TiO2光催化可用于污染物降解、水裂解制氢以及CO2减排[12,13],但是TiO2光的禁带宽度较大(3.2 eV)、对可见光的响应较弱(仅对波长小于387 nm的紫外光响应)、电子-空穴复合率过高[14~16]。C掺杂纳米硅藻土@TiO2能在TiO2中形成Ti-O-C键,使纳米硅藻土@TiO2的禁带宽度从3.0 eV降低到1.92 eV和提高纳米硅藻土@TiO2对油田废水的降解效果[17]。用溶胶凝胶法和水热法制备的TiO2/MoS2材料,其禁带宽度大大降低,使油田废水的油污和悬浮物去除率分别提高13.5%和10.8%[18]。一种在掺氟氧化锡(FTO)玻璃上生长具有核壳结构的ZnO/ZnSe/CdSe/Cu2 - x Se纳米线阵列复合材料,具有优异的光电化学(PEC)性能,最高光电流密度为20.57 mA/cm2,0 V时比Ag/AgCl高29.4倍,并且不施加偏置电势,在410 nm可实现87.6%的入射光子转换效率(IPCE),具有高效的光生电子-空穴分离和传输效率[19]。稀土元素掺杂[20]和贵金属[21]复合都能提高TiO2材料对油田废水的降解效果。掺杂[22]和复合[23]仍然是提高TiO2材料光催化性能的重要手段。
表1 F改性TiO2的研究现状
Table 1
| Preparation method | F source | Material | Degradation object | Degradation rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol gel method | NH4F | F-TiO2[31] | Methyl orange | 91.12% |
| Sol gel method | HF | N,F-TiO2 | Acid red B | 100% |
| Steam heating method | HF | Cu/F-TiO2 | Cationic blue | 99.8% |
| Sol gel method | NH4F | F0.2-TiO2 | Methyl orange | 97% |
| Precipitation-sol-hydrothermal crystallization method | NH4F | F-TiO2 | Rhodamine B | 83% |
| Photothermal method | HF | F-TiO2 | - | - |
| Sol gel method | NH4F | N/F-TiO2 | - | - |
| Sol gel method | NH4F | F-TO2@MAC | X-3B | 99.8% |
| Sol gel method | NH4F | N, F-TiO2 | C8H14ClN5 | 86% |
介质阻挡放电(DBD)等离子体是一种独特的物理化学过程,产生的大量活性粒子可使苛刻的反应变得容易。近年来,此法已经广泛用于材料改性和光催化降解污染物[25~27],Di等[28]用Ar/H2等离子体处理制备的Pt/TiO2-P材料,具有更小的粒径(Pt的平均粒径为1.7 nm),其光催化速率是普通介孔TiO2的两倍。Wang等[29]合成TiO2/ACF(TiO2涂层活性炭纤维)催化剂,考察了DBD输出高功率对TiO2/ACF降解TCC (三氯卡班)的影响。Hyung等[30]用介电阻挡放电射流(DBD射流)合成了TiO2纳米颗粒,其阳极光转换效率提高了约50%。鉴于此,本文以C2H2F4为F源,用等离子体放电实现TiO2的氟改性。以模拟污染物亚甲基蓝溶液和中海油湛江市分公司油田污水为降解对象,研究外部环境对光催化降解油田废水的影响,并以苯醌(BZQ)、叔丁醇(TBA)为自由基捕获剂,验证活性自由基在油田废水降解过程中的贡献并探讨其光催化机理。
1 实验方法
1.1 实验用试剂盒仪器
实验用试剂有:无水乙醇(分析纯),钛酸丁酯(分析纯),去离子水(自制),冰乙酸(分析纯),氩气/四氟乙烷(上氟科技)以及亚甲基甲蓝(分析纯)。
实验用仪器有:高压反应釜,烘箱,马弗炉,等离子体反应器。
1.2 TiO2 催化剂和F掺杂TiO2 的制备
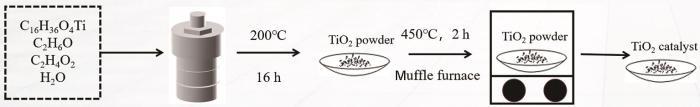
用溶剂热法制备纯TiO2 (图1)。先将40 mL无水乙醇、10 mL钛酸丁酯、1 mL纯水和3.5 mL冰乙酸超声混合均匀,搅拌30 min后移至聚四氟乙烯内衬200℃的高压反应釜中,保温16 h反应结束后倒掉上层清夜,用去离子水洗涤产物并将沉淀置于真空烘箱中充分干燥,将其研成粉末后在450℃马弗炉中煅烧2 h,制得TiO2催化剂。
图1
如图2所示,将0.1 g的TiO2催化剂均匀分散于等离子体反应器中,调节Ar/C2H2F4混合气体的流量以经等离子体反应器的空气排尽,随后调节等离子体发生器电压电流,将处理后的TiO2标记为DBD-F-TiO2。将只用Ar等离子体处理的TiO2催化剂标记为DBD-TiO2。将通入Ar/C2H2F4混合气不进行等离子体放电处理的TiO2催化剂标记为Ar/C2H2F4-TiO2。
图2
图2
等离子体F改性TiO2催化剂的制备过程
Fig.2
Preparation process of plasma F modified TiO2 catalyst
1.3 性能表征
