将高温与等静压结合的热等静压(HIP)技术,是消除铸件内部显微孔洞和疏松缺陷、提高铸件致密度的有效方法[10]。目前,对某些发动机用高温合金精铸件进行热等静压处理,已经成为生产加工流程的一道固定工序。近年来,热等静压也逐渐应用于铸造单晶高温合金[11~13]。Epishin等[14]的研究表明,在CMSX-4单晶合金的热等静压过程中合金内部5~10 μm的小尺寸固溶微孔迅速消失,大尺寸凝固孔经过稍长时间也有效闭合,微孔数量显著减少。Roncery等[15]对ERBO/1合金进行合适的热等静压完整热处理工艺,不仅显著降低了微孔的数量密度,还细化了合金γ/γʹ相微观组织结构,从而使合金在750℃/800 MPa条件下的持久蠕变寿命提高。Cervellon等[16]的研究发现,显微孔洞是影响单晶高温合金超高周疲劳性能最重要的因素。经过热等静压处理的小尺寸样品其内部显微孔洞数量少,与传统快速凝固工艺(HRS)和液态金属冷却工艺(LMC)制备的样品相比其超高周疲劳寿命明显提高。但是,也有研究者[17]认为,热等静压虽然能显著消除CMSX-4单晶合金的铸造孔洞,但是在1150℃/100 MPa条件下的蠕变持久寿命并没有明显延长,TCP相的形成或许是限制高温蠕变性能的关键因素。另外,对于单晶高温合金,若热等静压参数及后续热处理制度选择不当,还可能使合金发生再结晶或引入其它新显微组织缺陷,严重降低合金的使用性能。
鉴于此,本文以用HRS凝固工艺制备的第三代镍基单晶高温合金DD33为研究对象,通过对铸态、标准热处理态、热等静压及不同制度后续热处理态合金的微观组织进行对比表征观察,选出最佳热等静压后续热处理制度。再利用XCT准原位定量统计合金中显微孔洞在热等静压过程中的演变规律,比较单晶高温合金在热等静压前后的持久性能差异并分析原因,以期为单晶高温合金叶片结构设计积累数据,为制订单晶叶片的热等静压工艺提供理论依据。
1 实验方法
实验材料是用含4%Re(质量分数)的第三代镍基单晶高温合金DD33,其化学成分列于表1。
表1 实验用高温合金的名义成分
Table 1
| Alloy | Cr | Co | W | Mo | Al | Ta | Re | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD33 | 3.5 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 | Bal. |
采用高速凝固工艺(HRS)制备单晶试棒,整个凝固流程在Bridgman真空炉中完成。单晶试棒定向凝固结束后,对铸态单晶试棒进行宏观腐蚀。腐蚀液的配比为1∶1的H2O2和HCl混合溶液。观察单晶试棒中是否存在杂晶、雀斑等缺陷,并利用背散射电子衍射(EBSD)技术测定单晶试棒的晶体取向,选取偏离[001]取向10°以内的合格单晶试棒进行实验。
表2 实验所涉及热等静压参数及热处理制度
Table 2
| Specimen | State | Heat treatment process |
|---|---|---|
