航空发动机的热端部件受交变机械载荷和交变温度载荷的叠加作用,产生的损伤使其疲劳寿命严重降低[1~9]。GH4169是应用最广的热端部件材料,研究其热机械疲劳行为,对设计部件的结构和预测其寿命都极为重要。Evans等[10]研究了IN718的同相位和反相位的热机械疲劳,在R=0(应变比)和R=-∞条件下研究了这种材料的热机械疲劳寿命和应变幅的关系。Jacobsson等[11]也进行了IN718多个应变比的同相位及反相位热机械疲劳实验,研究裂纹扩展并分析了疲劳断口。Johan J等对IN718进行热机械疲劳实验,研究了保持时间对裂纹扩展的影响[12, 13]。德国弗赖堡弗劳恩霍夫材料力学研究院也进行了IN718的热机械疲劳实验,发现低应变速率导致较高的裂纹扩展速率。随着实验设备的更新和实验水平的提高,中国学者也开始了材料的热机械疲劳实验研究[14~19]。但是,对GH4169合金的研究只限于改进制作工艺和讨论高温低周疲劳性能,缺少热机械疲劳实验数据。鉴于此,本文对GH4169合金进行不同温度区间的机械疲劳实验,研究相位、温度、应变速率等因素对其热机械疲劳特性的影响。
1 实验方法
表1 GH4169合金的化学成分
Table 1
| C | Cr | Mo | Al | Ti | Nb | Fe | Si | B | P | Mn | S | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 | 18.92 | 3.3 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 5.35 | 17.6 | 0.07 | 0.011 | 0.022 | 0.02 | 0.002 | Bal. |
图1
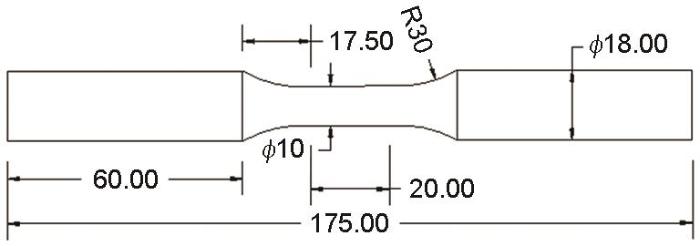
热机械疲劳实验在MTS809疲劳实验机上完成,实验温度由射频感应加热系统控制,使用热电偶采集,用感应线圈加热,用空气压缩机通过多个喷嘴进行冷却;用高温引伸计采集应变数据。
依据标准《金属材料热机械疲劳实验方法》(GJB6213-2008)进行实验,实验加载包括温度和机械应变。在进行热机械疲劳实验时,温度处于循环变化状态,温差的变化产生热应变,因此在热机械疲劳实验前必须补偿热应变以得到机械应变,从而实现机械加载循环的实时控制,具体方法见GJB 6213-2008。疲劳实验时用总应变控制的三角波加载,总应变为热应变与机械应变之和。本文对多个工况进行了应变控制的热机械疲劳实验,应变比R=-1,循环周期分别为100、125、200 s;实验温度范围为200~450℃和400~650℃;机械应变幅包括±0.55%(反相位),±0.6%(同,反),±0.8%(同),±0.9%(同)。对于每个工况进行两次实验,取两次实验结果的平均值。热机械疲劳实验后,用扫描电镜(SEM)观察疲劳断口。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 GH4169合金在不同工况下的热机械实验结果
热处理后GH4169合金的晶粒长大,晶粒度约为5级,晶粒直径为80 μm~100 μm;晶界比较平直,晶界和晶内均无明显δ相析出,晶内有较多的孪晶。这种合金处理后析出大量的强化相
表2列出了不同工况下的实验结果。本文为应变控制的热机械实验,输入载荷为机械应变,根据实验数据可直接得出寿命、塑性应变、最大应力、最小应力及平均应力。从表2可见,相位角、温度范围(ΔT)、周期(T)、机械应变(