用X.PERT PROX射线仪测量TiO2的XRD(X射线粉末衍射)谱,根据Scherrer公式计算样品的晶粒尺寸;用Hitachi S-4800场发射扫描电子显微镜和FEI TecnaiG2 F20透射电子显微镜(SEM)观察样品的形貌;用JEOL JEM-2100F(RH)场发射电子显微镜测试透射电子显微镜(TEM)和高分辨率透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)图像;用Tensor 27,Bruker,傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)分析TiO2的F改性;用Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250XI的X射线光电子光谱仪(Al Kα,150W,C1s 284.8 eV)进行样品的XPS分析;用F-7000 DC-0506仪器(激发波长λ = 300 nm)对TiO2进行荧光光谱(PL)分析;用UV-1800型紫外可见光分光度计检测亚甲基蓝溶液的吸光度;用MI-80K COD检测降解过程中油田废水的COD值。
F改性TiO2催化剂光催化性能的测试:(1) 使用氙灯作为可见光源,亚甲基蓝溶液浓度为10 mg/L。将0.1 g的TiO2光催化剂与100 mL的亚甲基蓝溶液混合后在黑暗中避光搅拌30 min以达到吸附-脱附平衡。开启光照后每间隔20 min取样离心一次,用紫外可见光分光光度计测试上层清夜的吸光度(λ =664 nm),测试结束后倒回溶液。(2) 用氙灯模拟可见光光源,降解中海油湛江分公司提供的油田废水。光催化实验前用自搭的过滤装置对油田废水进行预处理以除去表面油污和悬浮物,减小对光催化实验的干扰。其中,除去表面油污和悬浮物的油田废水COD含量为85 mg/L。将适量的TiO2光催化剂与100 mL油田废水混合后在避光条件下搅拌30 min,开启光源后间隔20 min计算上层清夜离心计算COD值,测试结束后立即倒回溶液。
亚甲基蓝溶液的降解率为
其中C0、A0分别为亚甲基蓝溶液初始浓度和初始吸光度,Ct、At分别为亚甲甲蓝溶液降解后的浓度和吸光度。
禁带宽度为
其中α为吸光度,h为普朗克常量,v为光频率,A为常数,Egap为禁带宽度。绘制(αhv)1/2-hv曲线,然后将其直线部分外推至与hv轴交点,交点坐标即为禁带宽度Egap。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 等离子体氟改性TiO2 的组成
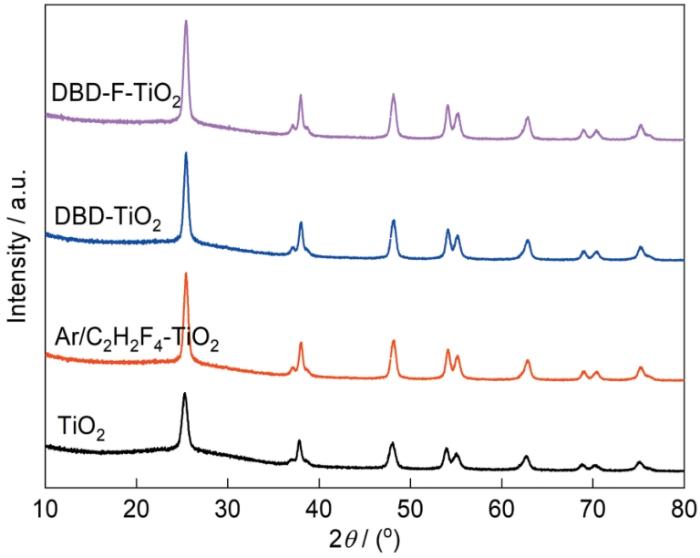
图3给出了等离子体氟改性TiO2的XRD谱。可以看出,所有的样品与纯TiO2的特征峰相似,都在2θ = 25.3°、37.7°、47.9°、53.9°、55.1°、62.6°、68.4°、70.5°出现了尖锐且狭窄的衍射峰,表明已经制备出了锐钛矿TiO2(PDF#21-1272)[40],也说明等离子体处理对TiO2的晶体结构没有影响[41]。根据Scherrer公式计算出DBD-F-TiO2、DBD-TiO2、Ar/F2-TiO2、TiO2催化剂的晶粒尺寸分别为13.2、11.8、11.7、11.7 nm。DBD-F-TiO2晶粒尺寸的增大可归因于F掺杂,使TiO2产生晶格畸变,从而晶粒尺寸增大。
图3
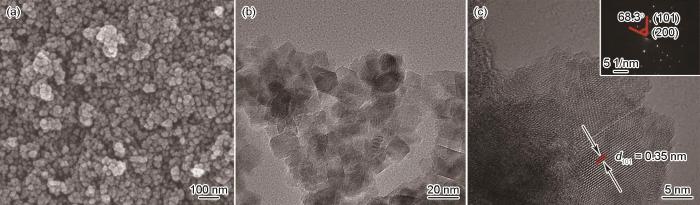
图4
图4
DBD-F-TiO2催化剂的SEM、TEM照片以及HRTEM图和电子衍射谱
Fig.4
SEM diagram of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst (a), TEM diagram of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst (b), HRTEM and electron diffraction pattern diagram (c) of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst
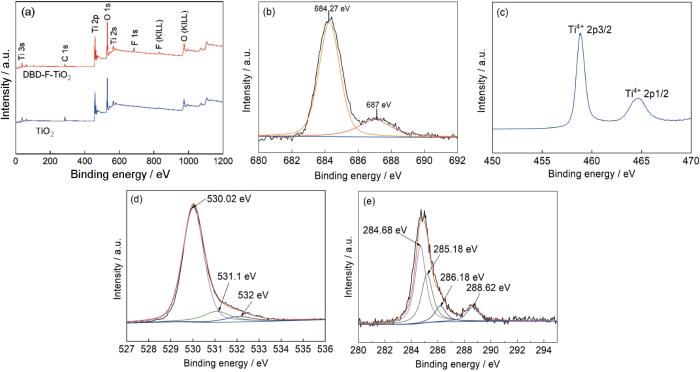
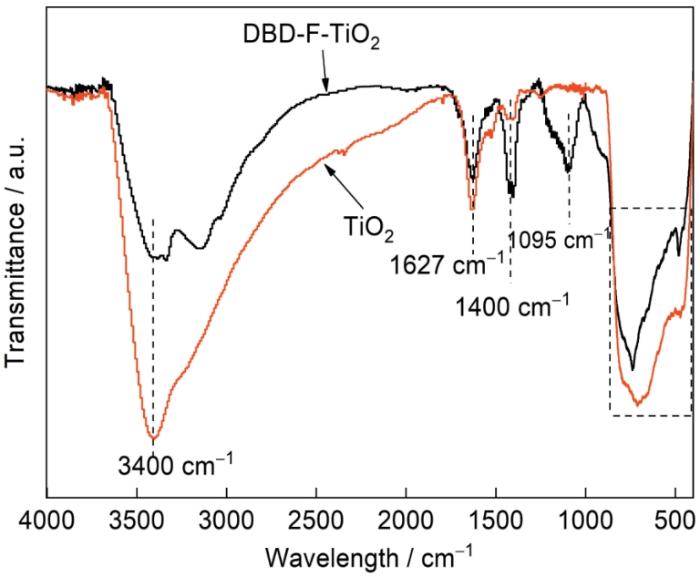
图5中给出了DBD-F-TiO2和TiO2的全谱,可见结合能约为458.00、530.00、684.00、284.00 eV。只出现了Ti、O、F、C的特征峰,没有出现杂质元素的特征峰。为了进一步研究三种元素的存在形式,图5b~e给出了Ti、O、F、C的高分辨谱,其中684.27 eV处的峰归因于表面≡Ti-F,687 eV处的峰归因于Ti-O-F-Ti(间隙F掺杂)[43]。这些结果表明,实现了TiO2的F掺杂改性,部分F元素进入TiO2晶格形成Ti-O-F-Ti键,但是没有形成取代F掺杂。458.60、464.30 eV处的峰归因于Ti4+ 2p/3/2和Ti4+ 2p/1/2[44],Ti的主要存在形式为Ti4+。530.01、531.10、532 eV处的峰,归因于Ti-O-Ti键、Ti-OH键、表面氧缺陷(Ov),其中表面氧缺陷归因于等离子体处理[45]。图5e给出了DBD-F-TiO2催化剂的C 1s高分辨谱,284.68、286.18、288.62 eV处的峰分别对应C—C键、C—O键、C=O键,其中未在结合能281.5 eV出峰,说明未形成C掺杂[46]。≡Ti-F、Ti-O-F-Ti、Ov的相对含量分别为2.58%、0.96%、5.4%。以上结果表明,F改性成功地在TiO2表面形成≡Ti-F键、氧缺陷和间隙F掺杂(Ti-O-F-Ti键)。
图5
图5
DBD-F-TiO2和TiO2的全谱以及DBD-F-TiO2催化剂的F 1s高分辨谱、Ti 2p高分辨谱、O 1s高分辨谱和C 1s高分辨谱
Fig.5
XPS spectrum of catalyst (a) full spectrum of DBD-F-TiO2 and TiO2, (b) F 1s high-resolution spectrum of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst, (c) Ti 2p high-resolution spectrum of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst, (d) O 1s high-resolution spectrum of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst, (e) C 1s high resolution spectrum of DBD-F-TiO2 catalyst
