1 电磁波吸收的基本理论和性能
1.1 电磁波吸收的基本理论
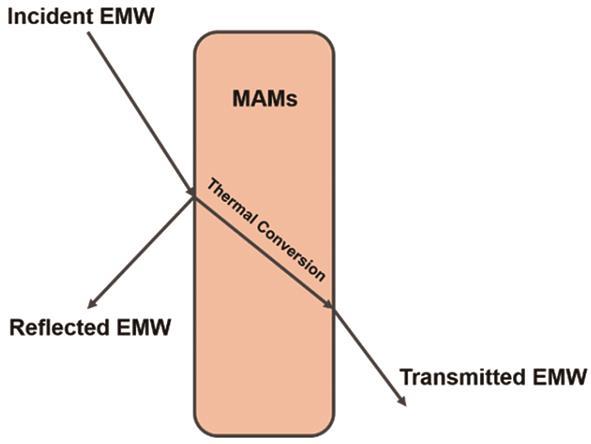
图1
图1
电磁波的传输及和吸波材料作用的示意图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of interaction between MAMs and microwaves
根据损耗机理,吸波材料分为介电损耗材料和磁损耗材料。介电损耗材料包括碳材料、非磁性金属粉末、导电聚合物、非磁性金属氧化物以及非氧化物陶瓷。这类材料的强度高、耐高温、导电性好和密度低,但是其有效吸收带宽(Effective absorption bandwidth,EAB)小和吸波性能不高。磁损耗材料,主要有磁性金属粉末及化合物、铁氧体以及羰基铁。磁损耗材料的应用受到密度高和稳定性低的限制。吸波材料的介电损耗因子和磁损耗因子分别定义为tanδE = ε″/ε′和tanδM = μ″/μ′,用以表征其介电损耗能力和磁损耗能力。介电损耗性能,主要源于电导损耗和极化弛豫损耗。电磁波进入吸波材料后载流子在电场作用下形成电流,电能转化为热能或其他形式的能量而耗散。如果电导率过高,则入射电磁波大量反射,从而使电磁波的衰减性能降低[14,15]。极化弛豫损耗,包括离子极化损耗、电子极化损耗、偶极子弛豫极化损耗和界面极化损耗。离子极化是正负离子之间的相对位移引起的,电子极化源于组成原子相对于原子核位置的变化引起的偶极矩的改变。这两种极化损耗发生在紫外线、可见光和红外光频率,微波频率范围的损耗可以忽略。偶极弛豫极化,是偶极矩沿电场方向旋转产生的,对介电损耗的影响较大。可根据德拜方程[16,17]
分析弛豫损耗。复介电常数的实部(ε′)与虚部(ε″)的关系为
其中εs、ε∞和τ分别为静态介电常数、相对介电常数和极化松弛时间。复介电常数的实部与虚部的关系是一个半圆,称为Cole-Cole半圆,每一个Cole-Cole半圆代表一次极化松弛过程。半圆上的点分别对应由德拜方程计算出的介电常数在某一频率下的实部和虚部。界面极化出现在非均质介质的界面,是电子或离子在外电场作用下在界面处聚集引起的。介电材料具有宽频带微波吸收性能,但是其低频吸收效果较差。
其中μ0、σ、d分别为真空磁导率、电导率和吸波剂厚度。由
基于以上理论,合理设计结构和组成协同耦合效应使其具有复合杂化粒子微结构,可实现性能指标的优化配置,从而制备出具有特定组成、结构和性能的石墨烯基多功能复合吸波材料。
1.2 电磁波的吸收性能的测量
图2
使用同轴线法(图2a)时,被测样品是一个同轴圆环,外部直径为7 mm,内部直径为3.04 mm。这种方法的主要优点是使用相同的样品可在任何频率范围进行测量,所需试样量少,其缺点是重复性差。波导方法(图2b)使用矩形样品,波导的尺寸取决于测量频率。值得注意的是,波导的尺寸随着测试频率的增加而减小。这种方法的主要优点是制备简单,缺点是测试频率范围较窄,且需要的波导的数量较多。另外,用波导方法测量须将样品与波导腔完好密封以排除空气间隙产生的测量误差。自由空间法(图2c)的接触测量系统由被测样品两侧的两个天线组成,一个用于发射信号,另一个接收信号,分别通过天线与矢量网络分析仪的发射、接收端口相连。可调节两个喇叭天线的位置改变电磁波的入射角,以测量吸波材料在不同入射角的电磁波反射损耗值。这个方法的突出优点,是可覆盖较宽的测量频率范围、进行变温测量且不会破坏试样。此法的主要缺点是所需样品较多,且不能在低频段测试。弓形法是由弓形装置和信号源、网络分析仪等设备组成的测试系统。分别测量样品台上放置的标准板和试样,根据入射电磁波经标准板和试样反射回来的电磁波的功率计算材料的吸波性能。屏蔽室法,是用屏蔽室内外的接收和发射天线测试透射波的衰减,用于计算屏蔽效能。
2 不同维度石墨烯基复合吸波材料
独特的蜂窝状孔壁和单原子层厚度的二维片层状结构,使石墨烯具有优异的性能,如轻质、高比表面积、高电导性和较高的介电常数。同时,石墨烯边缘的大量悬空键在外电场作用下更易产生极化弛豫而衰减电磁波;用氧化还原法制备的还原氧化石墨烯,其表面有大量残余的含氧官能团和缺陷。这些含氧官能团和缺陷,不仅降低石墨烯的电导率和提高自身阻抗匹配特性,还作为极化中心有利于电磁波的吸收和衰减[22]。更为重要的是,高比表面积的石墨烯很适合做为基体负载功能化纳米粒子,可提高纳米粒子的分散性和减少团聚,还能在微纳米尺度优化设计结构和性能,从而制备出具有特定结构、组成和性能的多功能石墨烯基吸波复合材料。
2.1 石墨烯片层复合吸波材料
石墨烯吸波材料较高的电导率使电磁波反射,且因没有能带隙而不易调控其介电性能。在石墨烯中进行原子掺杂或与其他损耗型吸波材料复合,可改善其电磁匹配特性和提高吸波性能。
