电控离子交换技术(ESIX)利用电活性离子交换材料传递电子和离子,施加不同的电位可调控对目标离子的吸附/脱附并能避免二次污染[11,12]。与其他共存阴离子相比,磷酸根离子的水合离子半径较小、带电荷数较多,极易与金属离子络合。层状双金属氢氧化物(Layered double hydroxides, LDHs)[13~16]是由两种及以上金属氢氧化物层及阴离子和水分子占据插层空间的二维层状水滑石材料,其层板金属离子更易结合离子半径小、带负电荷多的磷酸根阴离子形成配体化合物。但是,LDHs单独使用时导电性弱、不易成膜和极易团聚。石墨烯(Graphene, G)的导电性良好和机械稳定性较高[17],可为磷酸根离子提供结构稳定的传输通道。聚吡咯(Polypyrrole, PPy)是一种杂环共轭型导电高分子,对其施加不同电位时吡咯环氮原子上质子可在PPy和LDHs间来回迁移,能促进PO
1 实验方法
1.1 实验用材料
硝酸钴(Co(NO3)2·6H2O);硝酸镍(Ni(NO3)2·6H2O);吡咯(纯度99%);石墨烯;N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)和磷酸三钠(Na3PO4·12 H2O ≥ 98%)。实验中所有水溶液均用去离子水(2~5 μS·cm-1)配制,所有化学试剂的纯度均为分析级。
1.2 膜电极材料石墨烯掺杂PPy膜和PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的制备
导电基体的预处理:将面积为2.2 cm × 1.5 cm的碳布浸泡在1.0 mol/L H2SO4∶无水乙醇(体积比)为4∶1的混合溶液中2 h,以除去碳布表面的氧化物等杂质。将其取出后用去离子水冲洗干净,静置过夜后晾干备用。
所有电化学实验均使用三电极体系,对电极是1 cm2铂片电极,参比电极为Ag/AgCl。
制备石墨烯掺杂PPy膜(记为PPy-G):将0.1015 g的吡咯和1 mL DMF放入容量瓶中并加水定容到50 mL,将其倒入烧杯中并加入5 mg石墨烯,超声搅拌使石墨烯均匀分散在混合液中。将这种混合液用作电解液,工作电极是处理后的碳布,在0.8 V电位下进行恒电位电解反应600 s制备出石墨烯掺杂的PPy-G膜电极。用去离子水将PPy-G膜充分冲洗,晾干后备用。
制备PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜:将PPy-G膜用作工作电极,电解液是40 mL 0.1 mol/L Ni(NO3)2和20 mL 0.1 mol/L Co(NO3)2·6H2O混合溶液。采用恒电位电解法在-1.2 V的电位下反应600 s制备PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜电极,将其充分冲洗后晾干。
1.3 性能表征
使用辰华电化学工作站CHI760e测试PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的离子交换性能;用离子色谱仪IC(CIC-D150)检测电解液中离子的浓度。所有实验均在常温(20~25 ℃)下进行。文中提到的电位,均相对于Ag/AgCl参比电极。
用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Rigaku MiniFlex600)测定杂化膜的XRD谱,以分析其晶格结构,测试条件为Cu Kα,扫描范围为5°~85°;用扫描电子显微镜(SEM, ZEISS Gemini 300)和透射电子显微镜(TEM, FEI TalosF20)观察杂化膜的表面微观形貌;用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS, Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250XI)测定杂化膜的XPS谱以分析其氧化前后的元素组成、含量以及价态。
选用100 mL Na3PO4溶液为模拟液,采用恒电位电解法测试PPy-G/CoNi-LDH的吸附性能。测试不同吸附电位和不同磷酸盐初始浓度条件下PPy-G/CoNi-LDH对磷酸根离子的吸附性能;在10 mg·L-1的PO
其中,ρ0和ρ分别为初始和检测时间点PO
2 结果和讨论
2.1 杂化膜的结构和组成
图1
图1
PPy-G、CoNi-LDH和PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的XRD谱
Fig.1
XRD patterns of PPy-G, CoNi-LDH, and PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid films
图2
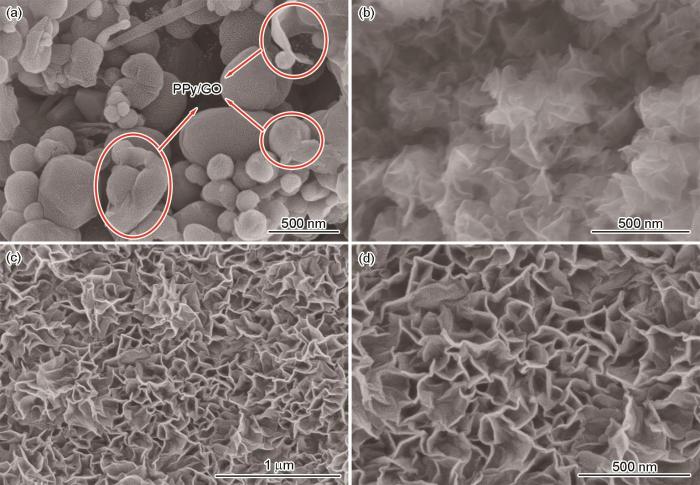
图2
PPy-G、CoNi-LDH、PPy-G/CoNi-LDH的SEM照片
Fig.2
SEM images of PPy-G (a), CoNi-LDH (b), and PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid films (c, d)
图3
图3
PPy-G/CoNi-LDH的TEM照片
Fig.3
