现代大型电力蒸汽管道的熔焊工艺,不可避免地会改变使焊缝(Welded zone, WZ)及其附近的显微组织 [8]。尽管蒸汽管道在建造过程中均采用焊后热处理以实现强韧性改性,但是长期在高温、高压条件下服役必然使P91钢管及其焊接部位的显微组织和力学性能老化。在焊接过程中热循环已经使焊缝及热影响区(Heat affected zone, HAZ)显微组织严重劣化,严重影响整个管道的服役寿命和安全。
1 实验方法
1.1 实验材料
实验用材料取自国内某电力系统未服役的P91钢管母材和在线服役136000小时的P91钢管的焊接接头。服役钢管由直管(281 mm×56.15 mm)和弯管(272 mm×69.95 mm)焊接而成,接头区域由母材、直管热影响区(Heat affected zone of straight pipe, SHAZ)、焊缝和弯管热影响区(Heat affected zone of bent pipe, BHAZ) 四部分组成,其宏观形貌如图1所示。接头的服役温度和压力,分别为541℃和17.47 MPa。此外,未服役钢管母材(Base metal of non-service steel pipe, NBM)和服役钢管接头各区域的化学成分列于表1。
图1
图1
长期高温在线服役P91钢管接头的宏观形貌
Fig.1
Macroscopic morphology of P91 steel pipe joint in long-term online service at high temperature
表1 未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的化学成分
Table 1
| C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Mo | V | Nb | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBM | 0.106 | 0.402 | 0.298 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 8.512 | 1.035 | 0.224 | 0.091 | Bal. |
| BM | 0.099 | 0.392 | 0.296 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 8.487 | 1.038 | 0.229 | 0.087 | Bal. |
| SHAZ | 0.103 | 0.403 | 0.299 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 8.504 | 1.042 | 0.235 | 0.092 | Bal. |
| WZ | 0.141 | 0.223 | 0.863 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 8.827 | 1.024 | - | 0.053 | Bal. |
| BHAZ | 0.101 | 0.385 | 0.304 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 8.497 | 1.039 | 0.231 | 0.085 | Bal. |
1.2 性能表征