Cao等[23]研究了超薄石墨烯复合材料在323~473 K和X波段的介电常数和微波吸收性能。结果表明,化学石墨化超薄石墨烯在高温下微波吸收性能较高。在323~473 K的X波段其最大损耗正切和最小反射损耗分别为1.32和-42 dB,吸收频带几乎覆盖了整个X波段。这表明,超薄石墨烯是一种很有前途的轻质高效微波吸收材料。Zheng等[24]用简便的原位热分解方法将超顺磁性Fe3O4纳米晶体锚定在疏水性石墨烯纳米片上,构筑出协同电磁波吸收剂(图3)。结果表明,Fe3O4纳米晶体以化学键结合方式均匀地负载在石墨烯纳米片的表面,没有明显的团聚或较大的空位。Fe3O4-石墨烯杂化物具有疏水性和超顺磁性,良好的阻抗匹配和协同作用其具有增强的电磁波吸收特性。
图3
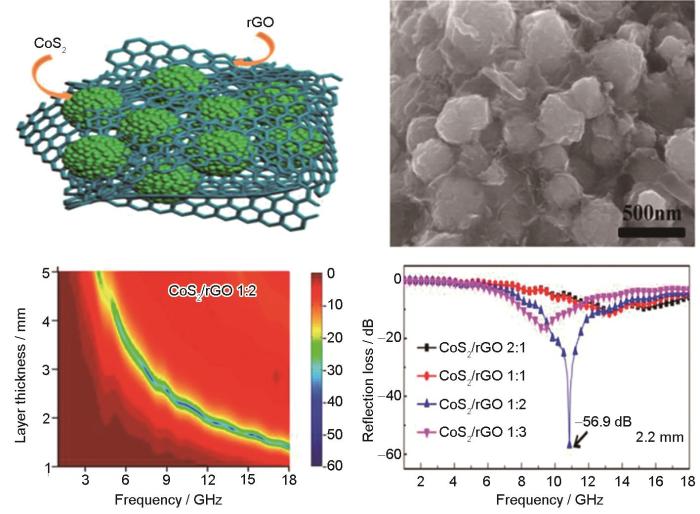
Yan等[28~30]基于纳米级柯肯德尔效应分别将超精细NiFe2O4、CoFe2O4、NiCo2O4空心纳米颗粒锚固在石墨烯片层表面,制备出不同中空纳米颗粒/还原氧化石墨烯杂化物复合吸波材料,都具有优异的电磁波吸收性能。Zhang等[31]用微波辅助水热法制备CoS2/rGO纳米杂化物(图4),研究了rGO比例不同的这种材料的微波吸收性能。形态分析结果表明,CoS2纳米颗粒均匀地嵌入rGO中而没有聚集。改变rGO比例,即可调节CoS2/rGO纳米杂化物的复介电常数。厚度为2.2 mm的CoS2/rGO 1∶2的复合材料,频率为10.9 GHz时最小反射损耗(RL)为-56.9 dB,有效吸收频带为4.1 GHz。
图4
2.2 石墨烯微球
石墨烯片层间的分子间作用力和π-π作用,极易使其发生堆叠团聚。构筑三维空心微球结构不仅能阻止石墨烯片团聚,还能使其结构规整、尺寸可调,且具有较大的比表面积和优异的性能。
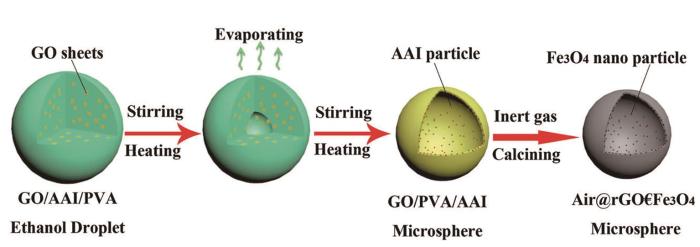
Li等[32]基于成分调控和微纳结构设计,用简单的溶剂热法和退火制备出具有分层结构的三维Co/CoO/RGO微球(CCOR)。调节磁性Co/CoO颗粒和高导电RGO纳米片之间的协同效应,即可调节其电磁参数。这样制备出的CCOR复合微球具有优异的微波吸收性能,其最大反射损耗值为-50.1 dB,有效吸收带宽达到6.56 GHz,覆盖整个X波段频率。Zeng等[33~35]用油包水(W/O)乳化与高温煅烧两步法相结合的自组装技术,将磁性纳米粒子引入具有空心结构的石墨烯微球中,制备出三种负载不同磁性纳米粒子的还原氧化石墨烯复合微球(Air@rGO€Fe3O4、Air@rGO€Co和Air@rGO€Ni)(图5)。结果表明,这三种磁功能化石墨烯复合微球都具有优异的吸波性能和强耐腐蚀性,其电磁波吸收强度和有效吸收频带均大于单一还原氧化石墨烯和纯磁性纳米粒子。
图5
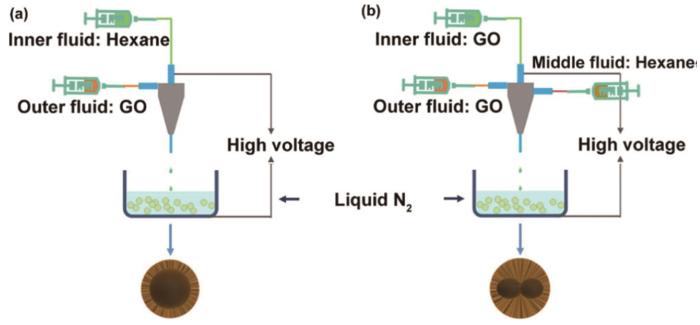
Li等[36]将多轴静电纺丝与冷冻干燥和煅烧工艺相结合制备了中空结构可控的石墨烯微球(HGAS)和球中球石墨烯微球(BGAS)(图6)。良好的介电损耗和阻抗匹配性能,使石墨烯微球(HGAS)在-52.7 dB的反射损耗最小和有效吸收带宽较宽(7.0 GHz)。厚度为3.4 mm的BGAS复合材料,其有效吸收频带达到9.3 GHz。Cui等[37]用简单快速的超声波喷涂技术制备出三维(3D)褶皱RGO/MXene/Fe3O4微球(FMCM),将还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)、MXene纳米片和Fe3O4纳米粒子组装在一起实现了综合优势互补。调整GOx、MXene和Fe3O4的比例,即可制备出不同Fe3O4含量的FMCM。FMCM-3复合材料具有最好的吸波性能,厚度为2.9 mm时最小反射损耗为-51.2 dB,有效吸收频带为4.7 GHz。FMCM优异的吸波性能,源于3D多孔结构和合理的材料组成。
图6
Liu Z H等[40]将超声喷涂技术与包覆工艺相结合将MoS2、氧化石墨烯(GO)和聚多巴胺组装成三维MoS2/RGO/NC褶皱微球。复杂的结构、互补的损耗机制和良好的阻抗匹配,使其具有优异的微波吸收性能。厚度为3.1 mm的MoS2/RGO/NC褶皱微球,其最小反射损耗达到-60.4 dB。调整微球的成分,厚度为2.9 mm时其有效吸收带宽高达6.1 GHz (11.9~18.0 GHz)。Wang等[41]用电荷驱动自组装方法制备出褶皱的还原氧化石墨烯包裹聚合物衍生碳(CS@rGO)微球。研究表明,这种独特的三维(3D)多界面结构使其具有更高的微波吸收性能。调整电荷驱动的自组装循环时间,可优化CS@rGO微球的介电性能和阻抗匹配特性。
2.3 石墨烯纤维
石墨烯纤维具有良好的导电性能、机械强度和柔性,做为轻质导线可在极宽的温度范围内工作。用石墨烯纤维还可制备出柔性织物穿戴在人体表面,作为纤维状电池或者电容器的电极使储能器件可穿戴,利用电热转换实现医疗保健、电磁屏蔽和微波吸收。
图7
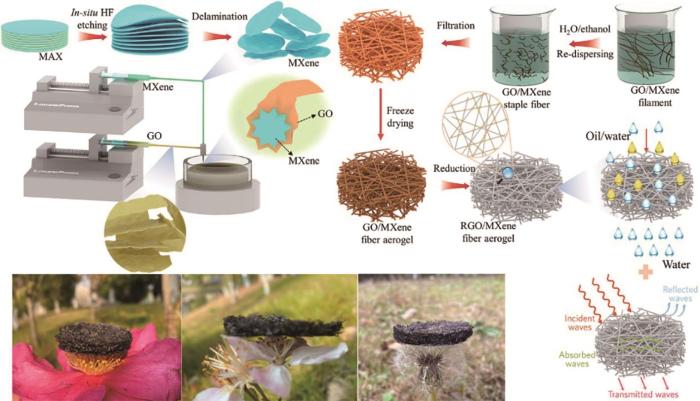