TEM images of PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film at different magnifications (a) TEM, (b) HRTEM
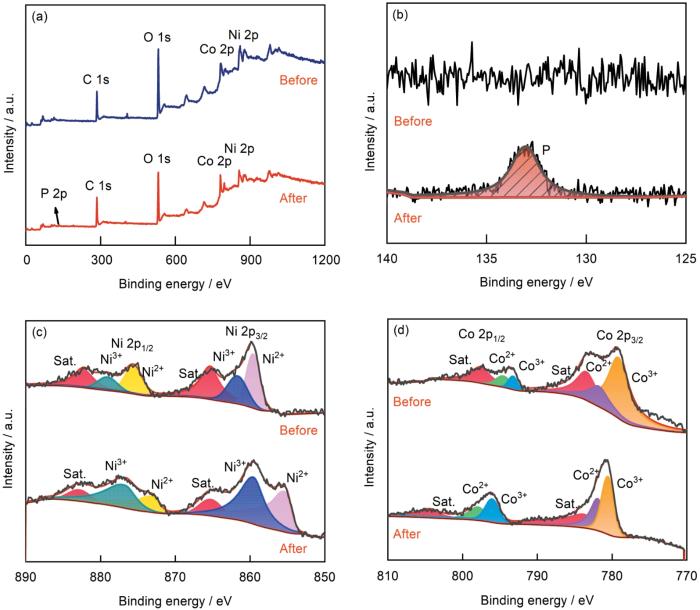
图4给出了PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜吸附前后的XPS谱,用以分析其吸附磷酸盐离子前后的元素组成和含量,其中上方的曲线为氧化前状态。图4a给出了对PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜吸附前后全谱的分析,主要分析了C、N、P、O、Co和Ni元素。可以看出,在吸附后的谱中出现了明显的P元素峰。这表明,对杂化膜施加氧化电位后溶液中的磷酸根离子被吸附进膜内。从图4b可以看出,氧化后在结合能133.00 eV处出现P元素的峰,表明磷酸根离子被吸附入膜内[22]。图4c给出了氧化前后Ni元素结合能的变化。862.79和881.32 eV处的峰为卫星峰,而在结合能855.80和873.81 eV处的峰为Ni2+的Ni 2p3/2和Ni 2p1/2的特征峰,结合能858.14 和877.71 eV处的峰是Ni3+的Ni 2p3/2和Ni 2p1/2的特征峰[23]。图4d给出了氧化前后Co元素结合能的变化。在800.6和783.77 eV处的峰为卫星峰,在自旋轨道为780.55和796.97 eV处的峰是Co3+的Co 2p3/2和Co 2p1/2的特征峰,在自旋轨道781.84 和779.97 eV处的峰是Co2+的Co 2p3/2和Co 2p1/2的特征峰[24]。对比氧化前后Ni 2p和Co 2p的谱,可见吸附后Ni3+的含量比Ni2+的高,Co3+的含量比Co2+的高。这表明,在氧化过程中LDH层板带的正电荷增加,对杂化膜与PO
图4
图4
在10 mg·L-1 PO
Fig.4
XPS spectrum of PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film in 10 mg·L-1 PO
2.2 杂化膜的电化学性能
石墨烯在吡咯单体溶液中的分散度以及LDH制备液中金属离子配比,对杂化膜的性能有极大的影响。实验考察了Ni:Co的摩尔比以及添加1 mL的DMF对杂化膜电化学活性的影响,以确定制备条件。第一步是制备石墨烯掺杂的PPy-G膜,第二步是电沉积制备不同Ni∶Co摩尔比的PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜。对一系列杂化膜进行电化学循环伏安(CV)测试,结果如图5a所示。Ni∶Co摩尔比为2∶1的杂化膜在磷酸盐溶液中的CV图积分面积和电流密度最大,即电化学活性最佳,交换磷酸根的性能最好。在PPy的制备过程中,有机溶剂DMF的添加提高了石墨烯的分散度,有利于其掺杂进入PPy膜中。图5b表明,添加DMF的杂化膜其CV图的电流密度明显比未添加DMF的高,其电化学活性更高。因此,Ni∶Co摩尔比为2∶1且添加DMF试剂是后续制备PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的条件。
图5
图5
在-1.2 V电位下不同镍钴摩尔比及有无DMF添加条件下PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的CV曲线
Fig.5
CV curves of PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film with different molar ratios of Ni∶Co (a) and with or without DMF (b) under -1.2 V potential
在PO
图6
图6
在不同初始PO
Fig.6
Adsorption kinetic curves of PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film for phosphate anions with different initial concentrations under 0.8 V oxidation potential
使用准一级和准二级吸附动力学模型分析了杂化膜的性能。表1列出了初始浓度不同的杂化膜的吸附速率和理论吸附量,其中准一级和准二级的动力学模型方程式为
表1
PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜在不同初始PO
Table 1
| ρ0 / mg·L-1 | qe(exp) / mg·g-1 | Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 / min-1 | qe(cal) / mg·g-1 | R2 | k2 / g·mg-1·min-1 | qe(cal) / mg·g-1 | R2 | ||
| 50 | 75.23 | 5.67 × 10-3 | 73.22 | 0.997 | 5.1 × 10--5 | 107.64 | 0.945 |
| 30 | 62.50 | 5.80 × 10-3 | 59.81 | 0.904 | 7.6 × 10-5 | 85.03 | 0.953 |
