放电等离子烧结技术(SPS)是一种新型连接技术,其优点是升温快、过程参数可精确调控,在微观间隙处的微弧放电产生局部高温将微区高质量结合,可用于连接异质板材。Miriyev A等[12]采用SPS制备了Ti-6Al-4V/AISI4330复合板,结果表明,连接温度直接影响界面扩散层,拉伸强度达到250 MPa。Umeda J[13]采用SPS连接Ti/AZ80复合板,可在短时间内制备出比传统扩散焊接质量更高的界面结合。Zhao等[14]也得到了类似的结论。Dong等[15]制备TiNi/2024Al复合材料时,将整个连接理解为电弧焊、电阻点焊及扩散压力焊的综合过程。本文用SPS连接钛合金/不锈钢复合板,先用ANSYS有限元模拟脉冲电流流经复合板材的电流密度分布及温度分布,然后用SPS连接钛合金和不锈钢异质板材,观察分析连接界面的微观组织和物相组成、测试其微观硬度和拉伸性能,研究异质板材的断裂机制。
1 实验方法
表1 443铁素体不锈钢的化学成分
Table 1
| Chemical composition | Cr | Ti | C | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 21.0 | 0.3 | 0.01 | Bal. |
表2 TC1钛合金的化学成分
Table 2
| Element | Al | Mn | Fe | C | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 1.0~2.5 | 0.7~2.0 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.10 | Bal. |
用放电等离子烧结技术(SPS-331LX, Dr Sinter) 连接钛合金/不锈钢。先将钛合金/不锈钢(Ra<0.2)圆片置于石墨模具内,从模具上下压头导入高能脉冲电流,在距离石墨模具内壁2 mm处用热电偶测温,调整脉冲电流参数使热电偶测温最高电流处理温度为1123 K,脉冲电流占空比为4∶5,连接过程中真空度≤5 Pa。为了使连接界面更为紧密,初期加载压力较小为10 MPa,以最大限度地实现连接界面处的微弧放电,进而去除板材表面的致密氧化膜;保温阶段的加载恒定压力为40 MPa。SPS连接复合板的示意图及工艺曲线,如图1所示。
图1
图1
SPS连接示意图和工艺曲线
Fig.1
Connection schematic diagram (a) and process diagram (b) of SPS process
用配有能谱EDS的扫描电子显微镜(JSM-6700F)观察钛合金/不锈钢异质板材的连接界面行为特征,用EBSD技术表征钛合金/不锈钢异质板材的连接界面,用Agilent-G200纳米压痕仪测试连接界面的微观硬度,加载载荷为50 mN。使用X射线衍射仪(D/MAX2400) 检测复合材料的物相;用电子万能拉伸试验机(DNS200)测试复合材料的拉伸性能,拉伸速率为0.2 mm/min。对拉伸断口进行SEM观察。
2 实验结果
2.1 有限元模拟
图2
图3
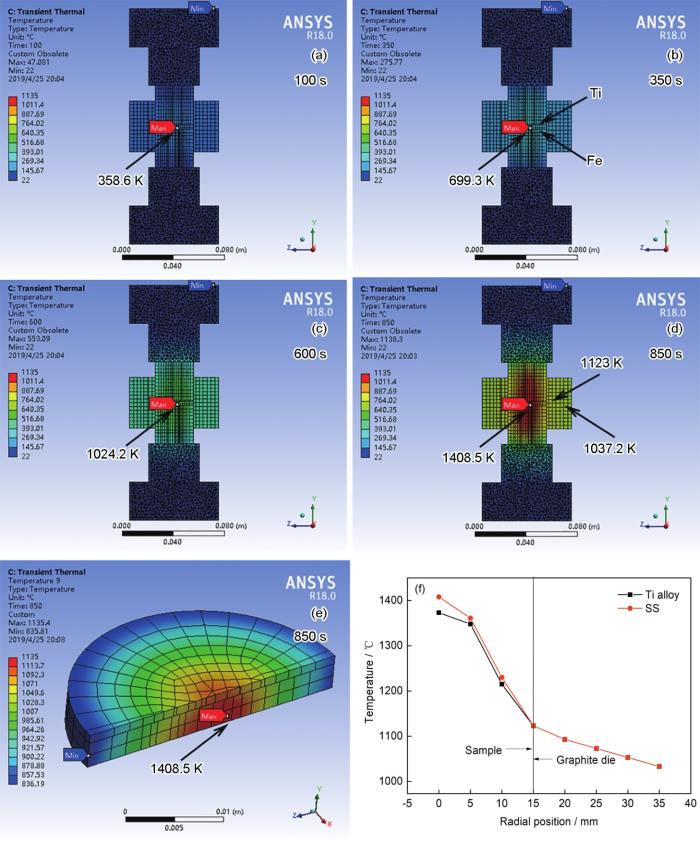
图4a给出了实验过程中温度最高时试样内部的温度分布。可以看出,二者的温度分布类似,均由中心向外圈逐渐递减。不锈钢的温度略高于钛合金,因为不锈钢的导热系数和比热容较小。表3和表4列出了443铁素体不锈钢和TC1钛合金的热物理参数。图4b给出了冷却后钛合金和不锈钢试样内部的残余应力分布。可以看出,不锈钢试样中心的残余应力较大且为拉应力,而钛合金试样则是外围存在较大残余拉应力。其原因是,不锈钢的线膨胀系数大于钛合金,且不锈钢中的温度高于钛合金,使不锈钢受热膨胀时产生较大的形变,但是这种膨胀趋势受到周围模具和钛合金试样的阻碍,使不锈钢试样中心产生可达1122.1 MPa的压应力。较高的温度使不锈钢试样中心产生的压缩变形(1122.1 MPa)超过了不锈钢的屈服极限(σb=483 MPa),于是产生了压缩塑性变形。因此,当温度冷却至室温时,若不锈钢试样中心处自由收缩则体积必然减小,而外圈不锈钢阻碍试样中心的自由收缩,使不锈钢试样的中心受拉而产生较大的残余拉应力。钛合金因反作用力产生与不锈钢相反类型的应力,于是钛合金/不锈钢复合试样中形成了一个平衡的残余内应力体系并长期存在。