Zheng等[44]提出一种高导电石墨烯包覆策略,首次用同轴湿纺和冷冻干燥制备出一种皮芯型异质结构石墨烯/MXene纤维气凝胶(图8)。这种气凝胶,具有高效持久的电磁屏蔽性能、高疏水性、高导电性、高效油水分离特性和高温隔热性能。Sheng等[45]用简便的湿法化学合成和静电自组装方法制备出具有分层核-壳结构和垂直排列的石墨烯边缘平面的3D rGO/Ni纳米纤维。这种独特的3D rGO/Ni纳米纤维较大的比表面积和有效的界面极化损耗,使其具有高效的微波吸收特性。调节rGO/Ni的质量比,即可控制纳米纤维的3D微观结构和吸收性能。rGO/Ni质量比为1∶3时,在只含15%rGO/Ni(质量分数)纳米纤维的情况下,其衰减为-50.52 dB,较薄匹配厚度为2.0 mm的材料其有效吸收带宽达到4.2 GHz。
图8
目前,湿法纺丝仍是制备高性能石墨烯纤维的主要工艺,通过基元材料优化、制备过程调控和采用高温热还原,可制备出热导率高于碳纤维和碳纳米管纤维的石墨烯纤维。但是与碳纤维和碳纳米管纤维相比,石墨烯纤维的强度和电导率等基本特性以及制备工艺技术的成熟度,依然有较大的差距。对纤维的结构分析表明,限制石墨烯纤维性能的因素主要有:(1) GO片层的制备过程产生不可避免的缺陷结构。GO是湿法纺制石墨烯纤维的主要原料,但是其表面有大量的含氧官能团及结构缺陷,进行高温还原和石墨化处理也难以将其完全去除。这些结构缺陷显著影响石墨烯纤维的力学强度、导电、导热性能;(2) 石墨烯纤维内微米级石墨烯片层的聚集态结构,包括片层的取向、结晶、间隙等二级结构,使石墨烯纤维内的片层形成部分褶皱结构,使石墨烯片层取向度降低而影响纤维的性能;(3) 石墨烯纤维的密度较低。现有的石墨烯纤维其密度仍低于碳纤维、石墨纤维以及碳纳米管纤维,较低的堆叠密度决定纤维内部的孔隙结构,限制了石墨烯的本征优异性能传递。因此,只有进一步优化石墨烯纤维的制备和处理过程、修复石墨烯的结构缺陷、提高石墨烯片层晶区尺寸和取向度等,才能制备出性能更高的石墨烯纤维。
2.4 石墨烯泡沫
构筑三维“泡沫型”结构石墨烯,可实现超宽频电磁响应。除了三维结构内的多重反射及散射机制,错综复杂的多孔网络结构充当耦合电路,使其在电磁场作用下产生感生电流而增强了电导损耗。与典型的二维结构石墨烯基吸波复合材料相比,这种具有特殊三维结构的“泡沫型”石墨烯具有更优异的电磁吸收特性
Chen等[46]进行各向异性设计,有针对性地构建出具有长程排列高度多孔结构的单向石墨烯泡沫 (UGF)、系统研究了2~18 GHz下的电磁吸收性能与入射电磁波方向和极化方向之间交叉角φ的函数关系。在平面内旋转样品即可调节UGF的反射损耗(RL)和峰值频率。同时,介电损耗和感应电流引起的双吸收机制,使单向石墨烯泡沫具有10.9 GHz的超宽吸收频带。Liu等[47]用自组装的水热反应和冷冻干燥工艺制备出具有高孔隙率和开放网状结构的超轻型N-掺杂石墨烯泡沫。与纯石墨烯泡沫相比,N杂原子有利于构建开放的网状壁并调整电性能,从而产生强大的电磁波吸收能力和较宽的吸收带宽,最大反射损耗在3.5 mm处为-53.9 dB,超过-10 dB的吸收带宽为4.56 GHz。根据吸波机理分析,高效的电磁波吸收性能主要源于增强的偶极/界面极化、多重散射、微米级圆形导电结构以及平衡的阻抗匹配。
图9
Xu等[50~52]用高温水热还原自组装法将不同磁性纳米粒子通过化学还原原位沉积在石墨烯片上,制备出多种具有优异电磁波吸收性能及强耐腐蚀性的磁性石墨烯泡沫复合材料(MGF@Co、MGF@Ni和MGF@Fe3O4) (图10)。与石蜡填充复合制备的微波吸收材料,其最小反射损耗值分别为-65.8、-58.7、-64.4 dB,最大有效吸收频带达到13.85、13.62、13.3 GHz,其综合性能均优于文献报道的大多数石墨烯基复合材料。Huang等[53]报道了一种基于3D石墨烯泡沫(3DG)的高效太赫兹波吸收器。由于表面反射微弱和巨大的内部吸收,在0.1~1.2 THz的频率范围内其太赫兹吸收性能极为出色。精确控制3DG的恒定特性,即可实现19 dB的反射损耗,有效吸收带宽覆盖法向入射时整个测量带宽的95%。更为重要的是,3DG的太赫兹吸收性能随着入射率的增加而明显提高,在入射角为45°时最大反射损耗值从19 dB增大到28.6 dB,有效吸收频带覆盖了测量带宽的100%。
图10
2.5 石墨烯气凝胶
根据其结构,可将石墨烯气凝胶(Graphene aerogels,GA)看作具有特殊结构或性能的石墨烯泡沫。作为典型3D多孔材料,优异的导热性、导电性以及轻质、高比表面积和孔隙率可控等特性,使其在锂电池、传感器、吸附、催化及电磁波吸收等领域有重要的应用前景。另外,高温退火处理可改善石墨烯气凝胶材料的介电性能和表面缺陷,有利于提高三维石墨烯网络的导电性和电导损耗,进而提高其电磁波吸收性能。
