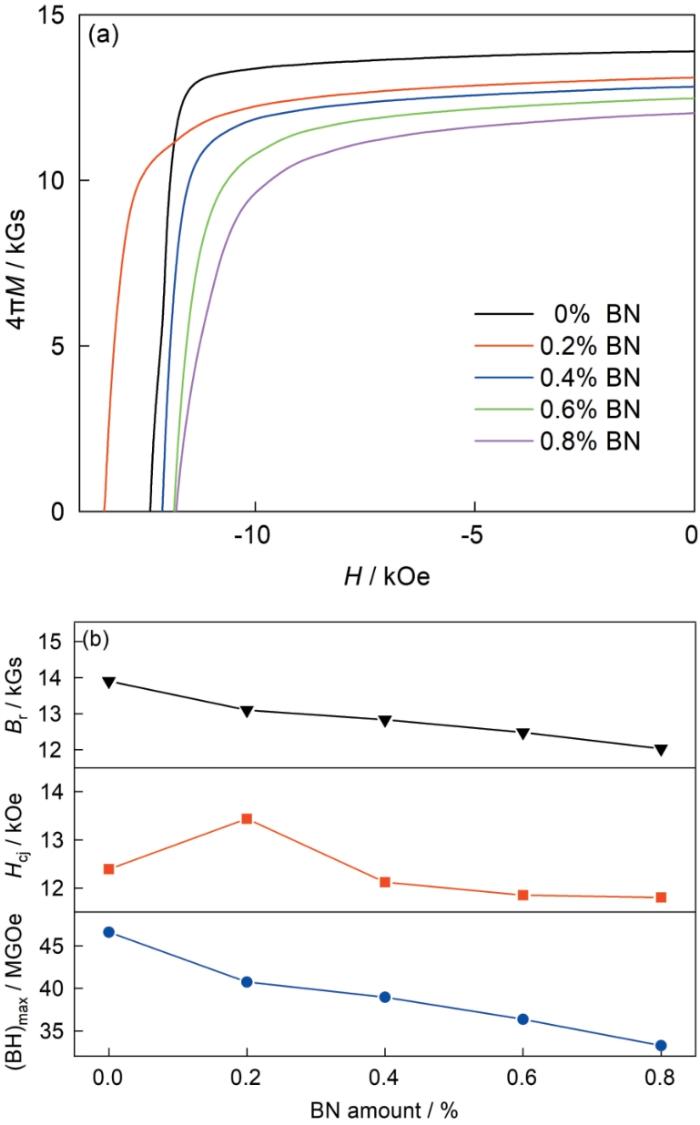
图3给出了BN喷涂量对热变形钕铁硼磁体磁性能的影响。图3a给出了不同BN喷涂量磁体的室温退磁曲线,图3b给出了不同BN喷涂量热变形磁体的剩磁、矫顽力和最大磁能积。可以看出,随着BN喷涂量的增加热变形磁体的磁性能呈下降的趋势。磁体的剩磁和最大磁能积,分别从未喷涂时的13.9 kGs和46.63 MGOe下降到喷涂0.8%BN的12.03 kGs和33.26 MGOe。与其相比,喷涂0.2%BN的磁体,其矫顽力出现了上升的拐点。其原因是,在常规热变形过程中熔点较高的BN颗粒以固态存在,从而阻碍了晶粒的生长而使磁体的矫顽力提高。但是,随着BN喷涂量的增加较多的BN在热变形过程中阻碍富Nd相的流动和晶粒转动,且非磁性相BN降低了磁性相的比例,从而使磁体的磁性能降低[23,24]。
图3
图3
不同BN喷涂量热变形磁体的室温退磁曲线和BN喷涂量对热变形磁体剩磁Br、矫顽力Hcj以及最大磁能积(BH)max的影响
Fig.3
Room temperature demagnetization curves of hot-deformed magnets with different BN spraying amount (a), the effect of different BN spraying amount on the remanence Br, coercivity Hcj and maximum magnetic energy product (BH)max of hot-deformed magnets (b)
2.4 喷涂BN磁体磁性的温度稳定性
图4给出了不同BN喷涂量热变形磁体在不同温度下的矫顽力。可以看出,磁体的矫顽力随着温度的升高而降低。这种磁体在一定温度(T0~T)范围内矫顽力的温度系数βHcj,为
图4
图4
不同BN喷涂量热变形磁体在不同温度下的矫顽力
Fig.4
Coercivity of hot-deformed magnets with different BN spraying amount at different temperatures
表1 不同BN喷涂量热变形磁体的矫顽力温度系数
Table 1
| BN amount / %, mass fraction | 20-80 oC | 20-100 oC | 20-120 oC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -0.67 | -0.64 | -0.60 |
| 0.2 | -0.74 | -0.69 | -0.65 |
| 0.4 | -0.78 | -0.72 | -0.67 |
| 0.6 | -0.80 | -0.74 | -0.68 |
| 0.8 | -0.79 | -0.73 | -0.69 |
2.5 BN喷涂热变形钕铁硼磁体的微结构
图5给出了不同BN喷涂量热变形钕铁硼磁体的XRD谱。可以看出,BN喷涂钕铁硼磁体的特征峰均属于Nd2Fe14B相,表明热变形磁体的C轴取向良好。根据(006)与(105)晶面的相对衍射强度比值可估计Nd2Fe14B主相晶粒的取向程度,比值越大表明取向织构越好。未喷涂BN的原始磁体的(006)与(105)比值为1.11,随着BN喷涂量的增加比值逐渐升高,BN喷涂量为0.6%时比值达到最大值1.91,BN喷涂量为0.8%时比值下降为1.58。这表明,喷涂适量的BN可改善热变形钕铁硼磁体的取向织构,但是非磁性相BN使磁体的性能下降。
图5
图5
不同BN喷涂量热变形钕铁硼磁体的XRD谱
Fig.5
XRD patterns of hot-deformed magnets with different BN spraying amount
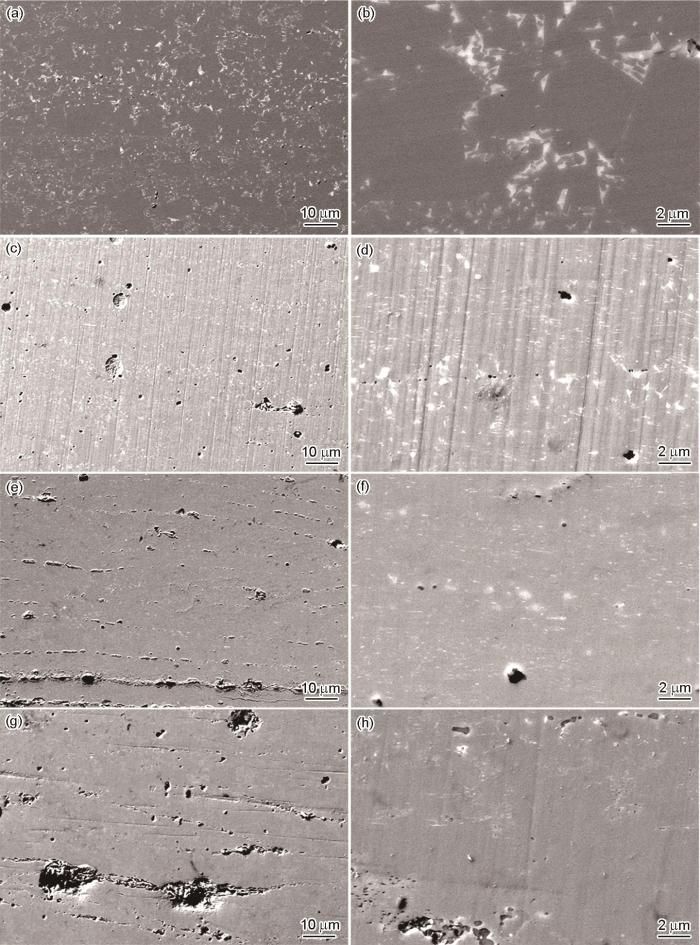
图6给出了不同BN喷涂量热变形钕铁硼磁体的SEM形貌。图中的白色部分为富Nd相,灰色部分为Nd2Fe14B相。图7给出了BN喷涂量为0.6%磁体的SEM照片和EDS线扫描图,图8 给出了EDS元素分布。可以看出,BN主要分布在富Nd相中。BN喷涂量较低的Nd2Fe14B主相晶粒排列较为规则,富Nd相呈平行的条状连续均匀分布,BN的分布呈线条状。随着喷涂量的增加BN在富Nd相中出现团聚,在富Nd相附近出现缺陷和孔洞。喷涂过多的BN,使磁体的致密性降低。BN的喷涂量为0.8%时磁体内沿着富Nd相的分布方向出现裂痕和较大的缺陷(图8)。其原因是,附着在钕铁硼磁粉表面的BN颗粒过多,在热压变形过程中高熔点的BN颗粒富集在富Nd相中,严重阻碍液态富Nd相的流动和磁体主相晶粒的转动,使磁体的塑性变形能力降低,影响磁体的各向异性和织构的形成,从而降低磁体的磁性能。