图6
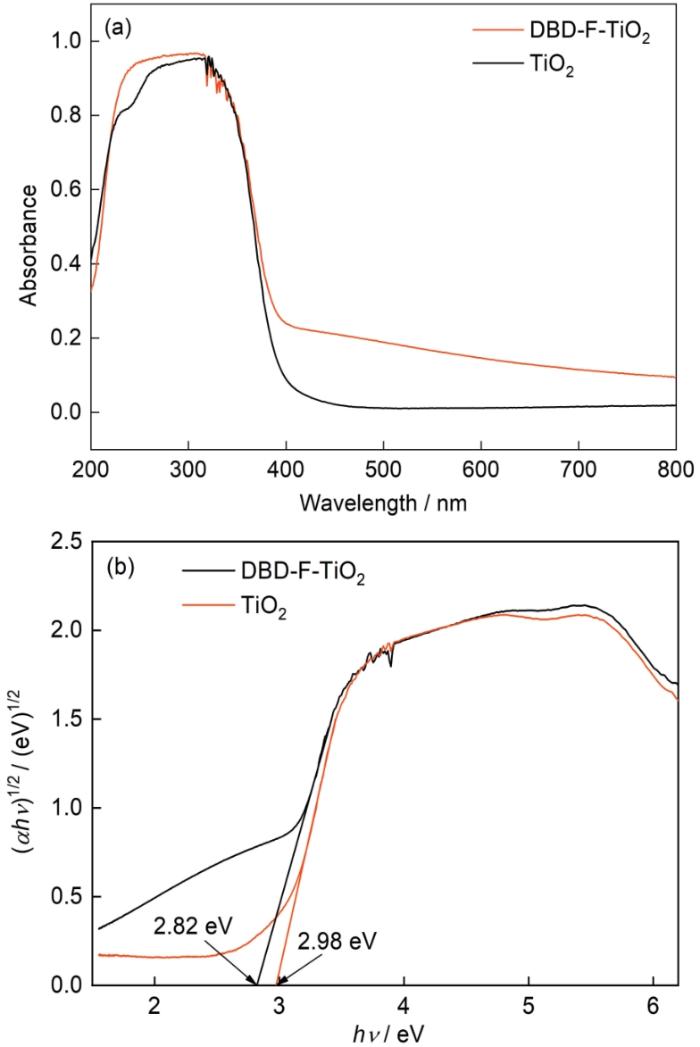
图7给出了UV-vis光谱和(αhv)1/2与(hv)的关系。可以看出,DBD-F-TiO2和TiO2催化剂具有典型的TiO2特征吸收带,在紫外光区域的吸收几乎相同,都表现出了强吸收,但是在可见光区域DBD-F-TiO2吸收明显增强。其中DBD-F-TiO2和TiO2的吸收阈值分别为440和416 nm,说明DBD-F-TiO2存在的红移现象。DBD-F-TiO2和TiO2的禁带宽度分别为2.82和2.98 eV,可归因于Ti-O-F-Ti(间隙F掺杂)和表面缺陷的共同作用,与XPS的分析结果符合。在TiO2价带上方的F掺杂和氧缺陷在导带下方形成杂质能级[51],可在一定程度上降低TiO2的禁带宽度,促进材料对可见光的吸收而使其光催化性能提高。
图7
图7
DBD-F-TiO2和TiO2的UV-vis光谱以及 (αhv)1/2与(hv)的关系
Fig.7
UV vis spectrogram of DBD-F-TiO2 and TiO2 (a) and relationship between (αhv)1/2 and (hv) (b)
图8
2.2 亚甲基蓝和油田废水的光催化降解性能
图9
图9
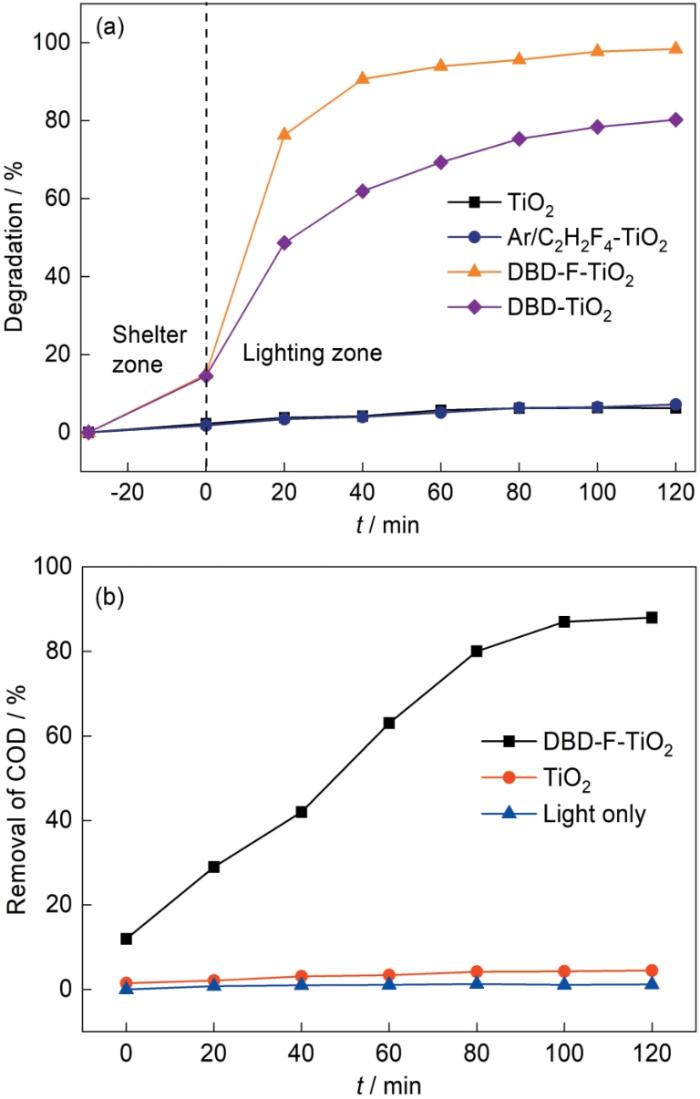
催化剂对亚甲基蓝溶液的降解率以及DBD-F-TiO2与TiO2体系对油田废水的COD去除率
Fig.9
Photocatalytic performance of materials (a) degradation rate of methylene blue solution by catalyst, (b) COD removal rate of oilfield waste-water by DBD-F-TiO2 and TiO2 systems
2.3 外部环境对DBD-F-TiO2 体系油田废水降解性能的影响
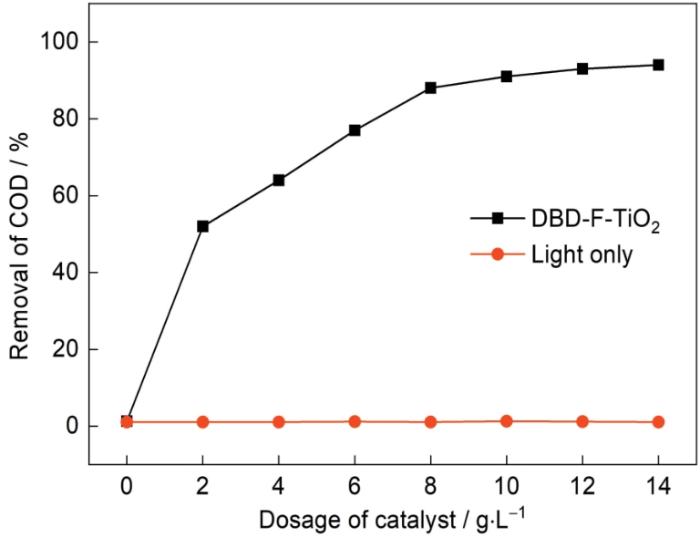
图10给出了催化剂的加量对油田废水COD去除率的影响。结果表明,随着添加量从2 g/L增加到14 g/L系统的氧化能力不断提高,油田废水的COD去除率随之提高。BD-F-TiO2体系的最佳催化剂加量为8 g/L。
图10
图10
催化剂的加量对油田废水COD去除率的影响
Fig.10
Effect of catalyst dosage on COD removal rate of oilfield wastewater
图11
图11
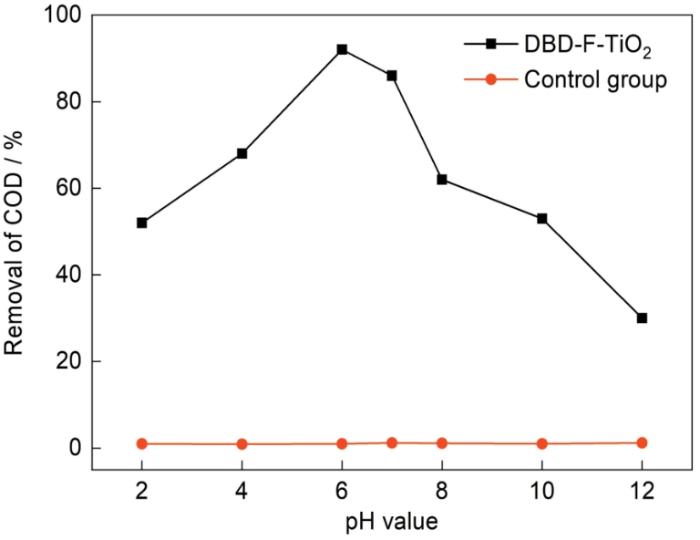
pH值对油田废水COD去除率的影响
Fig.11
Effect of pH value on COD removal rate of oilfield wastewater
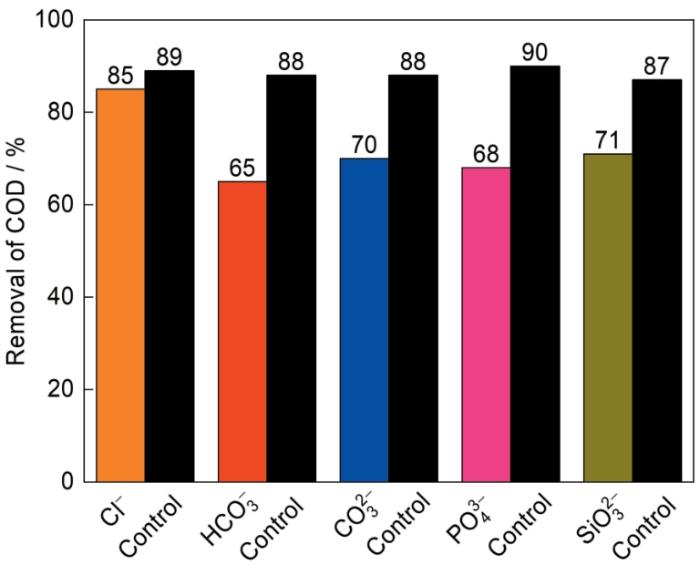
图12给出了五种阴离子(Cl-、$\mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}$、$\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}$、$\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}$、$\mathrm{SiO}_3^{2-}$)对DBD-F-TiO2光催化体系油田废水COD去除率的影响。为了验证阴离子对光催化反应的干扰,DBD-F-TiO2体系对油田废水的COD去除率中,对照组不添加任何阴离子。可以看出,除Cl-以外,$\mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}$、$\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}$、$\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}$、$\mathrm{SiO}_3^{2-}$明显地抑制了油田废水COD的去除。因为Cl-能与溶液中的羟基反应生成氯自由基[54](
图12
图12
阴离子类型对油田废水COD去除率的影响
Fig.12
Effect of anion types on COD removal rate of oilfield wastewater
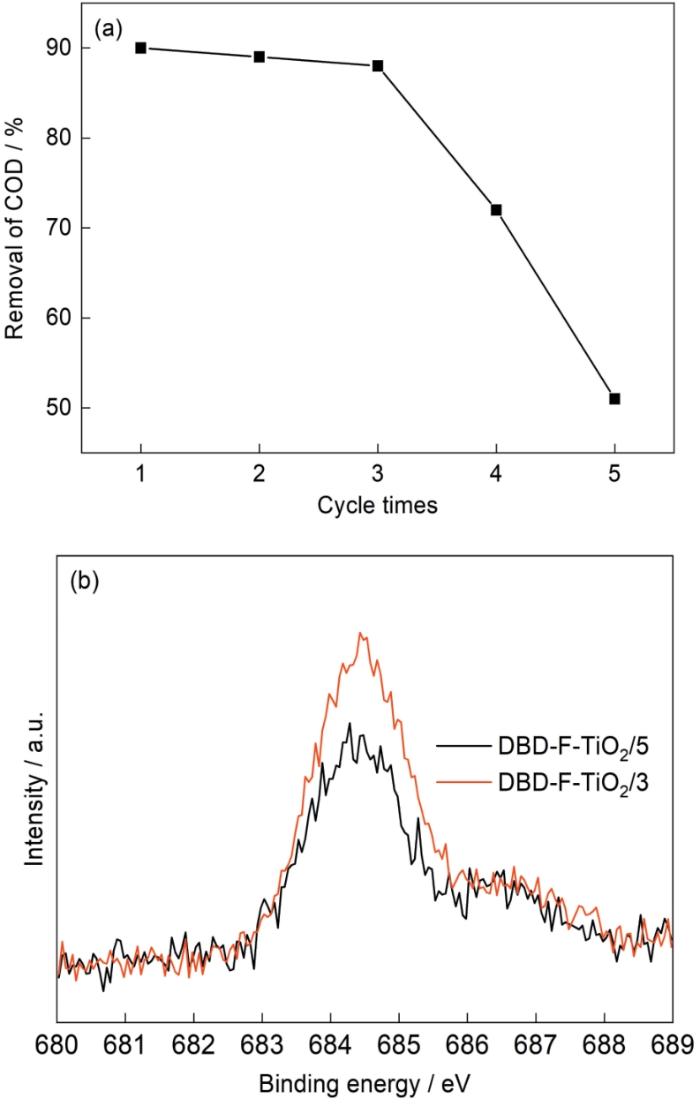
实验结果表明,DBD-F-TiO2/3(三个循环后催化剂)的光催化性能明显降低,其稳定性偏弱。对DBD-F-TiO2/3和DBD-F-TiO2/5(五个循环后催化剂)催化剂进行XPS表征,两种催化剂的F高分辨谱图如图13b所示。可以看出,第五次循环后位于结合能684.5 eV附近F的特征峰强度明显弱于第三次。经过循环后DBD-F-TiO2催化剂的F元素含量从3.30%下降到2.87%。这表明,多次循环后表面≡Ti-F遭到破坏,可能是催化剂循环后催化性能下降的主要原因。
图13
图13
催化剂的重复使用性能以及DBD-F-TiO2/3和DBD-F-TiO2/5催化剂的F1s高分辨谱
Fig.13
Catalystreuseperformance (a), F1s high resolut-ion spectrum (b) of 0.3F-Ti/3 and 0.3F-Ti/5 catalysts