Zhang等[54]用简单的阳离子辅助水热处理工艺制备了具有良好分散性能和界面极化性能的超轻RGO气凝胶。RGO/石蜡复合材料在8.0~18.0 GHz的宽频带范围内具有优异的微波吸收性能。Wang等[55]用简便的溶剂热合成法将CoFe2O4(CFO)纳米颗粒嵌入N掺杂的还原氧化石墨烯(N-rGO)气凝胶中,制备出具有3D多孔结构的CFO/N-rGO气凝胶微波吸收材料。调节CoFe2O4的添加量,即可改善CFO/N-rGO气凝胶的电磁参数。氧化石墨烯(GO)与CoFe2O4的质量比为1∶2、低填充量较低(20%,质量分数)的复合材料在14.4 GHz处具有强反射损耗(-60.4 dB),其有效吸收带宽达到6.48 GHz (11.44~17.92 GHz)。
Zhao等[56]用冷冻干燥结合热还原工艺制备出具有一维CoNi链和CNT修饰的杂化石墨烯气凝胶(GA-CNT-CoNi)(图11)。与GA和GA-CoNi气凝胶相比,浸入聚二甲基硅氧烷基体中的4%GA-CNT-CoNi(质量分数)具有最强的微波吸收性能。厚度为1.8 mm时最佳反射损耗值为-50.8 dB,有效吸收带宽达到8.5 GHz (18~26.5 GHz),覆盖整个K频段。Zhao等[57]用原位溶剂热和碳化工艺开发了一种新型的CoNi/还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)气凝胶吸收剂。制备出的CoNi/rGO气凝胶具有超低密度(7 mg·cm-3)、分层的多孔结构和高表面积。根据吸收机理,良好的介电损耗及磁损耗、优异的阻抗匹配和多孔结构有助于微波吸收。
图11
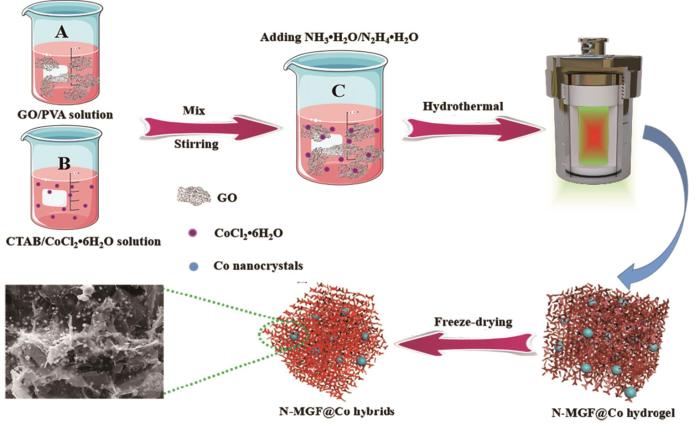
Xu等[58~60]用化学还原自组装法并结合高温煅烧工艺,将不同磁性纳米粒子通过高温原位热解负载在石墨烯片上,制备出多种电磁波吸收性能和超疏水性能优异的磁性石墨烯气凝胶复合材料(SHGA@Fe3O4、SHGA@Co和HGA@Ni)。这种磁性石墨烯气凝胶复合材料(SHGA@Fe3O4、SHGA@Co、HGA@Ni)具有高比表面积、轻质、(超)疏水性能和优异的微波吸收性能,填充量约为5%(质量分数)时其最小反射损耗值分别为-57.9、-51.6、-52.3 dB,最大有效吸收频带达到13.2、13.2、13.1 GHz。Cheng等[61]首次开发出具有可开/关微波吸收性能的还原型氧化石墨烯/VO2复合气凝胶(图12),其可开/关机制源于VO2的相变行为。随着温度的升高(> 68℃)VO2发生从单斜晶相到金红石相的相变,使其电导率和介电常数显着变化,从而使其具有关闭/打开可切换的微波吸收性能。
图12
2.6 其他类型的石墨烯复合材料
将石墨烯与纤维、树脂、陶瓷、金属粒子等复合制备的石墨烯基复合材料,可应用在能源、化工、生物、医药和超级电容器等领域。Zhang等[62]用热压法制备出PVDF/RGO复合材料,GO表面的含氧官能团能与PVDF上的含氟基团发化学反应使GO在PVDF中的分散性提高,然后用热压法又将GO还原而使其具有吸波和介电性能。RGO含量为3% (质量分数)的材料,其最大反射损耗为-25.6 dB出现在10.8 GHz,在8.48~12.80 GHz反射损耗均小于-10 dB。Ren等[63]以EP-CE树脂为基体材料、使用GNSs和GNSs/MWCNTs作为吸波剂,用溶液混合和浇注成型制备出树脂基吸波复合材料。加入GNSs能提高复合材料的吸波特性,GNSs用量为3%(质量分数)、匹配厚度为 4 mm的复合材料,其最小反射损耗为-21.4 dB。一维GNSs与二维MWCNTs之间的协同效应,使GNSs/MWCNTs/CE复合材料具有更高的吸波特性。Chen等[64]用原位生长(IS)和物理混合(PM)方法制备SiC晶须/还原氧化石墨烯气凝胶(SiCw/rGOA),并研究了C-Si异质结对微波吸收性能的影响。结果表明,与纯rGOA相比,SiCw的掺入改善了自由空间和吸收体之间的界面阻抗,从而使其具有优异的微波吸收性能。Lv等[65]用石墨烯纳米片(GN)和中空玻璃微球(HGM)制备水泥基复合材料,发现GN与HGM结合使吸收性能提高。随着玻璃微球填充率的提高,吸收峰值和低于-5 dB的带宽先增大后减小。一种由凯夫拉(Kevlar)/石墨烯/环氧树脂复合材料组成的单层雷达吸波结构(RAS),以铜薄膜作为背板或反射面RAS厚度为2.12 mm时12~18 GHz的回波损耗大于10 dB。美国加州大学制备的石墨烯基红外隐身涂层,改变反射光的波长以实现红外隐身。可将这种材料大面积涂覆在结构和平台表面,实现军事伪装。
3 吸波材料的发展趋势