图6
图6
不同BN喷涂量热变形钕铁硼磁体的SEM照片
Fig.6
SEM patterns of hot-deformed magnets with different BN spraying amount under different multiples (a, b) 0%, (c, d) 0.2%, (e, f) 0.6%, (g, h) 0.8%
图7
图7
BN喷涂量为0.6%的热变形钕铁硼磁体的SEM照片和EDS线扫描图
Fig.7
SEM (a) and EDS line scan (b) of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnet with 0.6%BN spraying amount
图8
图8
BN喷涂量为0.6%的热变形钕铁硼磁体的SEM照片和EDS元素分布
Fig.8
SEM (a) and EDS element distribution (b-d) of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnet with 0.6%BN spraying amount
3 结论
(1) 物理喷涂引入BN可提高热变形钕铁硼磁体的电阻率,BN喷涂量为0.8%的磁体其电阻率达到287.65 μΩ·cm,比未喷涂BN磁体的电阻率(153.5 μΩ·cm)提高了87%。
(2) 喷涂适量的BN可改善磁体的晶粒取向,喷涂少量BN有利于提高磁体的矫顽力,过量的BN在变形过程中阻碍液态富Nd相的流动和磁体主相晶粒转动,使磁体的致密性和磁体性能降低。BN喷涂量为0.6%的磁体综合性能较高。
参考文献
Perspective and prospects for rare earth permanent magnets
[J].
Rare earth permanent magnets and their place in the future economy
[J].
Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient
[J].
Research progress and prospect of high electrical resistivity NdFeB permanent magnetic materials
[J].
高电阻率NdFeB永磁材料的研究进展与展望
[J].
Recent development of high electrical resistivity rare earth permanent magnetic materials
[J].
高电阻率稀土永磁材料研究进展
[J].
Prospect of developing Nd-Fe-B-type magnet with high electrical resistivity
[J].
Significant progress for hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnets: a review
[J].
Magnetization and magnetic anisotropy of R2Fe14B measured on single crystals
[J].
Coercivity enhancement by inhibiting the formation of coarse grains region in hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnets with WC nano-particles addition
[J].
Texture and microstructure improvement of hot-deformed magnets with platelet-like nano h-BN addition