在未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域切取金相试样,将其研磨和抛光后用5%硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀15 s,然后用Nova NanoSEM 50型扫描电镜观察其显微组织、碳化物数量和尺寸。
从各拉伸试样上切取厚度为0.5 mm的薄片,机械减薄至90 μm后冲成直径为3 mm的小圆片,用砂纸打磨至30~40 μm后进行电解双喷制成透射试样。双喷液为7%高氯酸酒精溶液,电解电压和电流分别为10~15 mV和50~60 mA。用JEM-2100F型场发射透射电镜和能谱仪检测碳化物类型及其分布,并观察各区域位错密度的变化。
在未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域切取测试硬度和拉伸实验的试样。用EQUOTIP BAMBINO 2型里氏硬度计测定硬度。用AG-X100kN和AG-XPLUS100kN型电子万能试验机分别进行室温和高温拉伸实验,拉伸速率均为4 mm/min,实验温度分别为25和545℃。用JXA-8530F型场发射扫描电镜观察试样的室温和高温拉伸断口的形貌。
2 实验结果
2.1 长期服役对接头各区域硬度和显微组织的影响
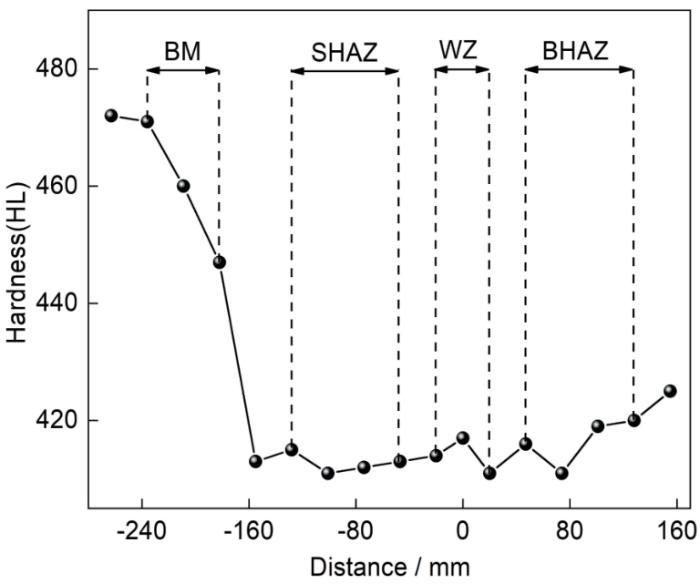
图2给出了服役钢管接头的硬度分布。可以看出,焊缝、直管和弯管热影响区的硬度相近(约为410~420HL),都明显低于未服役钢管母材的硬度(约为470HL)。这表明,在高温下长期服役使接头各区域硬度发生不同程度的退化,焊缝和热影响区的退化更为严重。
图2
图2
长期高温在线服役P91钢管接头的硬度分布
Fig.2
Hardness distribution of P91 steel pipe joint in long-term online service at high temperature
图3给出了未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的显微组织。可以看出,服役前后钢管显微组织都以回火马氏体为主。服役前的钢管晶粒细小均匀,未见明显的碳化物颗粒;服役后的钢管接头,母材、直管和弯管热影响区的晶粒尺寸未见明显变化,但是焊缝处的马氏体严重分解。同时,母材和焊缝的马氏体边界处析出的碳化物数量明显增多。这表明,经长时间高温服役后,接头各区域显微组织均出现一定程度的老化,焊缝的老化程度更高。
图3
图3
未服役钢管母材和高温长期在线服役钢管接头各区域的显微组织
Fig.3
Microstructure in base metal of non-service steel pipe and steel pipe joint in long-term online service at high temperature: (a) NBM, (b) BM, (c) SHAZ, (d) WZ, (e) BHAZ
2.2 长期服役对接头各区域拉伸性能的影响
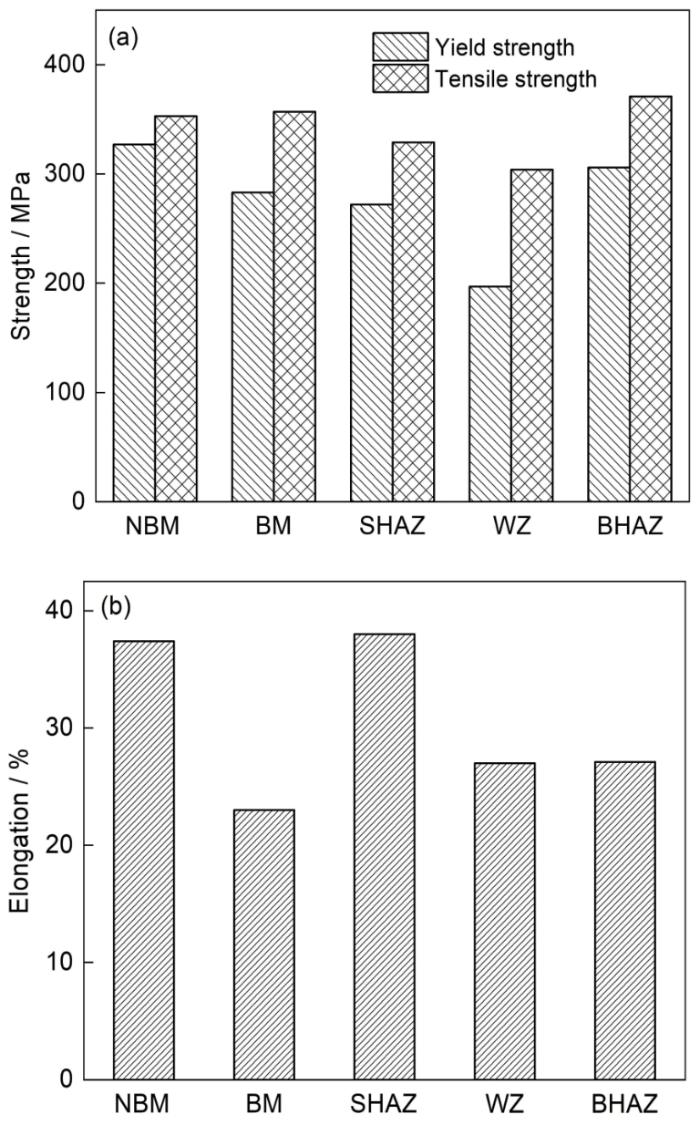
图4
图4
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的室温拉伸性能
Fig.4
Room temperature tensile property in base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service: (a) strength, (b) elongation
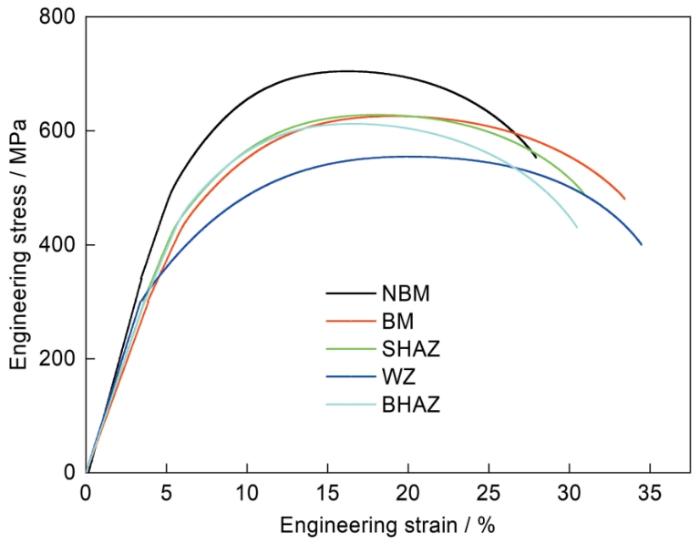
图5