| 10 | 40.23 | 5.07 × 10-3 | 41.11 | 0.995 | 1.0 × 10-4 | 44.21 | 0.817 |
| 5 | 16.04 | 1.45 × 10-3 | 16.54 | 0.947 | 3.5 × 10-4 | 85.32 | 0.386 |
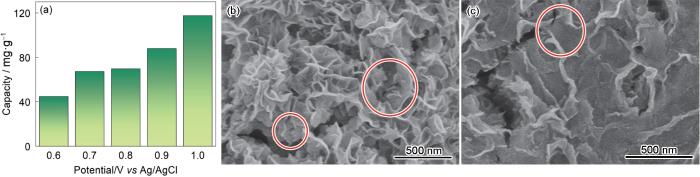
图7a给出了在100 mL浓度为50 mg·L-1的PO
图7
图7
在50 mg·L-1 PO
Fig.7
Adsorption capacity of PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film for PO
图8给出了浓度为10 mg·L-1的PO
图8
图8
在10 mg·L-1 PO
Fig.8
Effects of pH value on PO
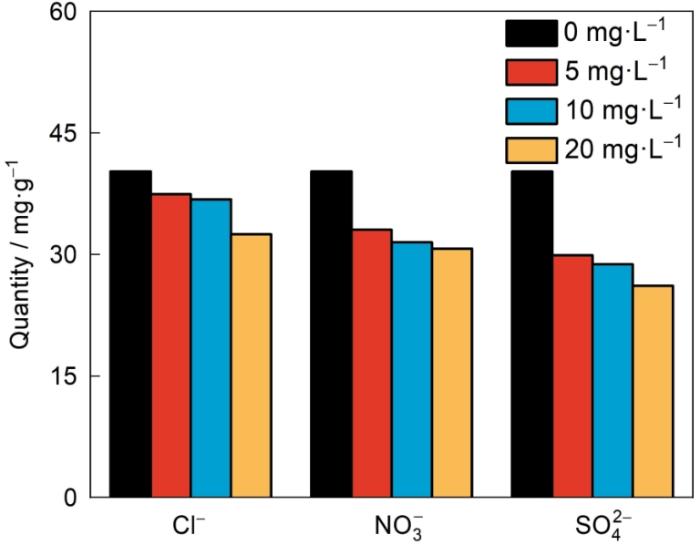
图9
图9
在10 mg·L-1 PO
Fig.9
Effect of competing anions with different concentrations on PO
2.3 PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的稳定性
图10
图10
PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜在10 mg·L-1 PO
Fig.10
The normalized adsorption capacity of PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film for phosphate ions in 10 mg·L-1 PO
2.4 PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜的吸附机理
为了揭示PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜对磷酸根的吸附机理,进行了空白对照实验。第一组,是PPy-G和CoNi-LDH对浓度为10 mg·L-1的PO
图11
图11
PPy-GO、CoNi-LDH及PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜对PO
Fig.11
Adsorption capacity of PPy-GO, CoNi-LDH and PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film (a), and PPy-G/CoNi-LDH hybrid film under different methods for phosphate ions (b) in 10 mg·L-1 PO
为了证实还有其它吸附,结合O 1s和N 1s的XPS数据进行进一步分析。图11c给出了对杂化膜氧化前后O 1s的XPS谱(上方为氧化前,下方为氧化后),其中531.06、531.97和532.80 eV处的峰分别对应M-O、O-H基团和H-O-H。与始态相比,吸附后的O 1s谱中M-O的含量提高,而O-H基团的含量降低。其原因是,在杂化膜氧化过程中LDHs层板与金属离子相连的O-H基团被PO
综上所述,PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜对磷酸根的吸附,其主要吸附机理有:(1)金属阳离子与磷酸根阴离子间的静电吸引;(2)磷酸根离子与层板间硝酸根离子间的离子交换;(3) LDH层板金属离子与磷酸根离子的络合反应;(4) PPy-G与CoNi-LDH之间的协同效应。
3 结论
(1) 先在碳布基体上制备石墨烯掺杂的PPy-G膜,然后将CoNi-LDH沉积于其上可制备PPy-G/CoNi-LDH杂化膜。Ni∶Co摩尔比为2∶1且添加DMF的杂化膜,其活性最佳。
(2) 随着PO
(3) 这种材料的吸附机理为:PO
参考文献
Phosphorus recovery and recycling-closing the loop
[J].
The potential phosphorus crisis: resource conservation and possible escape technologies: a review
[J].
Greening the global phosphorus cycle: How green chemistry can help achieve planetary P sustainability
[J].
The great Atlantic Sargassum belt