图4
表3 443铁素体不锈钢的热物理参数
Table 3
| Density / kg·m-3 | Thermal conductivity / W·(m·K)-1 | Specific heat capacity / J·(kg·K)-1 | Coefficient of linear expansion / K | Poisson's ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7678 | 17 | 480 | 1.1×10-5 | 0.28 |
表4 TC1钛合金的热物理参数
Table 4
| Density / kg·m-3 | Thermal conductivity / W∙(m∙K)-1 | Specific heat capacity / J∙(kg∙K) -1 | Coefficient of linear expansion / K | Poisson's ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4550 | 21 | 540 | 8.7×10-6 | 0.32 |
2.2 微观组织形貌和物相组成
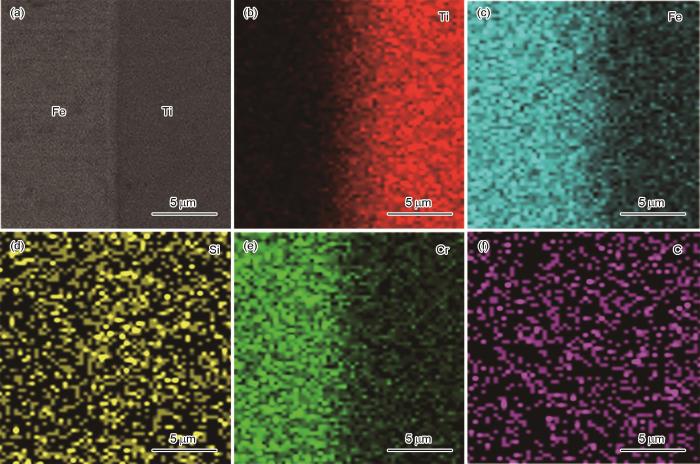
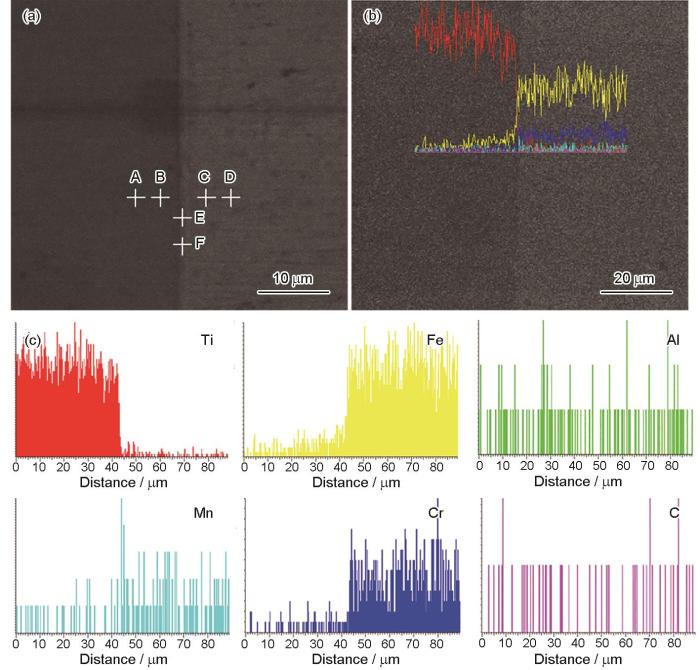
图5给出了SPS连接后复合板材的微观形貌及面扫描。由图5b、c、e可见,两者之间结合良好,没有明显裂纹和孔隙,接头的分界明显,Ti、Cr、Fe元素之间发生了一定程度的元素扩散 [18]。图6给出了SPS连接后复合板材的EDS分析,包括界面附近Ti、Fe、Al、Mn、Cr和C等主要元素的线扫描结果。为了进一步探究钛合金/不锈钢结合界面处的元素成分和物相种类,选定图6a所示的6个测试点A、B、C、D、E、F进行了EDS点扫描,其中E、F位于钛合金/不锈钢结合界面上,A、B位于结合界面附近钛合金侧,C、D位于不锈钢侧。界面附近的点扫描结果,如表6所示。由图6可以看出,结合A、B点的成分分析,Ti的含量均大于85%。由此可以推断,这两个点处应该是钛基固溶体以及少量的金属间化合物。结合C、D两点的成分分析可知,Fe的含量均大于80%,可推断D、E两点是铁基固溶体[19]。E、F属于钛合金和不锈钢的连接界面,E点处Ti的含量为56.84%,Fe的含量为38.22%,F点处的Ti的含量为61.53%,Fe的含量为32.62%。取E点和F点处的平均值,得到界面处Ti的含量为59.19%,Fe的含量为35.47%。Ti和Fe的原子比例为1.67:1。结合Ti-Fe二元相图可知,在TC1钛合金和443铁素体不锈钢的界面处生成了α钛、TiFe和TiFe2金属间化合物 [20~22]。
图 5
图 5
用放电等离子烧结技术连接的钛合金和不锈钢结合界面的微观形貌和面扫描图
Fig.5
SEM micrograph of the interface of titanium alloy and stainless steel jointed by spark plasma sintering (a, b) SEM micrograph; (b~f) map scanning
图6
图6
钛合金/不锈钢连接界面的EDS分析
Fig.6