图5
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域室温拉伸的应力-应变曲线
Fig.5
room temperature tensile stress-stain curve of base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service during
图6
图6
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的高温拉伸性能
Fig.6
High temperature tensile property of base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service (a) strength, (b) elongation
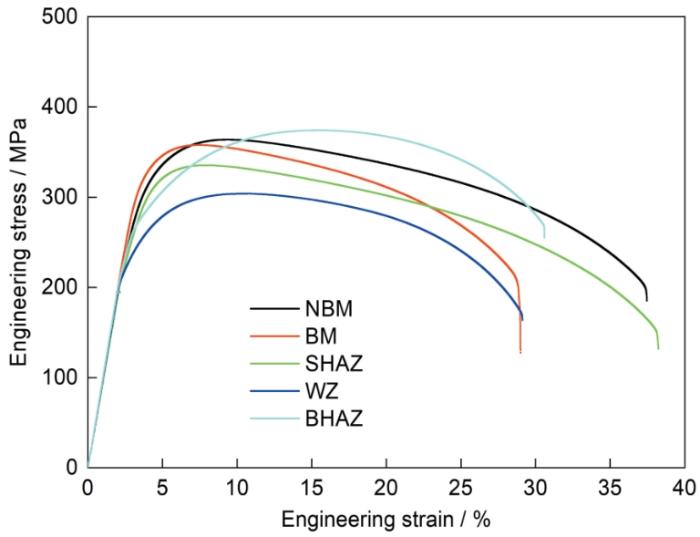
图7
图7
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的高温拉伸应力-应变曲线
Fig.7
High temperature tensile stress-strain curve of base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service during
2.3 长期服役对接头各区域断裂行为的影响
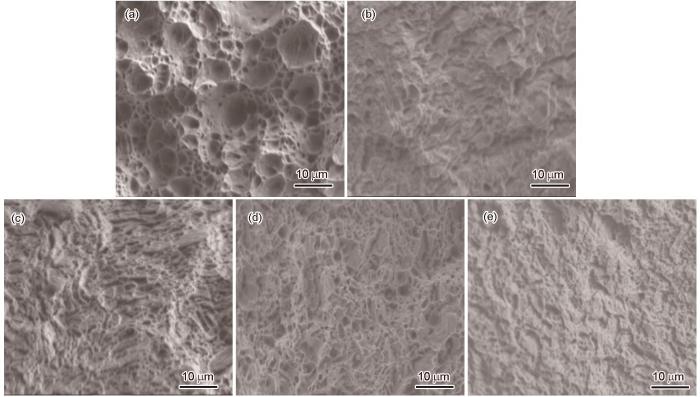
图8分别给出了未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的室温拉伸断口形貌。可以看出,未服役钢管母材的断裂面出现大量较深的韧窝,断裂形式为韧窝断裂。母材、直管和弯管热影响区的断裂面出现浅韧窝和准解理,其形式为韧窝和准解理复合断裂。焊缝的断裂面以韧窝为主还有少量准解理,尽管与接头其它区域的韧窝尺寸相比有所增大,但是仍比未服役钢管母材的韧窝尺寸小。这表明,长期高温服役后的接头各区域的断裂特征均发生变化,断裂形式由韧窝断裂向韧窝和准解理复合断裂转变。
图8
图8
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域室温拉伸断口的形貌
Fig.8
Room temperature tensile fracture morphology of base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service (a) NBM, (b) BM, (c) SHAZ, (d) WZ, (e) BHAZ
图9分别给出了未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的高温拉伸断裂形貌。可以看出,未服役钢管母材的断裂面出现许多韧窝,为韧窝断裂。接头各区域的断裂面差异不大,与未服役钢管母材相比韧窝数量明显减少,还出现少量准解理,断裂形式为韧窝和准解理复合断裂。
图9
图9
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域的高温拉伸断口形貌
Fig.9
High temperature tensile fracture morphology in base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service (a) NBM, (b) BM, (c) SHAZ, (d) WZ, (e) BHAZ