为了实现良好的电磁匹配,研究人员越来越重视合理调节电磁参数、元件形貌和微观结构以平衡阻抗,实现优异的微波吸收。将石墨烯与磁损介质、导电聚合物、陶瓷等材料复合制备具有复杂多孔网络结构和异形不同维度结构的石墨烯基吸波复合材料,可实现各部件的优势和增强损耗能力。但是,石墨烯基吸波复合材料尚未大规模应用,本文总结的材料大多不能满足实际应用的要求。同时,大规模生产廉价、高质量的石墨烯面临着巨大的挑战。重要的是,目前文献报道的石墨烯基吸波复合材料主要用于研究不同结构的电磁组分调控及吸波性能,制备的吸波复合材料有填充量高、涂层厚、有效吸收频带窄等诸多不足,电磁波吸收性能还远低于期望值。同时,功能性粒子的粒径、各向异性和形貌对吸收剂的磁性能有重要影响,从而影响微波吸收剂的吸收性能。因此,需要进一步研究用不规则形貌和不同粒径修饰的石墨烯基复合材料。微波吸收材料由基体材料和吸波剂组成,其聚合物基体、石墨烯的尺寸和分散性以及石墨烯与基体之间的界面相互作用都影响材料的吸波性能,而石墨烯基材料的分散性制约其实际应用。
4 展望
近年来研究者对于石墨烯基吸波材料方面的研究做了很多有价值的工作。尽管如此,高性能多功能石墨烯基复合吸波材料的设计与制备依旧是未来研究的重点与难点。未来吸波材料发展方向主要集中在以下几点:
(1) 智能化设计。材料根据外界环境的变化调节自身的结构,使其电磁特性对环境做出最佳响应。
(2) 结构与功能一体化设计。用计算机技术模拟设计纤维状、蜂窝状或团簇状等吸波材料,在降低材料密度的同时拓宽吸波频带,研发具备吸波和承载等多重功能的新型纳米复合材料。
(3) 多光谱兼容性设计。材料能兼容多波段吸收,提高对先进探测系统的识别能力。
(4) 低维形态设计。纳米微粒、纳米纤维、颗粒膜等低维材料,其吸收频带宽、兼容性好、吸收强、质量轻,具有极大的发展潜力。
参考文献
Synthesis of ternary core-shell structured ZnOC@CoC@PAN for high-performance electromagnetic absorption
[J].
Tunable electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of carbon nanotubes/carbon fiber composites synthesized directly and rapidly via an innovative induction heating technique
[J].
Corrosion-resistant graphene-based magnetic composite foams for efficient electromagnetic absorption
[J].
Ti3C2T x /rGO porous composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performances
[J].
CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@-TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption
[J].
Core-shell hybrid nanowires with Co nanoparticles wrapped in N-doped porous carbon for lightweight microwave absorption
[J].Exploration of lightweight and thin electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption materials is still urgent because of the issues related to EM pollution. In this work, one-dimensional core-shell nanowires with Co nanoparticles embedded in N doped porous carbon (Co@NPC NWs) have been successfully fabricated for microwave absorption. The obtained Co@NPC composites with a pea-like structure have high loading of Co nanoparticles (68 wt%) encapsulated by the defective carbon shell. Thanks to these special characteristics, the Co@NPC NWs exhibit superb microwave absorption properties in comparison with the pristine nano-Co powder and NPC. The strong reflection loss (RL) of -48 dB could be achieved at a thickness of only 1.45 mm. In addition, the effective absorption bandwidth is up to 5.2 GHz. These superb absorption properties coupled with thin thickness endow the Co@NPC NWs with great potential for application in lightweight EM wave absorption.