| AC | As-cast | - |
| SHT | Standard heat treatment | 1335℃/10 h/AC*+1180℃/4 h/AC*+870℃/24 h/AC* |
| AH | As-cast+HIP | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h |
| AHS1 | As-cast+HIP+solution treatment 1 | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/2 h/AC* |
| AHS2 | As-cast+HIP+solution treatment 2 | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/6 h/AC* |
| AHS3 | As-cast+HIP+solution treatment 3 | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/10 h/AC* |
| AHS3HT1 | As-cast+HIP+solution treatment 3+heat treatment 1 | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/10 h/AC* +1120℃/4 h/AC*+870℃/24 h/AC* |
| AHS3HT2 | As-cast+HIP+solution treatment 3+heat treatment 2 | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/10 h/AC* +1150℃/4 h/AC*+870℃/24 h/AC* |
| AHS3HT3 | As-cast+HIP+solution treatment 3+heat treatment 3 | 1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/10 h/AC* +1180℃/4 h/AC*+870℃/24 h/AC* |
经过标准热处理和热等静压及优选完整热处理后,将试棒加工成标准的持久性能测试试样,分别在850℃/650 MPa和1100℃/170 MPa条件下测试合金的持久性能。其它用于组织观察的试样,经过机械研磨和抛光处理后均进行化学腐蚀。所用的腐蚀剂成分为4 g CuSO4+10 mL HCl+20 mL H2O溶液,使用Zeiss Axiovert200MAT 光学显微镜(OM)和 带有EBSD探头的TESCAN MIRA3场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对合金铸态、标准热处理态、热等静压态及不同后续热处理态的组织进行采集和观察。所有的EBSD结果都使用Oxford HKL Channel 5软件处理,并使用软件 Image Pro Plus统计合金的一次枝晶间距、γʹ相体积分数和尺寸,每个试样至少采用5个视场进行统计,然后取结果的平均值。