EDS scanning results of the interface of titanium alloy and stainless steel (a) selected points of EDS point scanning; (b) EDS line scanning route; (c) results of EDS line scanning
表5 EDS点扫描结果
Table 5
| Ti | Cr | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point A | 89.50 | 1.26 | 9.24 |
| Point B | 85.61 | 1.77 | 14.73 |
| Point C | 4.42 | 15.38 | 80.20 |
| Point D | 1.84 | 16.24 | 81.92 |
| Point E | 56.84 | 4.84 | 38.32 |
| Point F | 61.53 | 5.86 | 32.62 |
表6 纳米压痕测试结果
Table 6
| Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point B | 2.942 | 2.893 | 2.994 | 2.943 |
| Point E | 3.152 | 3.201 | 3.175 | 3.176 |
| Point F | 3.501 | 3.611 | 3.559 | 3.557 |
| Point C | 2.690 | 2.723 | 2.738 | 2.717 |
图7
图7
SPS连接钛合金和不锈钢结合界面的EBSD图
Fig.7
EBSD diagram of bonding interface of titanium alloy and stainless steel produced by SPS (a) inverse pole figure; (b) recrystallization distribution
图8给出了钛合金/不锈钢连接界面处的XRD谱。由图8可见,连接界面处的主要物相为Ti、FeCr以及极少量的TiFe和TiFe2金属间化合物。结合Fe-Ti二元相图,Fe在1185~1667 K是面心立方结构的γ-Fe,低于1185 K为体心立方结构的α-Fe;Ti在1153 K以上为体心立方结构的β-Ti,1153 K以下是密排六方的α-Ti。脉冲电流的作用使微观接触界面的缝隙处产生微电弧而形成局部高温区,瞬时温度远超1123 K。在系统内1153~1185 K范围内Ti和Fe的晶格结构均为体心立方,这是形成连续固溶体的必要条件。同时,二者的原子半径比ΔR=(RTi-RFe)/RTi=14.3%<15%,满足形成连续固溶体的充分条件,因此在1153~1185 K范围Ti和Fe形成了体心立方连续固溶体,Fe原子充分溶解在Ti中。EDS点扫结果表明,钛合金/不锈钢结合界面处元素的原子数之比为 Ti∶Fe∶Cr=12∶7∶1,Ti占60%,Fe占35%,因Cr的含量较低可近似看成Ti-Fe二元系统。结合Ti-Fe二元相图可知,Fe含量约为35%的Fe-Ti合金在1473 K以上为液态,温度降低时先发生匀晶反应,平衡关系为L→TiFe,随后在1373 K左右发生固态相变析出TiFe和TiFe2。按照相图,同时发生TiFe→Ti2Fe+TiFe+β-Ti,且当温度低于1153 K时β-Ti发生同素异构转变为α-Ti。此时室温平衡组织为Ti2Fe+TiFe+TiFe2+α-Ti,但是上述反应比较微弱,因此该部分反应生成的Ti2Fe物相未被检测到。综上所述,TiFe+FeCr+TiFe2均为固态相变生成。
图8
图8
钛合金/不锈钢连接界面的XRD谱和钛-铁二元相图
Fig.8
XRD test results of the interface of titanium alloy and stainless steel (a) and Fe-Ti phase diagram (b)