为了进一步了解活性物质在含油废水在降解过程中的贡献,使用苯醌(BZQ)、叔丁醇(TBA)作为超氧自由基(·$\mathrm{O}_2^{-}$)和羟基自由基(·OH)的清除剂。如图14a所示,随着BZQ和TBA浓度的提高COD去除率都下降,而TBA的影响更甚。这表明,羟基自由基对该反应的影响起主导作用。
图14
图14
自由基捕获实验和光催化机理
Fig.14
Radical capture experiment (a) and photoca-talytic mechanism diagram (b)
根据表征分析结果及实验数据,可能的光催化机理图如图14b所示。TiO2等离子体氟改性后在TiO2表面产生了表面≡Ti-F和氧缺陷。这些表面≡Ti-F和氧缺陷,促进光生电子-空穴向TiO2表面转移并抑制电子-空穴的复合。同时,间隙F掺杂和表面氧缺陷在价带上方和导带下方形成杂质能级,减小TiO2禁带宽度,促进了对可见光的吸收。二者的协同作用,使催化剂的光催化性能提高。
3 结论
(1) 以钛酸丁酯为钛源使用溶剂热法可制备TiO2,以C2H2F4为氟源进行等离子体放电可实现TiO2的氟改性。
(2) 与纯TiO2相比,DBD-F-TiO2催化剂对亚甲基蓝降解率和油田废水的COD去除率大大提高。羟基自由基和超氧自由基是光催化反应的主要活性物质,而羟基自由基(·OH)的影响更为关键。
(3) 等离子体氟改性后在TiO2表面引入≡Ti-F键和表面氧缺陷,可实现TiO2的间隙F掺杂(Ti-O-F-Ti),≡Ti-F键和表面氧缺陷能促进光生电子空穴向TiO2表面转移并抑制光生电子-空穴的复合。F掺杂和氧缺陷能在价带上方和导带下方形成杂质能级,使TiO2禁带宽度减小和增强TiO2在可见光区域的吸收。二者的协同作用可提高对油田废水的光催化降解效率。
参考文献
Study and application on high effective treatment technology of operation wastewater in oilfield
[J].
高效处理油田作业废水技术的研究及应用
[J].
Treatment of oilfield wastewater in moving bed biofilm reactors using a novel suspended ceramic biocarrier
[J].In this study, a novel suspended ceramic carrier was prepared, which has high strength, optimum density (close to water), and high porosity. Two different carriers, unmodified and sepiolite-modified suspended ceramic carriers were used to feed two moving bed biofilm reactors (MBBRs) with a filling fraction of 50% to treat oilfield produced water. The hydraulic retention time (HRT) was varied from 36 to 10h. The results, during a monitoring period of 190 days, showed that removal efficiency of chemical oxygen demand was the highest in reactor 3 filled with the sepiolite-modified carriers, followed by reactor 2 filled with the unmodified carriers, with the lowest in reactor 1 (activated sludge reactor), at an HRT of 10h. Similar trends were found in the removal efficiencies of ammonia nitrogen and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Reactor 3 was more shock resistant than reactors 2 and 1. The results indicate that the suspended ceramic carrier is an excellent MBBR carrier.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Solar photocatalytic degradation of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected water