对于合金内部的显微孔洞三维信息(数量、体积分数、尺寸、形貌、分布位置),使用Versa XRM-500设备对样品进行准原位XCT定量表征,工作参数列于表3。综合考虑此XCT设备的最佳视场范围和分辨率条件,实验中用于XCT观察的样品为直径约1.5 mm、高度约10 mm的圆柱样品。所有数据都使用分析软件Avizo fire 7.1进行可视化处理。为确保结果的可靠性和准确性,将剔除结果中等效直径小于3 μm的微孔。
表3 XCT设备所采用的工作参数
Table 3
| Parameter | Xradia Versa XRM-500 |
|---|---|
| Energy | 120 kV |
| Voxel resolution | 1.5 μm |
| Scan time | 9 h |
| Field of view | 1.5 mm×1.5 mm×2.0 mm |
| Number of projections | 1600~2000 (360° rotation) |
| Exposure time | 8 s |
| Detector binning | ×2 |
2 结果和讨论
2.1 热等静压前合金的显微组织
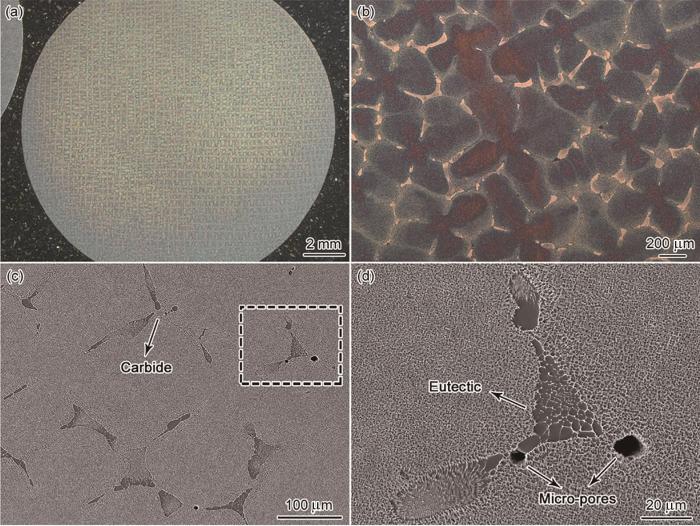
图1
图1
HRS铸态DD33合金的组织形貌
Fig.1
Microstructure of as-cast (AC) DD33 alloy processed by HRS (a, b) OM and (c, d) SEM
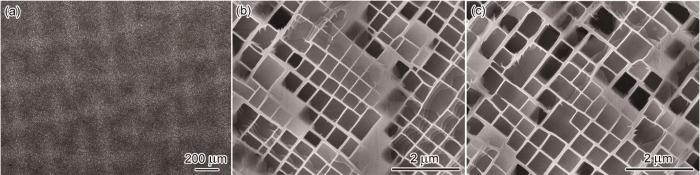
图2
图2
HRS标准热处理态DD33合金的组织形貌
Fig.2
Microstructure of standard heat treatment (SHT) DD33 alloy processed by HRS (a) OM, (b) dendrite region, and (c) interdendritic region
2.2 热等静压和后续热处理制度对合金组织的影响
图3给出了DD33铸态样品热等静压前后合金组织的对比。可以看出,经过热等静压后合金中没有出现初熔,但是合金枝晶干和枝晶间处的γʹ相立方化程度提高,且尺寸均有一定的增大,枝晶间γʹ的尺寸明显大于枝晶干γʹ的尺寸。其原因是,热等静压的样品的冷却方式是炉冷,比标准热处理的空冷慢,使γʹ相的尺寸增大。
图3
图3
HRS铸态和热等静压态DD33合金的组织形貌
Fig.3
Scanning electron micrographs of the HRS DD33 before and after HIP treatment (a, b) AC and (c, d) AH
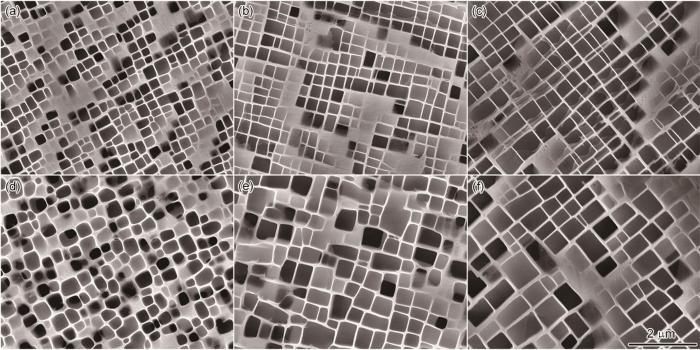