2.3 力学性能
图9
图9
钛合金/不锈钢连接界面的纳米压痕测试结果
Fig.9
Nanoindentation test results of the interface of titanium alloy and stainless steel
图10给出了钛合金/不锈钢复合板材的拉伸曲线。可以看出,在拉伸过程中443铁素体不锈钢先发生了断裂,TC1钛合金继续承受拉力直至断裂。在拉伸初期应力随着应变的升高而迅速增大,应力达到250 MPa时应力的增大减缓,此时复合板材达到屈服极限。此后应力继续随应变增大,应力达到最大值385.7 MPa后应变达到0.61时应力突然下降。这表明,SPS连接的复合板材的抗拉强度为385.7 MPa,是TC1钛合金抗拉强度的72 %和443铁素体不锈钢的80%。
图10
图10
钛合金/不锈钢复合板的拉伸曲线
Fig.10
Tensile curve of titanium alloy/stainless steel heterogeneous plates
图11给出了钛合金/不锈钢复合板材的拉伸断口形貌,上半部分为钛合金侧,下半部分为不锈钢侧。可以看出,在低倍镜下钛合金侧断口呈纤维状,色泽灰暗;在高倍镜下微观特征为韧窝。韧窝的实质是材料微区塑性变形形成的空洞聚集和长大导致材料断裂而形成的圆形或椭圆形凹坑。这表明,钛合金的断裂为韧性断裂。在低倍率下可见不锈钢侧的断口处较为平整,断裂方向与主应力的方向夹角为90 °,断裂部位表面有金属光泽;从高倍放大图像可见断裂截面的形态呈河流状花样,表明不锈钢的断裂为脆性断裂中的解理断裂。
图11
图11
钛合金/不锈钢复合板的拉伸断口形貌
Fig.11
Tensile fracture morphology of titanium alloy/stainless steel heterogeneous plates (a, b) macroscopic morphology; (c, d) titanium alloy side; (e, f) stainless steel side
3 结论
(1) 用SPS连接的钛合金/不锈钢复合板,界面结合紧密没有明显的裂纹。在连接过程中发生了Ti和Fe元素扩散。在界面附近生成的少量TiFe类金属间化合物和FeCr,使复合板具有适当的强度和塑性。
(2) 在钛合金/不锈钢复合板的拉伸过程中,在443铁素体不锈钢板发生解理断裂后TC1钛合金板承受拉力直至发生韧性断裂。
参考文献
A survey on dissimilar welding of stainless steel and titanium alloy
[J].
不锈钢和钛合金异种金属焊接研究进展
[J].
Plasma assisted diffusion joining of CP-titanium-304L stainless steel: Attributes of temperature and time
[J].
Research advancements on self-healing of cracks and evolution of microstructures of titanium alloy sheets induced by electropulsing
[J].
脉冲电流诱导钛合金板材裂纹愈合与组织演变研究进展
[J].
Effect of interfacial microstructure on mechanical properties of vacuum rolling clad pure titanium/high strength low alloy steel