[J].Bitumen mining in the Canadian oil sands creates large volumes of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW), the toxicity of which is due in part to naphthenic acids (NAs) and other acid extractable organics (AEO). The objective of this work was to evaluate the potential of solar photocatalysis over TiO2 to remove AEO from OSPW. One day of photocatalytic treatment under natural sunlight (25 MJ/m(2) over ∼14 h daylight) eradicated AEO from raw OSPW, and acute toxicity of the OSPW toward Vibrio fischeri was eliminated. Nearly complete mineralization of organic carbon was achieved within 1-7 day equivalents of sunlight exposure, and degradation was shown to proceed through a superoxide-mediated oxidation pathway. High resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) analysis of oxidized intermediate compounds indicated preferential degradation of the heavier and more cyclic NAs (higher number of double bond equivalents), which are the most environmentally persistent fractions. The photocatalyst was shown to be recyclable for multiple uses, and thus solar photocatalysis may be a promising "green" advanced oxidation process (AOP) for OSPW treatment.Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of surface oil from the Deepwater Horizon spill
[J].The photochemical behavior of Deepwater Horizon oil collected from the surface of the Gulf of Mexico was studied. Thin oil films on water were subjected to simulated sunlight, and the resulting chemical and optical changes were observed. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) showed substantial photodegradation, with larger PAHs being more rapidly decomposed. About 60% of the fluorescence at the excitation and emission maxima was observed with 12h of simulated solar irradiation equivalent to approximately 3d of sunlight. Synchronous scan fluorescence measurements showed 80-90% loss of larger PAHs with 12h of simulated solar irradiation. Absorbance of the oil decreased by only 20% over the same time period. Alkanes showed no significant photochemical losses. After irradiation, the toxicity of water in contact with the oil significantly increased, presumably due to the release of water soluble photoproducts that were toxic. Photocatalyst addition resulted in enhanced degradation rate for PAHs, and toxicity of the aqueous layer was altered in the presence of photocatalysts added to the oil film. Photochemistry is an important pathway for degradation of large PAHs, which are typically resistant to biodegradation. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Thickness-ultrathin and bismuth-rich strategies for BiOBr to enhance photoreduction of CO2 into solar fuels
[J].
Detection of left-sided and right-sided hearing loss via fractional Fourier transform
[J].
nanostructuredHierarchical 3D flowerlike BiOCl x Br1 - x semiconductors with exceptional visible light photocatalytic activity
[J].