为了消除热等静压过程中产生的γ'相粗化并生成与合金标准热处理组织基本相同的γ'相组织形貌,热等静压后样品的固溶温度一般应略低于标准热处理的最高固溶温度,以避免产生再结晶[19]。因此,在前人研究的基础上本文将DD33合金热等静压的后续固溶热处理温度设置为1325℃。图4给出了合金热等静压后经过不同后续固溶处理的组织形貌。可以看出,经过热等静压后的单晶高温合金后续固溶温度为1325℃分别保温2 h、6 h、10 h后,均未发现明显的再结晶。同时,随着保温时间的延长至10 h,样品内部的残余共晶基本消失,合金的微观偏析减轻,枝晶排布也更为均匀规则。因此,确定DD33合金热等静压后的固溶热处理制度为1325℃/10 h。
图4
图4
不同热等静压后续固溶处理态DD33合金的组织形貌
Fig.4
Microstructures (OM) of DD33 after AHS1 (a, b), AHS2 (c, d), and AHS3 heat treatment (e, f)
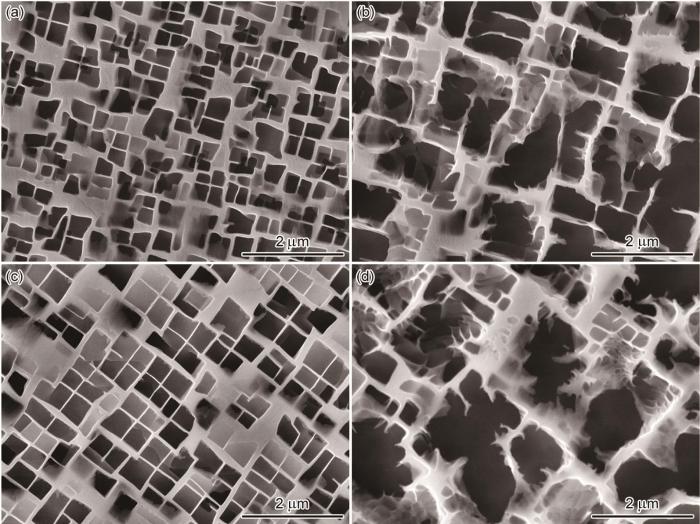
确定1325℃/10 h为最佳热等静压后续固溶制度后,又对此样品进行制度为1120℃/4 h/AC+870℃/24 h/AC、1150℃/4 h/AC+870℃/24 h/AC、1180℃/4 h/AC+870℃/24 h/AC的时效处理,得到的γʹ相形貌在图5中给出。从图5可以得出,随着时效温度的提高合金的γʹ相形状立方度逐渐提高,枝晶干与枝晶间的γʹ相尺寸更加接近。定量统计结果表明,AHS3HT3制度下的DD33合金γʹ相的平均尺寸为522.9 nm,体积分数为72.5%。与标准热处理后的样品相比(图2),1310℃/120 MPa/4 h+1325℃/10 h/AC+1180℃/4 h/AC+870℃/24 h/AC的AHS3HT3热处理制度为DD33合金的最佳热等静压及后续完整热处理制度,其γʹ相形貌、尺寸与体积分数与标准热处理样品基本相同。在本实验的AHS3HT3制度中,热等静压使合金处于高温高压条件下,使合金元素从高浓度区域向低浓度区域剧烈扩散,相当于高温均匀化热处理,降低了合金的偏析程度。
图5
图5
不同热等静压后续完整热处理态DD33合金γʹ 的组织形貌
Fig.5
Scanning electron micrographs of the DD33 after AHS3HT1 (a, d), AHS3HT2 (b, e) and AHS3HT3 heat treatment (c, f)
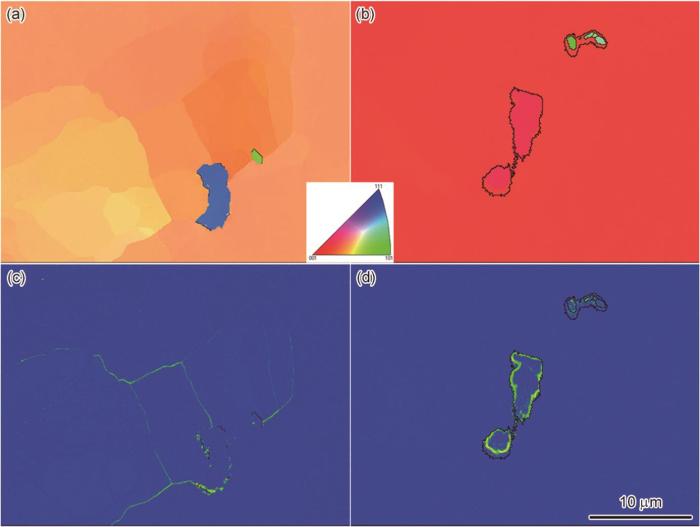
图6给出了热等静压态和热等静压及完整热处理后样品内部碳化物附近的EBSD结果。从图6a可以看出,DD33单晶高温合金经过1310℃/120 MPa/4 h热等静压后,在枝晶间的某些碳化物粒子周围出现了局部的二次取向旋转。其原因是,作为单晶高温合金基体中的脆性相,碳化物在变形过程中容易在基体界面处产生应力集中[21~23]。在图6c所示的KAM图中也可见碳化物附近产生了一定的应力集中,但是局部取向旋转在一定程度上释放了碳化物周围的应力集中,因此碳化物周围的应力状况不同。