表2 不同实验条件下的热机械疲劳实验结果
Table 2
| Phase | ΔT/℃ | T/s | N | Δεp/% | σmax/MPa | σmin/MPa | σm/MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IP | 200~ 450 | 0.6 | 125 | 2701 | 0.440 | 406 | -600 | -194 |
| 0.7 | 1747 | 0.442 | 504 | -723 | -219 | |||
| 0.8 | 103 | 0.446 | 580 | -866 | -286 | |||
| 0.9 | 55 | 0.898 | 636 | -736 | -100 | |||
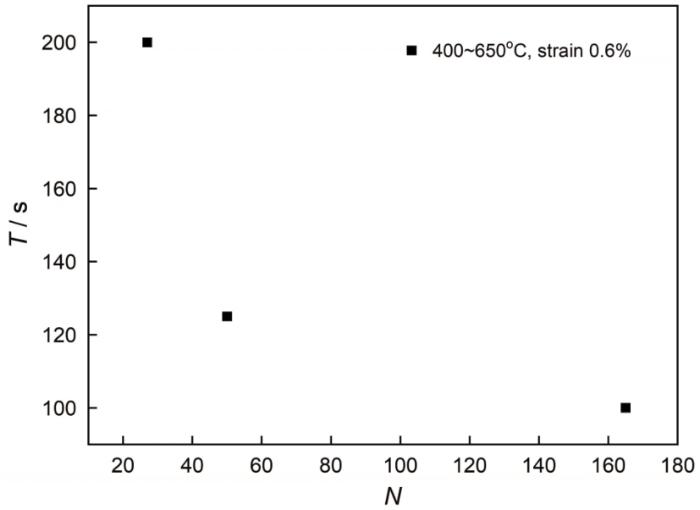
| IP | 400~ 650 | 0.6 | 100 | 165 | 0.105 | 840 | -998 | -158 |
| 0.6 | 125 | 50 | 0.103 | 735 | -937 | -202 | ||
| 0.6 | 200 | 27 | 0.068 | 820 | -1030 | -210 | ||
| OP | 400~ 650 | 0.55 | 125 | 196 | 0.471 | 816 | -705 | 111 |
| 0.6 | 125 | 170 | 0.393 | 1118 | -868 | 250 |
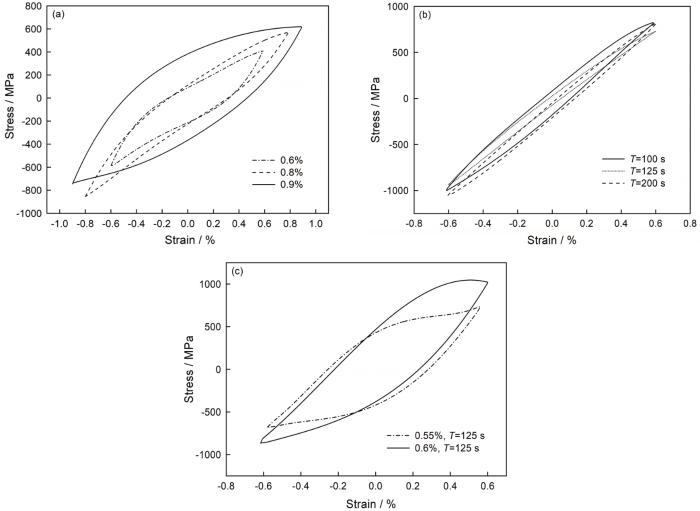
2.2 循环应力-应变特性
图2
图2
不同试验条件下的稳定滞回曲线
Fig.2
Stable hysteresis curves under different test conditions (a) 200~450℃, T=125 s, IP; (b) 400~650℃, strain 0.6%, IP; (c) 400~650℃, T=125 s, OP
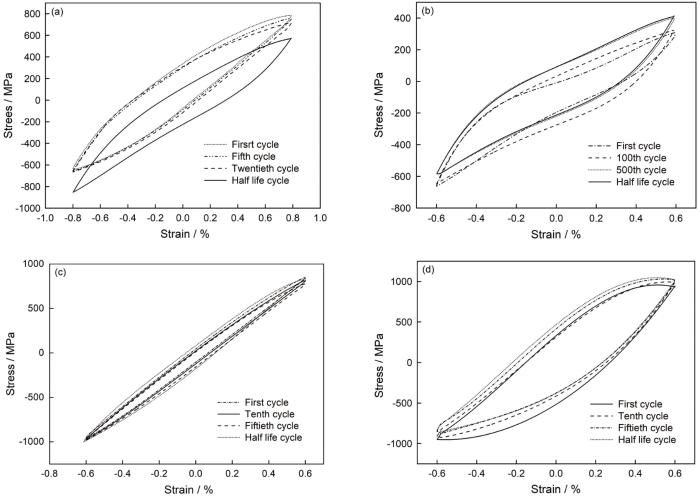
图3
图3
不同实验条件下的滞回曲线
Fig.3
Hysteresis curves under different test conditions (a) 200~450℃, 0.8%, T=125 s, IP; (b) 200~450℃, 0.6%, T=125 s, IP; (c) 400~650℃, 0.6%, T=100 s, IP; (d) 400~650℃, 0.6%, T=125 s, OP
2.3 循环应力响应特性
图4给出了GH4169的热机械疲劳应力响应曲线。可以看出,热机械疲劳时的GH4169合金其应力响应特性与等温疲劳的时不同,在拉伸和压缩半周应力响应特性并不具有对称性,拉伸和压缩半周的响应特性不一致:在同相位条件下,在循环初始阶段,材料在拉伸半周出现明显的软化,在压缩半周硬化不显著,几乎保持循环稳定。在反相位条件下,材料在拉伸半周趋近于循环稳定。在压缩半周,材料在循环初始阶段出现了轻微的循环软化,然后趋于循环稳定。由此可得出以下规律:在高温半周材料出现循环软化现象,在低温半周材料趋于循环稳定。
图4
图4
循环应力响应曲线
Fig.4