High-density anisotropy magnetism enhanced microwave absorption performance in Ti3C2T x MXene@Ni microspheres
[J].
A modified graphitic carbon nitride (MCN)/Fe3O4 composite as a super electromagnetic wave absorber
[J].
Porous graphene microflowers for high-performance microwave absorption
[J].Graphene has shown great potential in microwave absorption (MA) owing to its high surface area, low density, tunable electrical conductivity and good chemical stability. To fully realize graphene's MA ability, the microstructure of graphene should be carefully addressed. Here we prepared graphene microflowers (Gmfs) with highly porous structure for high-performance MA filler material. The efficient absorption bandwidth (reflection loss ≤ -10 dB) reaches 5.59 GHz and the minimum reflection loss is up to -42.9 dB, showing significant increment compared with stacked graphene. Such performance is higher than most graphene-based materials in the literature. Besides, the low filling content (10 wt%) and low density (40-50 mg cm) are beneficial for the practical applications. Without compounding with magnetic materials or conductive polymers, Gmfs show outstanding MA performance with the aid of rational microstructure design. Furthermore, Gmfs exhibit advantages in facile processibility and large-scale production compared with other porous graphene materials including aerogels and foams.
A review of three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels: synthesis, structure and application for microwave absorption
[J].
Nickel nanoparticle encapsulated in few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene supported by nitrogen-doped graphite sheets as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material
[J].
Solvothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their applications as enhanced synergistic microwave absorbers
[J].