[J].At different rolling temperatures of 850, 900 and 950℃ with constant vacuum level of 1×10<SUP>-2</SUP> Pa and total rolling reduction ratio of 90%, the three-layer clad plates of pure Ti/high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel/pure Ti were successfully fabricated via vacuum rolling cladding (VRC) without the addition of interlayer, and the influence of interfacial microstructures on the bonding properties of the clad interface was investigated in detail. At a rolling temperature of 850℃, the clad interface only contained continuous TiC layer 0.5 <ITALIC>μ</ITALIC>m in thickness, while at rolling temperatures of 900 and 950℃, the interface consisted of TiC and <ITALIC>β</ITALIC>-Ti. With increasing the rolling temperature, the interfacial thickness gradually increased. Under various rolling temperatures, an obvious ferrite band was detected in the HSLA steel side adjacent to the clad interface, and this width significantly increased as the rolling temperature increased. At a rolling temperature of 900℃, a maximum interfacial shear strength of 337 MPa with the fracture occurring at the interface between HSLA steel and TiC was achieved, and after 180° bending testing, no macro/micro-crack was generated at the clad interface, showing sound bonding properties of the clad plate through VRC.
界面微观组织对真空轧制复合纯钛/低合金高强钢界面力学性能的影响
[J].
Research progress on dissimilar materials joining
[J].
异种材料连接研究进展
[J].异种材料构件因其可实现不同材料的优异性能组合,极大提高设计和生产的灵活性,满足现代工程结构的功能和性能要求,具有更高的技术和经济价值,在各领域有广阔的应用前景。因此,异种材料的可靠连接尤为重要。然而,异种材料往往因物理及化学性能差异较大导致连接困难。本文综述了异种材料钎焊、激光焊、电子束焊、电弧焊以及搅拌摩擦焊的国内外研究进展和应用现状,总结了各焊接方法在异种材料连接过程中的研究焦点。在此基础之上,对异种材料连接进行了总结和展望,拟为未来异种材料连接的研究方向和技术突破提供参考。
Mechanical properties and interfacial structure of hot-roll bonding TA2/Q235B plate using DT4 interlayer
[J].