2.4 长期服役对接头各区域碳化物和位错密度的影响
图10
图10
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域碳化物的扫描电镜形貌
Fig.10
Scanning electron microscope morphology of carbides in base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service (a) NBM, (b) BM, (c) SHAZ, (d) WZ, (e) BHAZ
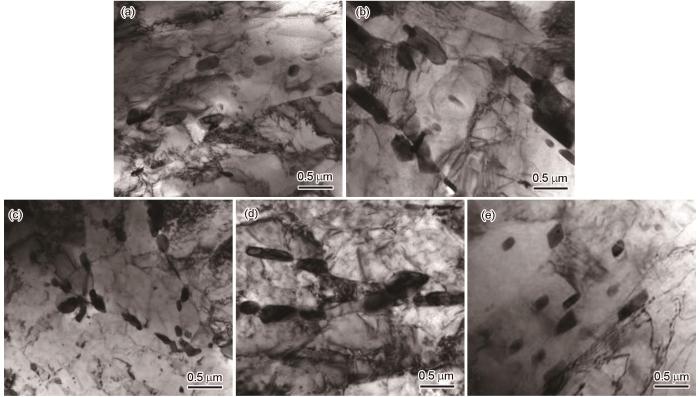
由图11可见,未服役钢管母材的碳化物多呈椭球状,主要分布在晶内。在长期高温服役后的接头中碳化物由椭球状转变为短棒状,且沿马氏体边界析出的比例增大,焊缝的碳化物沿马氏体板条边界连续析出。此外,与未服役的钢管母材相比,服役接头各区域的位错密度均明显降低,焊缝处降低的程度更高。
图11
图11
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头各区域碳化物的透射电镜形貌
Fig.11
Transmission electron microscope morphology of carbides in base metal of non-service steel pipe and each area of steel pipe joint in service (a) NBM, (b) BM, (c) SHAZ, (d) WZ, (e) BHAZ
图12
图12
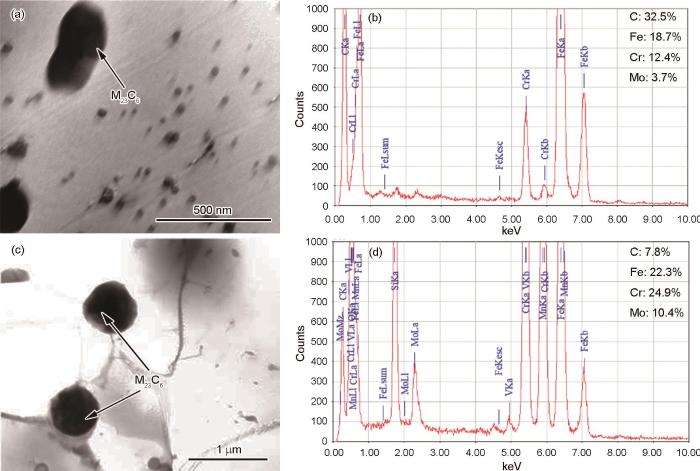
未服役钢管母材和服役钢管接头焊缝处碳化物的形貌和成分
Fig.12
Morphology and composition of carbides in base metal of non-service steel pipe and weld zone of steel pipe joint in service (a, b) NBM, (c, d) WZ
2.5 接头各区域力学性能的退化机制
以上结果表明,长期服役使P91钢管接头中的马氏体分解、碳化物的尺寸增大、位错密度降低,马氏体强化、位错强化、析出强化和固溶强化对硬度和强度的贡献减小,最终导致接头各区域的硬度、室温和高温拉伸性能退化。在蒸汽管道的焊接过程中焊缝处温度最高,严重的焊接热循环回火使焊缝的显微组织相比接头其它区域发生明显的老化,长时间服役使焊缝的显微组织的老化更加严重,因此焊缝的强度明显降低。
3 结论
(1) 长期高温在线服役的P91钢管接头显微组织明显老化,各区域的硬度均不同程度降低。在线硬度测试可有效反映显微组织明显老化P91接头的室温和高温拉伸性能退化行为。
(2) 与未服役的P91钢管母材相比,高温长期在线服役的P91钢管接头各区域的马氏体分解和碳化物粗化极为明显,使钢管的马氏体强化、沉淀强化和固溶强化效果明显减弱,最终使各区域的硬度、室温和高温拉伸性能明显退化。室温和高温拉伸断裂形式均由韧窝断裂转变为韧窝和准解理复合断裂。
(3) 高温长期在线服役的P91钢管焊缝区域的硬度和室温、高温拉伸性能的退化最为显著。服役前焊接产生的热循环严重回火与长期高温服役的耦合作用,是导致P91钢管焊缝力学性能显著退化的重要原因。
参考文献
Weldability and welding technology of P91 steel
[J].