Cyclic stress response curves (a) 400~650℃, IP; (b) 400~650℃, OP
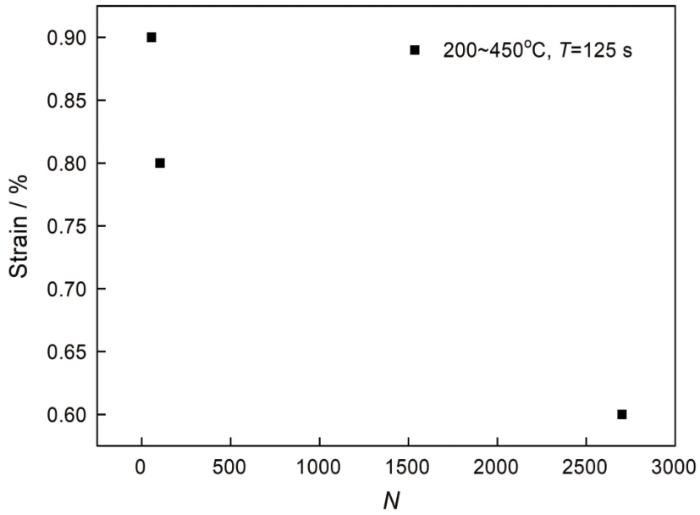
2.4 疲劳寿命
图5
图6
从表2可以看出,温度区间和应变幅都对寿命有较大的影响。随着温度的升高GH4169的寿命急速下降,因为较高的温度使晶界弱化,在机械载荷的作用下晶界滑动使晶界空洞和裂纹萌生和寿命降低。在相同的温度区间GH4169同相位时的疲劳寿命低于反相位时,因为裂纹的扩展出现在拉伸半周,同相位时拉伸半周与高温半周对应,高温使大量的晶界滑动,而在压缩半周中晶界滑动不能恢复。由此,在同相位热机械疲劳情况下高温使材料的疲劳损伤加剧。
2.5 疲劳断口的形貌
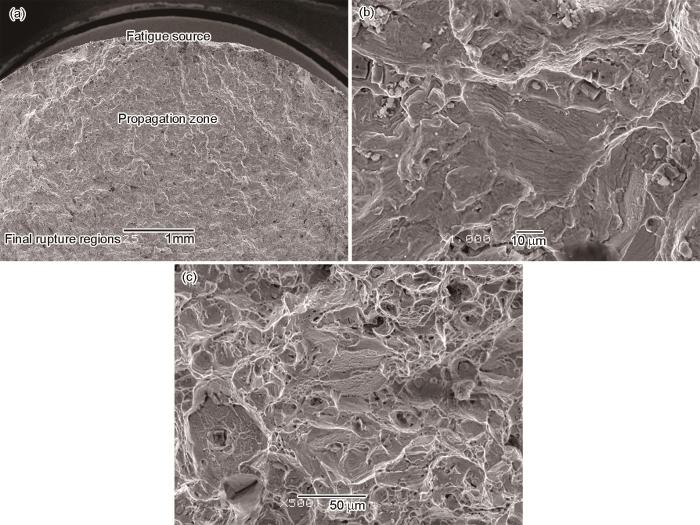
图7
图7
GH4169的断口形貌(同相位、应变幅±0.6%、400~650℃)
Fig.7
Fracture morphology of GH4169 (IP, strain amplitude ±0.6%, 400~650℃), (a) fatigue source; (b) propagation zone; (c) final rupture regions
图8
图8
GH4169的断口形貌(反相位、应变幅±0.6%、400~650℃)
Fig.8
Fracture morphologies of GH4169 (OP, strain amplitude ±0.6%, 400~650℃) (a) fatigue source; (b) propagation zone; (c) final rupture regions
3 结论
(1) 在热机械条件下,GH4169合金在不同温度半周力学性能不同,使其稳定迟滞回线明显不对称。在热机械疲劳条件下,平均应力总是指向低温半周。材料在较大应变幅(0.8%)条件下出现循环松弛现象。
(2) GH4169合金在高温半周先循环软化后循环稳定,在低温半周始终趋于循环稳定。温度对其应力特性的影响较为明显,高温半周更容易出现软化。应变速率也影响其应力响应特性,在中应变速率时应力响应相对平稳,较高或较低应变速率时应力响应行为比较强烈。
(3) 温度区间、周期、相位、机械应变幅等因素都影响GH4169的寿命,其同相位的疲劳寿命比反相位时低,其中温度区间和应变幅对寿命的影响最大。随着机械应变和周期的减小,热机械疲劳寿命延长。
参考文献
Development and technology of Inconel718 (GH4169) superalloy
[J].
Inconel718(GH4169)高温合金的发展与工艺
[J].
Application of alloy 718 in GE aircraft engines: past, present and next five years
[A].
Alloy 718 at pratt & whitney-historical perspective and future challenges
[A].
The initial years of alloy 718
[A].
Thermal-mechanical and isothermal fatigue of IN792 CC
[J].