[J].Pelagic Sargassum is abundant in the Sargasso Sea, but a recurrent great Atlantic Sargassum belt (GASB) has been observed in satellite imagery since 2011, often extending from West Africa to the Gulf of Mexico. In June 2018, the 8850-kilometer GASB contained > 20 million metric tons of Sargassum biomass. The spatial distribution of the GASB is mostly driven by ocean circulation. The bloom of 2011 might be a result of Amazon River discharge in previous years, but recent increases and interannual variability after 2011 appear to be driven by upwelling off West Africa during boreal winter and by Amazon River discharge during spring and summer, indicating a possible regime shift and raising the possibility that recurrent blooms in the tropical Atlantic and Caribbean Sea may become the new norm.
Treatment of perchlorate in drinking water: A critical review
[J].
Adsorptive removal of lead (II) Ion from water and wastewater media using carbon-based nanomaterials as unique sorbents: A review
[J].
Treatment of chlorpyrifos manufacturing wastewater by peroxide promoted-catalytic wet air oxidation, struvite precipitation, and biological aerated biofilter
[J].Chlorpyrifos manufacturing wastewater (CMW) is characterized by complex composition, high chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentration, and toxicity. An integrated process comprising of peroxide (H2O2) promoted-catalytic wet air oxidation (PP-CWAO), struvite precipitation, and biological aerated filters (BAF) was constructed to treat CMW at a starting COD of 34000-35000 mg/L, total phosphorus (TP) of 5550-5620 mg/L, and total organophosphorus (TOP) of 4700-4840 mg/L. Firstly, PP-CWAO was used to decompose high concentrations of organic components and convert concentrated and recalcitrant TOP to inorganic phosphate. Copper citrate and ferrous citrate were used as the catalysts of PP-CWAO. Under the optimized conditions, 100% TOP was converted to inorganic phosphate with 95.6% COD removal. Then, the PP-CWAO effluent was subjected to struvite precipitation process for recovering phosphorus. At a molar ratio of Mg2+:NH4+:PO43- = 1.1:1.0:1.0, phosphate removal and recovery reached 97.2%. The effluent of struvite precipitation was further treated by the BAF system. Total removals of 99.0%, 95.2%, 97.3%, 100%, and 98.3% were obtained for COD, total suspended solids, TP, TOP, and chroma, respectively. This hybrid process has proved to be an efficient approach for organophosphate pesticide wastewater treatment and phosphorus reclamation.