P91钢的焊接性及其焊接工艺
[J].
Evolution of phases in P91 steel in various heat treatment conditions and their effect on microstructure stability and mechanical properties
[J].
Analysis of creep behavior of P91 steel at high temperature based on deformation mechanism
[D].
基于变形机制的P91钢高温蠕变行为分析
[D].
Homogenization of P91 weldments using varying normalizing and tempering treatment
[J].
Optimization on heat-treatment process of P91 steel for high pressure bolier tubes
[J].
高压锅炉管用P91钢热处理工艺优化
[J].
Deformation-mechanism-based modeling of creep behavior of P91 steel
[J].
基于变形机制的P91钢蠕变行为分析
[J].
Microstructure aging, property degardation and residual creep life evaluation of high-chromium martensitic heat-resistant steel
[D].
高铬马氏体耐热钢组织老化、性能退化及剩余寿命评估
[D].
Effect of martensite weld microstructure on welding cold crack sensitivity of T91/P91 steel
[J].
马氏体焊缝组织对T91/P91钢焊接冷裂纹敏感性的影响
[J].
Laves phase formation and its effect on mechanical properties in P91 steel
[J].
Microstructure evolution of P92 steel weld metal after servicing at high temperature for 50000 h
[J].
高温服役50000 h后P92钢焊缝金属组织变化
[J].
600 MW subcritical unit T91 steel welded joints failure analysis
[J].
600 MW亚临界机组T91钢焊接接头失效分析
[J].
Microstructure and properties of welded joint of new martensitic heat resistant steel after long service
[J].
长期服役后新型马氏体耐热钢焊接接头的组织及性能
[J].
Exploration on application of hardness testing technology in power station boiler inspection
[J].
电站锅炉检验中硬度检测技术的应用探究
[J].
Conversion relationship between the leeb hardness and brinell hardness of P22 steel
[J].
P22钢的里氏硬度与布氏硬度的转换关系
[J].在电站锅炉实际检测中,通常会将现场检测的里氏硬度转换成布氏硬度,但现有的换算关系缺乏材料针对性,且硬度范围也较窄。对P22钢进行了顶端淬火和整体热处理试验,获得硬度范围更宽、分布更均匀的里氏硬度与布氏硬度,然后建立里氏硬度与布氏硬度之间的转换关系。结果表明:P22钢的里氏硬度与布氏硬度之间呈二次回归关系,其转换关系为H<sub>BW</sub>=0. 001 6H<sub>LD</sub><sup>2</sup>-0. 66H<sub>LD</sub>+155. 7。
Study on non-uniform softening and formation mechanism of P91 steel for high temperature steam pipeline during service
[J].
高温蒸汽管道用P91钢服役过程不均匀软化及形成机制研究
[J].
The characterization of soft fine-grained heat-affected zones in P91 weldments under creep exposure conditions
[J].
Microstructure and properties of P91 steel pipeline in abnormal low hardness parts
[J].
P91钢管道异常低硬度部位的组织和性能
[J].对电厂运行过程中发现的P91钢主蒸汽管道的低硬度部位进行了微观组织观察、短时力学性能试验和高温持久强度试验,分析了其硬度偏低的原因。结果表明,低硬度区域P91钢组织为铁素体+析出物,位错密度较低,M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>相在晶界处粗化聚集,同时析出新相Laves相,使得P91钢的短时力学性能和高温持久强度下降严重。
Strenfth degradation behavior of P91 steel for a supercritical unit
[J].