Research status and prospect of welding technology for Ti/steel laminated composite plate
[J].
钛/钢层状复合板焊接技术的现状与展望
[J].
Production process and performance of titanium-steel vacuum roll-cladding plates
[J].
真空制坯热轧钛/钢复合板工艺及性能
[J].
Investigation on dissimilar materials bonding process of TC4 titanium alloy and 316L stainless steel with selective laser melting
[D].
TC4钛合金与316L不锈钢异质材料选区激光熔化连接研究
[D].
Effects of technological parameters of phase transformation diffusion bonding on joint strength of Ti/stainless steel
[J].
相变扩散连接工艺参数对钛与不锈钢接头强度的影响
[J].
Study on microstructure and properties of TA2/S316 diffusion welding joints
[D].
TA2/S316扩散焊接头组织与性能研究
[D].
Titanium to steel joining by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technology
[J].
Bonding mechanism of Ti/AZ80 dissimilar materials fabricated by spark plasma sintering
[J].
Diffusion bonding of Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy by spark plasma sintering
[J].
Understanding the spark plasma sintering from the view of materials joining
[J].
Spark plasma sintering and thermoelectric evaluation of nanocrystalline magnesium silicide (Mg2Si)
[J].
Densification of pure magnesium by spark plasma sintering-discussion of sintering mechanism
[J].
Microstructure and property of diffusion welded titanium alloy/stainless steel joint with Nb and Cu as composite interlayer
[J].With Nb sheet and Cu sheet as composite interlayer materials, the vacuum diffusion welding was carried out on TC4 titanium alloy and 15-5PH stainless steel on a Gleeble-1500 thermomechanical simulator. The tensile strength of the joint was tested. The morphology at the interface and of the tensile fracture of the joint was observed, and the micro area composition was analyzed. The results show that the composite interlayer of Nb and Cu was helpful to restrain the interdiffusion of Ti, Fe and Cr, which came from titanium alloy and stainless steel. The strong bonding at stainless steel/Cu, Cu/Nb and Nb/titanium alloy interfaces was formed by atomic diffusion. A small amount of fine Nb-Fe intermetallic compound was formed at the Cu/Nb interface, which had little effect on the tensile strength of the joint. The maximum tensile strength reached 540 MPa. During tensile fracture the cracks propagated through the Cu layer, the Nb layer and the intermetallic compounds.
以铌+铜为复合中间层扩散焊接钛合金/不锈钢接头的组织与性能
[J].以铌片+铜片为复合中间层材料,在Gleeble-1500型热力模拟试验机上对TC4钛合金和15-5PH不锈钢进行真空扩散焊,测试了接头的抗拉强度,观察了接头界面区和拉伸断口形貌并进行了微区成分分析。结果表明:铌+铜复合中间层可以有效阻碍钛合金和不锈钢之间钛、铁、铬元素的相互扩散;不锈钢/铜、铜/铌、铌/钛合金这3个界面通过原子扩散形成良好的连接,在铜/铌界面处局部生成的少量细小的铌铁金属间化合物对接头抗拉强度的影响不大,最高抗拉强度达到540 MPa;拉伸断裂时裂纹穿过铜层、铌层和金属间化合物扩展。
Diffusion bonding between Ti-6Al-4V alloy and ferritic stainless steel
[J].
Titanium to steel joining by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technology
[J].
Diffusion brazing of Ti-6Al-4V and AISI 304: an EBSD study and mechanical properties
[J].
Plasma assisted diffusion joining of CP-titanium-304L stainless steel: Attributes of temperature and time
[J].