Regulation of salt tolerance in bacteria and its application in hypersaline BNR process
[J].The biological nutrients removal (BNR) process is inevitably affected by salinity changes. Understanding how bacteria adapt to high-salinity environments and regulating the operation mode of the system are crucial essential to maintain the stability of the system economically and efficiently. This study summarizes current research findings, demonstrating that salt-tolerant microorganisms are capable of quickly exchanging water, small molecules of amino acids, glycerol, polysaccharides and inorganic substances such as potassium and sodium ions with the environment to coordinate osmotic pressure with the change of environmental salinity. Extremophilic bacteria have developed unique cellular structures that take advantage of various types of energy sources, including light, electricity, and electron donors with lower chemical potentials than fatty acids, to achieve the energy-enriched-biopolymers accumulation (e.g. polysaccharides, polyphosphates, polyhydroxyalkanoates and polysulfides). Employing alternating anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic biofilm processes, along with cyclic accumulation and uptake of various energetic substances, introducing saline-adapted biomass, and feeding the reactor with seawater to acclimate biofilm communities, can enhance the efficiency of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (phosphorus removal) in hypersaline environments. Finally, the study points out that how to configure a reasonable process with good stability, and to enhance microorganisms salt tolerance by appropriate external energy amendments are of urgent importance in the future research as well as in the BNR engineering practices.
细菌的耐盐调控及其在高盐BNR工艺中的应用
[J].
Application of membrane separation processes in phosphorus recovery: A review
[J].
Effect of pore size distribution and particle size of porous metal oxides on phosphate adsorption capacity and kinetics
[J].
Electroactive ion exchange materials: current status in synthesis, applications and future prospects
[J].
A potential-controlled ion pump based on a three-dimensional PPy@GO membrane for separating dilute lead ions from wastewater
[J].
Selective phosphate removal using layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide (LDH/rGO) composite electrode in capacitive deionization
[J].
Graphdiyne-modified NiV-layered double hydroxide nanostructures for supercapacitor applications
[J].
Graphene/LDHs hybrid composites synthesis and application in environmental protection
[J].
Preparation and delaminating of glycine-Mg3Al LDHs and its intercalation compounding with montmorillonite
[J].
甘氨酸-Mg3Al水滑石的制备、剥离以及与蒙脱土的插层组装
[J].用共沉淀法制备甘氨酸(简称Gly)插层Mg<sub>3</sub>Al水滑石(简称Gly-Mg<sub>3</sub>Al LDHs), 利用甘氨酸等电点的性质实现了Mg<sub>3</sub>Al水滑石在pH=3~4水溶液中的剥离, 并将剥离出的LDHs纳米片层与蒙脱土进行插层组装, 制备出Mg<sub>3</sub>Al水滑石/蒙脱土层状复合材料。用X射线粉末衍射、红外光谱、N<sub>2</sub>吸附-脱附以及电泳仪等手段对样品进行了表征。结果表明, 制备出的Gly- Mg<sub>3</sub>Al LDHs结构规整, 晶相单一, 甘氨酸以42°的倾角排列于水滑石层间。在n<sub>Gly</sub>∶n<sub>NO3</sub><sup>-</sup>=1∶2的条件下制备的Gly-Mg<sub>3</sub>Al LDHs剥离效果最好, 剥离后形成的无机聚合粒子的zeta电位介于35 mV~ 40 mV之间, 剥离液可以稳定存在72 h。所得层状复合材料的层间距为1.44nm, 此值为单元LDHs片层与单元蒙脱土片层的厚度之和, 证明LDHs纳米片层与蒙脱土进行了有序交叉叠层。
A high-performance electroactive PPy/rGO/NiCo-LDH hybrid film for removal of dilute dodecyl sulfonate ions
[J].