Selective oxofunctionalization of cyclohexane over titanium dioxide-based and bismuth oxyhalide (BiO X, X = Cl-, Br-, I-) photocatalysts by visible light irradiation
[J].
The progress of the wastewater treatment by micro-electrolysis technology
[J].
微电解法处理废水研究进展
[J].
Research status and prospect of film separation technology for oilfield wastewater treatment
[J].
膜分离技术处理油田废水研究现状及展望
[J].
Research on a honeycombed micro-electrolysis reactor based on flow improvement and its application in oil field wastewater treatment
[J].
基于流态改进的仓式微电解反应器处理油田废水研究
[J].
Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode
[J].
Metal-organic frameworks based photocatalysts: architecture strategies for efficient solar energy conversion
[J].
TiO2 nanotubes: synthesis and applications
[J].
Preparation of S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts and their photocatalytic activities under visible light
[J].
Study on the treatment of organic compounds in oilfield wastewater by Cu2+/ZnO/TiO2 composite photocatalyst
[D].
Cu2+/ZnO/TiO2复合光催化剂处理油田废水中有机物研究
[D].
Adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of oilfield wastewater by C-doped diatomite@TiO2 catalyst
[J].
C掺杂纳米硅藻土@TiO2催化剂吸附-光催化降解油田废水
[J].
Preparation and application of TiO2/MoS2 photocatalyst in oilfield wastewater treatment
[J].
复合材料TiO2/MoS2的制备及对油田废水处理
[J].
Enhanced photoelectrochemical properties of ZnO/ZnSe/CdSe/Cu2 - x Se core-shell nanowire arrays fabricated by ion-replacement method
[J].
Recent progress on rare earth elements doped nano-titanium dioxide photocatalysts
[J].
稀土掺杂二氧化钛光催化剂的研究进展
[J].
Study of loaded photocatalysts by precious metals on the photocatalytic reactivity
[J].
负载贵金属光催化剂的光催化活性研究
[J].
Preparation and photocatalytic activity of Fe/Yb co-doped titanium dioxide hollow sphere
[J].Composites of Fe/Yb co-doped TiO2 hollow spheres (Fe/Yb-TiO2HS) were prepared by template method and then characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TG). The photocatalytic performance of the composites was assessed with a simulated wastewater of 20 mg/L methyl orange solution under radiation of visible light. The results show that the degradation efficiency of doped titanium dioxide hollow spheres for the methyl orange could be significantly improved. The composite doped with 0.1% Fe and 1% Yb presents the optimal photocatalytic performance with degradation efficiency up to 92.57% for the methyl orange.
铁/镱掺杂二氧化钛空心球的制备及其光催化性能
[J].用模板法制备铁/镱共掺杂二氧化钛空心球(Fe/Yb-TiO<sub>2</sub>HS),使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察和X射线衍射(XRD)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)、热失重(TG)等测试方法对对其进行了表征。使用浓度为20 mg/L的甲基橙溶液模拟废水,研究了铁/镱共掺杂二氧化钛空心球的催化性能。结果表明:铁/镱共掺杂的二氧化钛空心球对甲基橙的降解效果较好,铁掺杂量为0.1%和镱掺杂量为1%的催化剂其光催化性能达到92.57%。
Preparation of TiO2/ZnO composite photocatalyst and its photocatalytic performance
[J].
TiO2/ZnO复合光催化剂的制备及其光催化性能研究
[J].
Enhanced remote photocatalytic oxidation on surface-fluorinated TiO2
[J].The mobile nature of active oxygen species generated on the UV-illuminated TiO2 surface is now well-recognized. Surface oxidants not only migrate two-dimensionally but also desorb from the surface to be air-borne oxidants. The remote photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) of stearic acids over the surface-fluorinated TiO2 (F-TiO2) film was carried out in the ambient air to study the effects of fluorination on the desorption of oxidants from the surface. The F-TiO2 film was faced to a stearic acid-coated glass plate separated by a small gap (typically 30 microm), and the photocatalytic degradation of the stearic acid was monitored by Fourier transform infrared measurement or gas-chromatographic CO2 production analysis. Remote photocatalytic degradation of stearic acids was markedly faster with F-TiO2 than with the pure TiO2 film, which indicates that the generation of air-borne oxidants is enhanced over the F-TiO2 surface. The remote PCO activity was higher with a higher surface fluoride concentration, higher UV intensity, and smaller gap. The remote photocatalytic activity of F-TiO2 was maximal at a relative humidity of 50% and did not show any sign of deactivation with repeated reactions. The production of CO2 that evolved as a result of the remote PCO of stearic acids was enhanced when H2O2 vapor was present but was strongly inhibited in the presence of ammonia gas that should scavenge OH radicals. Judging from various evidences, the air-borne oxidants in remote PCO are most likely OH radicals and the surface fluorination of TiO2 seems to facilitate the desorption of OH radicals.
Functionalization of cellulose nanocrystal films using Non-Thermal atmospheric -Pressure plasmas
[J].
Surface adhesive properties of continuous PBO fiber after air-plasma-grafting-epoxy treatment
[J].
Preparation and rheological study of pentaerythritol triacrylate grafted onto polypropylene induced by air plasma
[J].
A facile method for preparing Pt/TiO2 photocatalyst with enhanced activity using dielectric barrier discharge
[J].
Degradation of triclocarban in water by dielectric barrier discharge plasma combined with TiO2/activated carbon fibers: effect of operating parameters and byproducts identification
[J].
Mesoporous TiO2 films fabricated using atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge jet
[J].
Preparation of F- doped TiO2 and its photocatalytic degradation performance on methyl orange
[J].
F-掺杂TiO2制备及光降解甲基橙性能研究
[J].以钛酸四丁酯为钛源,氟化铵为掺杂源采用溶胶-凝胶法制备了F掺杂二氧化钛(F/TiO2),通过甲基橙降解实验研究了掺杂量和外部加入氟化钠对光催化性能的影响.采用X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、紫外可见漫反射光谱(UV-vis DRS)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对样品进行了表征.实验结果显示:氟离子掺杂会影响TiO2的结晶程度、晶粒尺寸、形貌和光吸收带边,热处理过程F几乎没有损失;550℃煅烧和350 W金卤灯照射75min,10; F/TiO2对甲基橙的降解率达到了91.12;,未掺杂样品在相同条件下降解率只有45.6;;在甲基橙溶液中事先加入氟化钠,能加快催化剂对甲基橙的降解,在相同条件下照射60 min,10; F/TiO2对甲基橙的降解率达到了96.46;,未掺杂二氧化钛在相同条件下降解率为59.40;.550℃煅烧时,F掺杂使得二氧化钛的光吸收带边发生一定的蓝移.
Preparation of N, F-codoped TiO2 and its photocatalytic activity under visible light
[J].
氮氟掺杂二氧化钛(N,F-TiO2)的制备及可见光催化活性的研究
[J].
Preparation of fluorine and copper co-doping TiO2 hollow microspheres and its visible light photocatalytic performance
[J].
氟铜共掺杂TiO2空心微球的制备及可见光催化性能
[J].
Preparation and photocatalytic property of f-modified TiO2
[J].