Thermomechanical fatigue behavior of the intermetallic γ-TiAl alloy TNB-V5 with different microstructures
[J].
Aspects of high-temperature low-cycle thermomechanical fatigue of a single crystal nickel-base superalloy
[J].
Thermo-mechanical fatigue of Mar-M247
[J].
Thermo-mechanical fatigue and fracture of INCO718
[J].
Thermo-mechanical fatigue crack propagation experiments in Inconel 718
[J].
Hold-time effect on the thermo-mechanical fatigue crack growth be-haviour of Inconel 718
[J].
Experimental investigation of the time and temperature dependent growth of fatigue cracks in Inconel 718 and mechanism based lifetime prediction
[J].
Thermomechanical fatigue properties and life prediction of IC10 alloy
[J].
IC10合金热机械疲劳性能与寿命预测
[J].
Thermal mechanical fatigue properties of 316LN stainless steel for nuclear power
[J].
核电用316LN不锈钢的热机械疲劳性能研究
[J].
Study on thermomechanical fatigue behavior of cast nickel base superalloy K417
[J].
K417铸造镍基高温合金热机械疲劳行为的研究
[J].
Effect of heating rate on thermomechanical fatigue properties
[J].
升温速率对热机械疲劳性能的影响
[J].
Study on thermomechanical fatigue behavior and micromechanism of nickel base superalloy
[D].
镍基高温合金热机械疲劳行为及微观机制研究
[D].
Thermomechanical fatigue properties of IN718 nickel base superalloy
[J].
IN718镍基高温合金的热机械疲劳性能
[J].
Shearing of γ″ precipitates and formation of planar slip bands in Inconel 718 during cyclic deformation
[J].
Effect of long term aging on microstructure evolution and low cycle fatigue behavior of GH4169 alloy
[J].
长期时效对GH4169合金组织演化及低周疲劳行为的影响
[J].