Bimetallic electron-induced phase transformation of CoNi LDH-GO for high oxygen evolution and supercapacitor performance
[J].
Fabrication and supercapacitor performance of metal organic framework Zn-BTC/rGO nanocomposites with different morphologies
[J].
金属有机骨架Zn-BTC/rGO复合材料的制备和性能
[J].用超声震荡法合成不同形貌的石墨烯负载Zn-BTC金属有机骨架材料,并将其用做电极组装超级电容器。用TG曲线、SEM观察、XRD谱、Brunauer-Emmett-Teller模型和Raman谱等手段表征材料的结构、形貌和电化学性能,使用电化学工作站和三电极体系测试了超级电容样品的电化学性能。结果表明,合成的一维棒状Zn-BTC均匀锚定在褶皱的石墨烯纳米片层上,其比电容为182.4 C·g<sup>-1</sup> (1 A·g<sup>-1</sup>),优于石墨烯负载的二维片状Zn-BTC (139.3 C·g<sup>-1</sup>)、石墨烯(97.9 C·g<sup>-1</sup>)和一维棒状Zn-BTC (62.8 C·g<sup>-1</sup>)。使用石墨烯负载的一维棒状Zn-BTC组装的对称超级电容器,在电流密度为1 A·g<sup>-1</sup>、比容量为57.7 F·g<sup>-1</sup>、功率密度为1390 W·kg<sup>-1</sup>条件下的最大能量密度为1.99 Wh·kg<sup>-1</sup>,经过2000次充放电循环后其比容量保持率为90.3%。
Core-branched NiCo2S4@CoNi-LDH heterostructure as advanced electrode with superior energy storage performance
[J].
Hierarchical NiCo-LDH/NiCoP@NiMn-LDH hybrid electrodes on carbon cloth for excellent supercapacitors
[J].
Specific separation and recovery of phosphate anions by a novel NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid film based on electroactivity-variable valence
[J].
Hierarchical NiCo-LDH@NiOOH core-shell heterostructure on carbon fiber cloth as battery-like electrode for supercapacitor
[J].
Preparation by Co metal-organic framework template and capacitive properties of NiCo-layered double hydroxide/nickel foam composites
[J].
Co金属有机骨架模板制备NiCo水滑石/泡沫镍复合材料及电容性能
[J].
Impact of the charge transfer process on the Fe2+/Fe3+ distribution at Fe3O4 magnetic surface induced by deposited Pd clusters
[J].
Potential induced reversible removal/recovery of phosphate anions with high selectivity using an electroactive NiCo-layered double oxide film
[J].Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for organisms growth and a major cause of eutrophication in water bodies. Thus, it is crucial for both of the removal and recovery of phosphate from wastewater. In this work, the NiCo-layered double oxide (NiCo-LDO) was successfully fabricated on carbon cloth conductive substrate via the in-situ calcination of the NiCo-layered double hydroxide (NiCo-LDH) and served as the electrochemically switched ion exchange (ESIX) film electrode for the removal and recovery of PO4 3-. The performance of NiCo-LDO for PO4 3- removal by ESIX and ion exchange (IX) was compared, while the selectivity and stability of NiCo-LDO for PO4 3- removal were also investigated. The results revealed that, in (10.00±0.05) mg/L PO4 3- solution, the ion exchange quantity of the NiCo-LDO for PO4 3- removal by ESIX process was about twice over that by IX. Moreover, compared with Cl -, NO3 -, SO4 2- and I -, the NiCo-LDO exhibited much higher selectivity towards PO4 3-. In addition, the ion exchange quantity still retained 92% of its initial value after 5 uptake and release cycles. Coupled with XPS analysis, it was found that ESIX process of NiCo-LDO film electrode for PO4 3- removal and recovery mainly consisted of 3 steps, which were an irreversible “memory effect” structure recovery process, the redox reaction of metal ion in lamellar and the ligand exchange between PO4 3- and O-H groups.