氟改性TiO2的制备及光催化性能研究
[J].以钛酸丁酯为钛源,氟化铵为氟源,采用溶胶凝胶法制备氟改性二氧化钛光催化剂,并用扫描电镜(SEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)、紫外可见光分度计(UV-Vis)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、光致发光荧光光谱仪(PL)、氮气吸附-脱附等方法对样品进行表征.以甲基橙(MO)为模拟污水,研究其光催化活性.结果 表明:F改性TiO2为纳米锐钛矿相,比表面积为141 m2/g.F以化学吸附态存在于TiO2的表面,形成(=)Ti-F基团,F的加入使得TiO2的吸收带边发生了红移,在甲基橙浓度为20 mg/L,紫外光照射时间为80 min时,F改性TiO2的脱色率最大达到了97;,具有较高的光催化活性.
Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic performance of anatase F doped TiO2 sol
[J].
氟掺杂锐钛矿型TiO2溶胶的制备、表征及催化性能
[J].以四氯化钛为前驱物, 采用改性的沉淀-溶胶-水热晶化法制备了一种具有锐钛矿型结构的氟掺杂的二氧化钛(F-TiO<sub>2</sub>)溶胶. 研究了氟掺杂、水热晶化的温度、时间及介质pH值对溶胶粒子的晶型和晶化度的影响. 采用XRD, TG-DTA, TEM, UV-Vis-DRS, FTIR, XPS技术及吸附、表面酸度测定手段对溶胶粒子的结构进行了表征. XRD分析结果表明: 氟的掺入可以降低水热晶化反应的温度或减少反应时间、提高粒子的晶化度, 溶胶粒子具有锐钛矿型结构; TEM分析显示: 粒子呈圆球型, 平均粒径大约为6.5 nm. XPS测定结果表明; 氟在溶胶粒子中以吸附态和结合态两种形式存在; 吸附、表面酸度及光催化活性测定表明: 与P25型TiO<sub>2</sub>及纯TiO<sub>2</sub>溶胶粒子相比, F-TiO<sub>2</sub>溶胶粒子具有更大的吸附能力、更强的表面酸度及更高的光催化活性. 还从光生载流子分离效率等方面探讨了掺杂对催化剂活性影响的机理.
Synthesis of F-TiO2 nanosheets and its photocatalytic oxidation of benzene to phenol
[J].
Preparation of gold-modified F,N-TiO2 visible light photocatalysts and their structural features comparative analysis
[J]. J.
Photocatalytic properties of magnetic activated carbon supported F-doped TiO2
[J].
磁性活性碳负载F掺杂纳米二氧化钛的光催化性质研究
[J].
Enhancement of the intrinsic photocatalytic activity of TiO2 in the degradation of 1,3,5-triazine herbicides by doping with N,F
[J].
Ag-doped TiO2 composite films prepared using aerosol-assisted, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition
[J].TiO2 is a promising photocatalyst, but its large bandgap restricts its light absorption to the ultraviolet region. The addition of noble metals can reduce the bandgap and electron-hole recombination; therefore, we prepared TiO2-Ag nanoparticle composite films by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) using a mixture of aerosolized AgNO3, which was used as a Ag nanoparticle precursor, and titanium tetraisopropoxide, which acted as the TiO2 precursor. Notably, the use of PECVD enabled a low process temperature and eliminated the need for pre-preparing the Ag nanoparticles, thereby increasing the process efficiency. The structures and morphologies of the deposited films were characterized by ultraviolet (UV)—visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and the effects of the AgNO3 concentration on the photocatalytic activity of the deposited films were determined by assessing the degradation of methylene blue under UV light irradiation. The Ag ions were successfully reduced to metallic nanoparticles and were embedded in the TiO2 film. The best photocatalytic activity was achieved for a 1 wt% Ag-loaded TiO2 composite film, which was 1.75 times that of pristine TiO2.
Preparation and characterization of TiO2-TiOF2 photocatalyst
[J].
TiO2-TiOF2光催化剂的制备及其性能表征
[J].采用水热法制备了TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>异质半导体复合材料。以废水中的盐酸四环素(TTCH)为目标污染物,研究了TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>的光催化活性。在催化剂投加量为0.3 g/L的条件下,光催化反应30 min,对质量浓度为10 mg/L的TTCH去除率高达85.4%,且TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>催化剂具有较好的重复使用性能。催化剂的表征结果显示,TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>特殊的花簇状结构使其比表面积显著增大,有利于催化剂表面产生更多的吸附位点。TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>具有更多的氧空位,且电子空穴对的复合率较低。由于 TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>在紫外区域有很强的吸收,且能吸收部分可见光,使得TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>能更大程度地利用太阳光,提高污染物氧化的量子效率。自由基捕获实验结果表明,·O<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>和·OH在TiO<sub>2</sub>-TiOF<sub>2</sub>催化降解TTCH的过程中起到了重要的作用。
Modification of the photocatalytic properties of anatase TiO2 (101) surface by doping transition metals
[J].
过渡金属掺杂锐钛矿TiO2(101)表面的改性
[J].
Photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous ammonia over fluorinated TiO2 with exposed (001) facets
[J].
Catalytic wet oxidation of aniline over Ru catalysts supported on a modified TiO2
[J].
改性二氧化钛负载贵金属Ru催化剂催化降解苯胺溶液
[J].苯胺类废水污染物具有结构复杂、浓度高、不易生物降解、生物毒性大等特点,传统的苯胺降解措施存在着许多弊端,很难达到排放标准.催化湿法氧化技术(CWAO)主要针对降解高浓度难降解的有机废水,表现出降解效率高、反应时间短、对生物毒性物质的废水降解效果良好等优点,越来越受到人们的重视.但催化剂在使用过程中,需要在高温高压下进行,且有机物降解产生了有机酸,使得催化剂的活性组分流失和载体的物理化学性质发生变化,导致其催化活性下降.因此,需要开发出一种降解活性高,性能稳定的催化剂成为此技术在工业中广泛应用的关键.本文采用溶胶凝胶法对二氧化钛进行改性,制备了Ti<sub>0.9</sub>Zr<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub>和Ti<sub>0.9</sub>Ce<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub>载体,采用过量浸渍法将三氯化钌负载到载体表面制备了2% Ru/Ti<sub>0.9</sub>Zr<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub>和2% Ru/Ti<sub>0.9</sub>Ce<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub>催化剂.在高温高压反应条件下,以苯胺为催化湿法氧化污染物,对不同催化剂湿法降解苯胺进行比较研究,系统地探究了催化降解的反应温度和反应压力对苯胺降解的影响.此外,利用HPLC-MS鉴定出催化降解产生的中间产物,确定了催化降解的反应路径图.在改性的催化剂中,2% Ru/Ti<sub>0.9</sub>Zr<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub>催化剂表现出最高的催化降解活性和稳定性.在初始苯胺浓度4 g/L,催化剂浓度4 g/L,反应温度180℃,O<sub>2</sub>压力1.5 MPa下,反应时间5 h后,苯胺完全转化,COD转化率达88.3%.并且催化剂进行三次循环试验后,苯胺转化率仍接近100%.X射线衍射和N<sub>2</sub>物理吸附结果表明,Ce,Zr掺杂到TiO<sub>2</sub>晶格中形成了共溶体,其晶格尺寸更小,比表面积和孔体积更大.负载贵金属后,并未出现其他晶相,说明贵金属均匀分散在载体表面.透射电镜结果表明,贵金属负载在改性TiO<sub>2</sub>上表现出较好的分散性和较小的颗粒尺寸,为催化降解苯胺提供更多的催化活性位点,而Ru/TiO<sub>2</sub>催化剂表面,贵金属发生团聚现象且颗粒尺寸大.X射线光电子能谱结果表明,Ce,Zr的掺杂使得TiO<sub>2</sub>表面活性氧和四价Ru的含量增加,更多的表面活性氧成为催化降解苯胺的直接原因.H<sub>2</sub>程序升温还原结果表明,在300-400 ℃处还原峰对应于催化剂载体晶格氧的还原,改性后,其还原峰增至2倍,即使在贫氧环境下,改性催化剂可以及时从载体中释放晶格氧,为催化降解苯胺提供更多的活性氧.