A through-thickness arrayed carbon fibers elastomer with horizontal segregated magnetic network for highly efficient thermal management and electromagnetic wave absorption
[J].
3D ultralight hollow NiCo compound@MXene composites for tunable and high-efficient microwave absorption
[J].The 3D hollow hierarchical architectures tend to be designed for inhibiting stack of MXene flakes to obtain satisfactory lightweight, high-efficient and broadband absorbers. Herein, the hollow NiCo compound@MXene networks were prepared by etching the ZIF 67 template and subsequently anchoring the Ti3C2Tx nanosheets through electrostatic self-assembly. The electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption property can be distinctly or slightly regulated by adjusting the filler loading and decoration of Ti3C2Tx nanoflakes. Based on the synergistic effects of multi-components and special well-constructed structure, NiCo layered double hydroxides@Ti3C2Tx (LDHT-9) absorber remarkably achieves unexpected effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) of 6.72 GHz with a thickness of 2.10 mm, covering the entire Ku-band. After calcination, transition metal oxide@Ti3C2Tx (TMOT-21) absorber near the percolation threshold possesses minimum reflection loss (RLmin) value of − 67.22 dB at 1.70 mm within a filler loading of only 5 wt%. This work enlightens a simple strategy for constructing MXene-based composites to achieve high-efficient microwave absorbents with lightweight and tunable EAB.\"Image missing\"
Synthesis of pomegranate-like Mo2C@C nanospheres for highly efficient microwave absorp-tion
[J].
Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption
[J].
Multiphase molybdenum carbide doped carbon hollow sphere engineering: the superiority of unique double-shell structure in microwave absorption
[J].
Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of matrimony vine-like iron oxide/reduced graphene oxide prepared by a facile method
[J].
A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption
[J].
Multidimension-controllable synthesis of MOF-derived Co@N-doped carbon composite with magnetic-dielectric synergy toward strong microwave absorption
[J].
Advances in electromagnetic shielding properties of composite foams
[J].
Hollow porous Fe2O3 microspheres wrapped by reduced graphene oxides with high-performance microwave absorption
[J].
Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites
[J].
Hydrophobic graphene nanosheets decorated by monodispersed superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals as synergistic electromagnetic wave absorbers
[J].
Hierarchical graphene@Fe3O4 nanocluster@carbon@MnO2 nanosheet array composites: synthesis and microwave absorption performance
[J].The fabrication of novel hierarchical graphene@Fe3O4 nanocluster@carbon@MnO2 nanosheet array composites has been successfully carried out for the first time. The fabrication process involves the deposition of Fe3O4 nanoclusters on graphene's surface using a simple in situ hydrothermal method, subsequent introduction of carbon on the surface of graphene@Fe3O4 nanoclusters by combining the hydrothermal reaction and thermal treatment process, and finally formation of the hierarchical composites via a simple in situ redox replacement reaction between potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and carbon on the surface of graphene@Fe3O4 nanoclusters. Moreover, the microwave absorption properties of both graphene@Fe3O4 nanoclusters and hierarchical graphene@Fe3O4 nanocluster@carbon@MnO2 nanosheet array composites were investigated between 2 and 18 GHz microwave frequency bands. The electromagnetic data demonstrate that graphene@Fe3O4 nanocluster@carbon@MnO2 nanosheet array hierarchical composites exhibit significantly enhanced microwave absorption properties compared with graphene@Fe3O4 nanoclusters, which probably originate from the unique hierarchical structure and larger surface area.
Facile design of 3D hierarchical NiFe2O4/N-GN/ZnO composite as a high performance electromagnetic wave absorber
[J].
Construction of CuS nanoflakes vertically aligned on magnetically decorated graphene and their enhanced microwave absorption properties
[J].
An ultra-small NiFe2O4 hollow particle/graphene hybrid: fabrication and electromagnetic wave absorption property
[J].
Growth of CoFe2O4 hollow nanoparticles on graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers
[J].
Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption induced by void spaces in hollow nanoparticles
[J].We developed a facile method for the growth of hollow structured NiCoO nanoparticles on a graphene sheet (NiCoO-h/G). The hollow NiCoO nanoparticles have an average diameter of approximately 10.0 nm and a shell thickness of merely 2.5 nm. The NiCoO-h/G hybrid exhibited excellent electromagnetic wave absorption with minimal reflection loss below -20 dB at absorber thickness ranging from 2.0 to 5.0 mm, outperforming the solid NiCoO nanoparticles on the graphene sheet. Remarkably, even for a thickness as small as 1.5 mm, the efficient absorption bandwidth and the minimal reflection loss of the hybrid can reach 2.6 GHz and -20.3 dB, respectively. Experimental results and theoretical calculations indicate that the void space in the hollow NiCoO nanoparticles plays a crucial role in the excellent electromagnetic wave absorption property, which greatly increases the dielectric loss and impedance matching characteristics. Our results demonstrate that growing the hollow nanoparticles on a graphene sheet is an efficient way to produce high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers.
Microwave absorption properties of CoS2 nanocrystals embedded into reduced graphene oxide
[J].
Hierarchical magnetic-dielectric synergistic Co/CoO/RGO microspheres with excellent microwave absorption performance covering the whole X band
[J].
Air@rGO€Fe3O4 microspheres with spongy shells: self-assembly and microwave absorption performance
[J].