电活性镍钴双金属氧化物高选择性去除/回收水中磷酸盐离子
[J].磷是植物体生长的重要营养素, 也是引发水体富营养化的重要因素, 因此废水中磷酸盐的去除与回收均至关重要。本研究采用单极脉冲电沉积法在炭布上制备镍钴双氢氧化物, 并于管式炉中原位焙烧制得镍钴双金属氧化物(NiCo-Layered Double Oxide, NiCo-LDO), 将其用于电控离子交换(Electrochemically Switched Ion Exchange, ESIX)过程实现PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>的去除与回收。实验对比了ESIX与离子交换(Ion Exchange, IX)过程中NiCo-LDO对PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>的去除性能, 并考察了其选择性及循环稳定性。结果表明, 在(10.00±0.05) mg/L的PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>溶液中, ESIX过程中膜对PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>的离子交换量约为IX的2倍; NiCo-LDO对PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>具有高选择性, 且经过5次循环后, 离子交换量仍可达到初始值的92%以上; 结合XPS分析, 发现NiCo-LDO对PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>的ESIX过程包括一个不可逆的“记忆效应”结构恢复过程及两个可逆的层板金属离子氧化/还原和PO<sub>4</sub> <sup>3-</sup>与O-H基团的配体交换过程。
Separation of low concentration of cesium ion from wastewater by electrochemically switched ion exchange method: Experimental adsorption kinetics analysis
[J].
Highly efficient defluoridation using a porous MWCNT@NiMn-LDH composites based on ion transport of EDL coupled with ligand exchange mechanism
[J].
Efficient defluoridation of water using reusable nanocrystalline layered double hydroxides impregnated polystyrene anion exchanger
[J].Water decontamination from fluoride is still a challenging task of global concern. Recently, Al-based layered double hydroxides (LDHs) have been extensively studied for specific fluoride adsorption from water. Unfortunately, they cannot be readily applied in scaled-up application due to their ultrafine particles as well as the regeneration issues caused by their poor stability at alkaline pHs. Here, we developed a novel (LDH)-based hybrid adsorbent, i.e., LALDH-201, by impregnating nanocrystalline Li/Al LDHs (LADLH) inside a commercial polystyrene anion exchanger D201. TEM image and XRD spectra of the resultant nanocomposite confirmed that the LDHs particles were nanosized inside the pores of D201 of highly crystalline nature and well-ordered layer structure. After impregnation, the chemical and mechanical stability of LALDH were significantly improved against pH variation, facilitating its application at a wide pH range (3.5-12). Fluoride adsorption onto LALDH-201 was compared to D201 and activated alumina, evidencing the preferable removal fluoride of LALDH-201. Fluoride adsorption onto LALDH-201 followed pseudo-second-order model, with the maximum capacity (62.5 mg/g from the Sips model) much higher than the other two adsorbents. Fixed-bed adsorption run indicated the qualified treatable volume of the fluoride contaminated groundwater (4.1 mg/L initially) with LALDH-201 was about 11 times as much as with the anion exchanger D201 when the breakthrough point was set as 1.5 mg/L. The capacity of LALDH-201 could be effectively refreshed for continuous column operation without observable loss by using the mixed solution of 0.01 M NaOH + 1 M NaCl. The above results suggested that the hybrid adsorbent LALDH-201 is very promising for water defluoridation in scaled-up application.Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
A facile potential-induced in-situ ion removal trick: fabrication of high-selective ion-imprinted film for trivalent yttrium ion separation
[J].
Polypyrrole-grafted peanut shell biological carbon as a potential sorbent for fluoride removal: Sorption capability and mechanism
[J].In this study, an effective defluoridation adsorbent was developed by depositing polypyrrole (PPy) on granular peanut shell biological carbon (BC) via in situ chemical oxidative polymerization. The variables of defluoridation process (i.e., adsorbent dosage, fluoride solution pH, and anionic interference) were tested. The mechanism was determined by isotherm and kinetic studies, Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method, scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and automatic titration. The PPy-grafted BC (PPy/BC) composite performed commendably from pH 2.0 to 10.0, and exhibited high selectivity for fluoride in the presence of several co-existing anions. The experimental data were described well by a Langmuir isotherm curve, and the maximum adsorption capacity was 17.15 mg g(-1). Kinetic studies illustrated the adsorption process was accomplished via surface adsorption as well as by intraparticle diffusion. In addition, mesoporous diffusion was the rate-controlling step in intraparticle diffusion process. BET and SEM analysis revealed the sponge-like polymer adhered to the BC and plugged the pores. XPS, FTIR, and SEM confirmed that fluoride removal was accomplished via the replacement of doped ionizable chloride ions (Cl(-)) coupled with positively charged nitrogen (N(+)), computation of XPS data enabled the formulation of a three-layer-deep hypothesis for PPy. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.