Photocatalytic performance of TiO2 nanocrystals with/without oxygen defects
[J].
无缺陷和氧缺陷二氧化钛的光催化活性 (英文)
[J].随着全球工业的发展,大量有机污染物排放到水中,已经威胁到人类健康.自1972年Fujishima和Honda发现TiO<sub>2</sub>半导体材料可在光照下分解水以来,光催化技术作为一种新型污水处理方法引起广泛重视.近几十年来,光催化已被广泛研究,已成为水体净化领域最有前途的方法之一.TiO<sub>2</sub>光催化剂由于具有无毒、耐腐蚀、高稳定和低成本等特点,在光催化领域受到广泛关注,是最具有开发前景的光催化材料之一.然而,TiO<sub>2</sub>的禁带较宽,只能吸收仅占太阳光4%的紫外光部分,这严重限制了TiO<sub>2</sub>光催化材料对太阳光的有效应用.最新研究结果表明,适量缺陷的存在可以拓展TiO<sub>2</sub>对可见光的响应,从而通过提高其对太阳光的利用效率来有效提升TiO<sub>2</sub>的光催化活性.因此,研究半导体缺陷与其光催化剂性能的关系,对于提升光催化污染物降解性能具有重要意义.本工作采用水热法和溶胶-凝胶法分别制备了具有氧缺陷的和无缺陷的TiO<sub>2</sub>,用于研究氧缺陷对TiO<sub>2</sub>光催化活性的影响.所制备的氧缺陷TiO<sub>2</sub>纳米材料为浅蓝色,光的吸收波长向可见光区(~420nm)拓展.拉曼光谱和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)测试均证明溶胶-凝胶法制备的TiO<sub>2</sub>中氧空缺位的浓度低于水热合成TiO<sub>2</sub>的氧空缺位浓度.光化学测试结果表明,氧缺陷TiO<sub>2</sub>在模拟太阳光下的光电流响应增强,这是由于氧缺陷的引入导致能带隙内出现了新的电子态,使得禁带宽度变窄.在光降解亚甲基蓝(MB)的实验中,氧缺陷TiO<sub>2</sub>材料表现出更高的光催化活性.根据密度泛函理论(DFT)计算和荧光光谱测试结果,讨论了氧缺陷TiO<sub>2</sub>的光催化机理.
A heterogeneous Fenton reaction system of N-doped TiO2 anchored on sepiolite activates peroxymonosulfate under visible light irradiation
[J].
Synthesis and characterization of visible light responsive N-TiO2 mixed crystal by a modified hydrothermal process
[J]. J.
Improvement of photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation by heterojunction of Cu ion loaded WO3 and Cu ion loaded N-TiO2
[J].
Effect of annealing on the structure, morphology and photocatalytic activity of surface-fluorinated TiO2 with dominant {001} facets
[J].
Nitrogen and fluorine codoped, colloidal TiO2 nanoparticle: tunable doping, large red-shifted band edge, visible light induced photocatalysis, and cell death
[J].
Photocatalytic activity of TiO2 photocatalyst Co-doped with indium and X(X = B, Ce)
[J].
In, X(X = B, Ce)共掺杂TiO2光催化活性研究
[J].室温下,以硼酸、硝酸铟和硝酸铈为前驱体,采用超声辅助的溶胶-凝胶法制备B,In-TiO<sub>2</sub>和In,Ce-TiO<sub>2</sub>光催化剂,并用XRD、XPS、UV-Vis DRS、FT-IR和SEM等对其进行表征。以罗丹明B(RhB)为模拟污染物,考察其在太阳光照射下催化活性。结果表明,共掺杂能显著改善TiO<sub>2</sub>表面形态,增加活性氧物种的数量,所制备的TiO<sub>2</sub>催化剂均为锐钛矿;在B,In-TiO<sub>2</sub>中,填隙B离子的B2p与O2p轨道杂化形成混合价带,部分In取代TiO<sub>2</sub>晶格中的Ti,形成Ti-O-In结构,使带隙变窄,光催化活性增强。在In,Ce-TiO<sub>2</sub>中,Ce的氧化物能与TiO<sub>2</sub>形成异质结间的相互作用及共掺杂In和Ce元素对TiO<sub>2</sub>电子结构的协同作用,使TiO<sub>2</sub>的吸收边红移,带隙变窄。太阳光照射下,B,In-TiO<sub>2</sub>和In,Ce-TiO<sub>2</sub>降解RhB的速率常数分别为0.7907和0.8525 min<sup>-1</sup>,RhB降解率超过了99%。
Photocatalytic oxidation degradation study for operation wastewater treatment in oil field
[J].
油田作业废水光催化氧化降解研究
[J].
Adsorption behavior and mechanism of chloramphenicols, sulfonamides, and non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals on multi-walled carbon nanotubes
[J].The adsorption behavior of different emerging contaminants (3 chloramphenicols, 7 sulfonamides, and 3 non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals) on five types of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and the underlying factors were studied. Adsorption equilibriums were reached within 12h for all compounds, and well fitted by the Freundlich isotherm model. The adsorption affinity of pharmaceuticals was positively related to the specific surface area of MWCNTs. The solution pH was an important parameter of pharmaceutical adsorption on MWCNTs, due to its impacts on the chemical speciation of pharmaceuticals and the surface electrical property of MWCNTs. The adsorption of ionizable pharmaceuticals decreased in varying degrees with the increased ionic strength. MWCNT-10 was found to be the strongest adsorbent in this study, and the Freundlich constant (KF) values were 353-2814mmol(1-n)L(n)/kg, 571-618mmol(1-n)L(n)/kg, and 317-1522mmol(1-n)L(n)/kg for sulfonamides, chloramphenicols, and non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals, respectively. The different adsorption affinity of sulfonamides might contribute to the different hydrophobic of heterocyclic substituents, while chloramphenicols adsorption was affected by the charge distribution in aromatic rings via substituent effects. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.