[J].
Improvement of comprehensive magnetic properties for hot-deformed NdFeB magnets via intergranular additions of nano-TiC
[J].
Impact of nano-particles with high-melting point on magnetic properties and microstructures of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnet
[J].
高熔点纳米颗粒添加对热变形Nd-Fe-B磁体性能与微观结构的影响
[J].
Microstructure and properties of die-upset Nd-Fe-B/Dy2O3 composite magnets
[J].
Dysprosium nitride-modified sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets with increased coercivity and resistivity
[J].
Electrical and magnetic properties of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnets with different DyF3 additions
[J].
Effect of CaF2 addition on the microstructure and magnetic and electrical properties of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets
[J].
Microstructure, magnetic properties, and electrical resistivity of Nd-Fe-B/NdF3 composite magnets
[J].
High-resistivity anisotropic hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnets prepared from DyF3 electrophoretic deposited powders
[J].
Microstructure, magnetic and electrical properties of the composite magnets of Nd-Fe-B powders coated with silica layer
[J].
Electrical resistivity measurements: a review
[A].
Simultaneous enhancement of magnetic properties and electric resistance of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B magnets by doping insulating nano-diamonds
[J].
Effect of Al2O3 doping on resistivity and magnetic properties of sintered NdFeB magnets
[J].
Al2O3掺杂对烧结钕铁硼磁体电阻率和磁性能的影响
[J].
Effect of co-doping of nano-Al and Cu65Ga35on magnetic properties and thermal stability of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets
[J].
纳米Al及Cu65Ga35共掺杂对烧结钕铁硼磁体磁性能及热稳定性的影响
[J].
Phosphating passivation of vacuum evaporated Al/NdFeB magnets boosting high anti-corrosion performances
[J].