某超临界机组用P91钢的强度退化行为
[J].从马氏体亚结构、析出相、固溶元素以及位错密度等方面探究了某超临界机组蒸汽管道用P91钢服役8.8万h后其强度下降的原因。结果表明:服役后P91钢中M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>型碳化物的平均粒径由78.0 nm增加到190.6 nm,同时析出了平均粒径为393.2 nm的Laves相,M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>型碳化物的粗化使得析出相对屈服强度的贡献值下降了38.7%,Laves相的析出对屈服强度的贡献很小;M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>型碳化物的Ostwald熟化与粗大Laves相的析出消耗了基体中的碳、铬、钼、硅元素,降低了固溶强化效果;服役后P91钢中马氏体板条块尺寸与板条宽度增大,对该钢屈服强度降低有一定贡献;服役P91钢中的位错密度为6.4×10<sup>13</sup> m<sup>-2</sup>,低于未服役P91钢的(9.7×10<sup>13</sup> m<sup>-2</sup>),位错对基体的强化效果降低了18.8%;在所有因素的作用下,服役后P91钢的屈服强度降低了27.0%。
Microstructure and mechanical properties of GMAW weld metal of 890 MPa class steel
[J].
Precipitation behavior and martensite lath coarsening during tempering of T/P92 ferritic heat-resistant steel
[J].
Effects of multiple post weld heat treatments on microstructure and precipitate of fine-grained heat affected zone of P91 weld
[J].
Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of dissimilar material diffusion-bonded joint for high Cr ferrite heat-resistant steel and austenitic heat-resistant steel
[J].High Cr ferrite heat-resistant steel has excellent geometric structure stability, low radiation swelling rate, and good corrosion resistance of liquid metal. TP347H austenitic heat-resistant steel is based on the traditional 18-8 austenitic steel with the addition of a certain amount of Nb and a small amount of N to precipitate MX-type carbonitride, which results in superior high-temperature properties. Steam with high temperature and pressure flowing through supercritical thermal power units may exhibit heterogeneous connections between high Cr ferrite and austenitic heat-resistant steel components in the supercritical thermal power units. In this study, the vacuum diffusion-bonding of dissimilar materials between high Cr ferritic and TP347H austenitic heat-resistant steel was performed, the effects of diffusion-bonding time and post weld heat treatment (PWHT) process on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of the diffusion-affected zone was examined. The results indicated that with the extension of diffusion-bonding time, the interfacial bonding rate gradually increased. The interaction due to the difference in deformation storage energy and dislocation slips resulted in dynamic recrystallization, and the fine grains formed at the diffusion-bonding interface evolved into a serrated interface. Fine and dispersed MX and M23C6 phases were precipitated in the austenite grain boundaries and at the grain boundaries of the diffusion-bonding zone. After PWHT, the grains in the diffusion-bonding zone were further refined, dislocations were stable, dislocation density reduced, small-angle grain boundaries increased, and element diffusion was more sufficient. Tensile tests at different temperatures showed that the fractured sites were all in the matrix, which indicates that high-quality diffusion-bonding joints of dissimilar materials were achieved.
高Cr铁素体耐热钢与奥氏体耐热钢的异种材料扩散连接接头组织演变及力学性能
[J].
The effect of phase parameter variation on hardness of P91 components after service exposures at 530-550℃
[J].
Microstructure, properties and safety evaluation of low hardness P91 steel tube after long service
[J].Microstructure, properties and safety evaluation of low hardness P91 steel after 10<sup>5</sup> h service were studied by means of microstructure observation, energy dispersive spectrum(EDS) analysis, room temperature and high temperature mechanical property test, room temperature impact test and high temperature stress rupture test. The results show that the microstructure of low hardness P91 steel tube(157 HBW) after long service is composed of massive ferrite and large size M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub> phase. Compared with the normal hardness tube, its mechanical properties at room temperature and short time mechanical properties at high temperature decrease greatly, and its extrapolation value of 10<sup>5</sup> h endurance strength is 36% lower than that of the standard recommended value. The residual life of low hardness straight tube section of high-pressure steam pipe is 54 075 h, which means the operation of the power plant unit has great security risks.
低硬度P91钢管长时服役后的组织性能和安全性评价
[J].