Self-assembly of ternary hollow microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption and controllable microwave absorption properties
[J].In this study, we report a simple and efficient two-step method consisting of water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion technique and subsequent annealing process for synthesizing the hollow reduced graphene oxide microspheres embedded with Co nanoparticles (Air@rGO€Co). The microspheres showed good electromagnetic properties because of the coexistence of magnetic loss and dielectric loss to microwaves. The minimum reflection loss (RL) value of S reaches -68.1 dB at 13.8 GHz with a thickness of 2.2 mm, and the absorption bandwidth (lower than -10 dB) is 7.1 GHz covering from 10.9 GHz to 18.0 GHz. More interestingly, we can easily controll the microwave absorbing properties of the microspheres by changing the ratio of the two components in the composites. The excellent electromagnetic match at the corresponding resonance peaks for dielectric and magnetic loss play an important role in improving microwave absorption property. Our study provides a good potential method for preparation of lightweight microwave absorbing materials.
3D graphene-Ni microspheres with excellent microwave absorption and corrosion resistance properties
[J].
Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption
[J].
Preparation of pleated RGO/MXene/Fe3O4 microsphere and its absorption properties for electromagnetic wave
[J].
Graphene/carbonyl iron powder composite microspheres enhance electromagnetic absorption of 3D printing composites
[J].
Facile and scalable preparation of ultralight cobalt@graphene aerogel microspheres with strong and wide bandwidth microwave absorption
[J].
Wrinkled 3D MoS2/RGO/NC composite microspheres: optimal composition and microwave absorbing properties
[J].
Development of wrinkled reduced graphene oxide wrapped polymer-derived carbon microspheres as viable microwave absorbents via a charge-driven self-assembly strategy
[J].
Tough, strong, and conductive graphene fibers by optimizing surface chemistry of graphene oxide precursor
[J].
Hygroscopic holey graphene aerogel fibers enable highly efficient moisture capture, heat allocation and microwave absorption
[J].Aerogel fibers have been recognized as the rising star in the fields of thermal insulation and wearable textiles. Yet, the lack of functionalization in aerogel fibers limits their applications. Herein, we report hygroscopic holey graphene aerogel fibers (LiCl@HGAFs) with integrated functionalities of highly efficient moisture capture, heat allocation, and microwave absorption. LiCl@HGAFs realize the water sorption capacity over 4.15 g g, due to the high surface area and high water uptake kinetics. Moreover, the sorbent can be regenerated through both photo-thermal and electro-thermal approaches. Along with the water sorption and desorption, LiCl@HGAFs experience an efficient heat transfer process, with a heat storage capacity of 6.93 kJ g. The coefficient of performance in the heating and cooling mode can reach 1.72 and 0.70, respectively. Notably, with the entrapped water, LiCl@HGAFs exhibit broad microwave absorption with a bandwidth of 9.69 GHz, good impedance matching, and a high attenuation constant of 585. In light of these findings, the multifunctional LiCl@HGAFs open an avenue for applications in water harvest, heat allocation, and microwave absorption. This strategy also suggests the possibility to functionalize aerogel fibers towards even broader applications.© 2022. The Author(s).
Interfused core-shell heterogeneous graphene/MXene fiber aerogel for high-performance and durable electromagnetic interference shielding
[J].
Self-assembled reduced graphene oxide/nickel nanofibers with hierarchical core-shell structure for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption
[J].
Tunable and high performance electromagnetic absorber based on ultralight 3D graphene foams with aligned structure
[J].
Synthesis of lightweight N-doped graphene foams with open reticular structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption
[J].
Synergistically assembled MWCNT/graphene foam with highly efficient microwave absorption in both C and X bands
[J].
Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam
[J].
In situ deposition of α-Co nanoparticles on three-dimensional nitrogen-doped porous graphene foams as microwave absorbers
[J].
3D nitrogen-doped porous magnetic graphene foam-supported Ni nanocomposites with superior microwave absorption properties
[J].
Superior corrosion-resistant 3D porous magnetic graphene foam-ferrite nanocomposite with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties
[J].
Ultra-broadband wide-angle terahertz absorption properties of 3D graphene foam
[J].
Ultralight reduced graphene oxide aerogels prepared by cation-assisted strategy for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption
[J].
CoFe2O4/N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels for high-performance microwave absorption
[J].
Lightweight graphene aerogels by decoration of 1D CoNi chains and CNTs to achieve ultra-wide microwave absorption
[J].
Ultralight CoNi/rGO aerogels toward excellent microwave absorption at ultrathin thickness
[J].
Self-assembly synthesis and microwave absorption properties of magnetic functionalized graphene aerogels
[J].
磁功能化石墨烯气凝胶自组装合成及吸波性能
[J].
In situ growth and pyrolysis synthesis of super-hydrophobic graphene aerogels embedded with ultrafine β-Co nanocrystals for microwave absorption
[J].
Synthesis of magnetic graphene aerogels for microwave absorption by in-situ pyrolysis
[J].
Intelligent off/on switchable microwave absorption performance of reduced graphene oxide/VO2 composite aerogel
[J].
Fabrication of multi-functional PVDF/RGO composites via a simple thermal reduction process and their enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and dielectric properties
[J].
Cyanate ester filled with graphene nanosheets and multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a microwave absorber
[J].
Construction of C-Si heterojunction interface in SiC whisker/reduced graphene oxide aerogels for improving microwave absorption
[J].