但是,经过合适的后续固溶与时效热处理后,样品内部并未再出现碳化物附近明显的取向旋转,如图6b和d所示。其原因是,随着后续热处理的进行维持局部取向旋转的内应力已逐渐释放,碳化物附近的局部取向差基本消除,而碳化物因其硬度较高在基体界面依然存在一定的应力集中。综上所述,DD33单晶高温合金经过合适的热等静压及完整热处理可产生与标准热处理态基本相同的微观组织形貌,不会出现明显的再结晶倾向。
图6
图6
热等静压态和热等静压后续完整热处理态DD33合金中碳化物附近的EBSD结果
Fig.6
EBSD data of the (a, c) AH and (b, d) AHSHT specimens nearby carbide: (a, b) IPF-X maps, (c, d) KAM maps
2.3 热等静压对合金中显微孔洞的影响
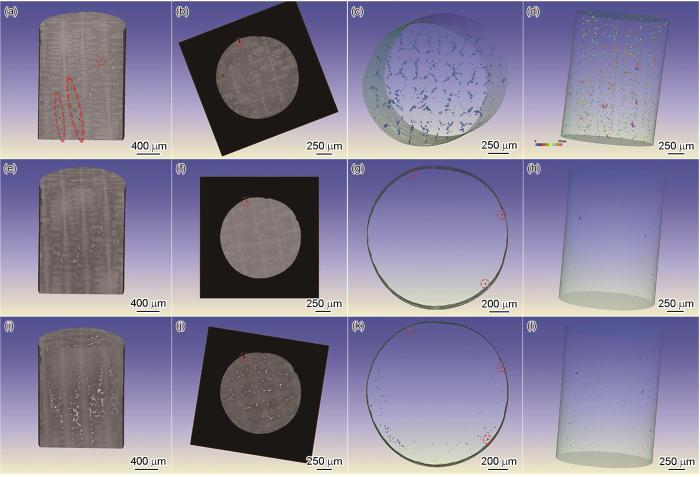
热等静压与后续热处理工艺对DD33合金显微孔洞的影响,如图7所示。图7a~d给出了样品铸态(AC)不同横纵截面视角下的显微孔洞三维分布,图7e~h给出了同一样品相同位置的热等静压态(AH)的显微孔洞三维分布,图7i~l给出了同一样品相同位置热等静压及后续热处理态(AHS3HT3)的显微孔洞三维分布。可以看出,热等静压处理后DD33合金内部的显微孔洞(见图7a中红色圆圈内)明显消除,只在样品外表面有些与外界联通并未压实的孔洞。完成后续热处理后样品内部中心并没有出现新的微孔,只是在样品近表面处出现一些新的小尺寸微孔。产生这些小孔的主要原因是,在固溶热处理过程中各元素扩散速度不同产生了柯肯达尔效应 [24,25]。由于热等静压的后续热处理是在非真空环境下进行的,Al易向表面扩散形成Al2O3等氧化产物,使合金近表面的Al浓度远低于平衡浓度,形成的贫Al层其扩散程度远大于合金内部,因此在近表面出现了一定数量的固溶孔[26]。
图7
图7
准原位观察DD33铸态样品热等静压前后微孔的演化
Fig.7
Ex-situ XCT observation of the evolution of micro-pores in DD33 AC sample before and after HIP heat treatment (a, b, c, d) AC, (e, f, g, h) AH, (i, j, k, l) AHS3HT3
XCT定量结果也表明,铸态合金的微孔体积分数为0.0582%,热等静压后样品的微孔体积分数减少了2个数量级至0.0007%,再经后续完整固溶及时效热处理样品微孔的体积分数略有增加至0.0025%。热等静压使合金内部显微孔洞闭合的原因[27]:一方面,是蠕变机制。在高温等静压条件下微孔附近基体中<011>{111}滑移系上位错的开动使微孔周围材料发生塑性变形,即应力诱发孔洞蠕变闭合。另一方面,是扩散机制。微孔周围原子受梯度应力的作用,孔洞内表面易发生定向扩散而使孔洞紧密结合。这表明,在热等静压过程中样品内部微孔体积分数的显著减少是蠕变机制与扩散机制双重作用的结果。
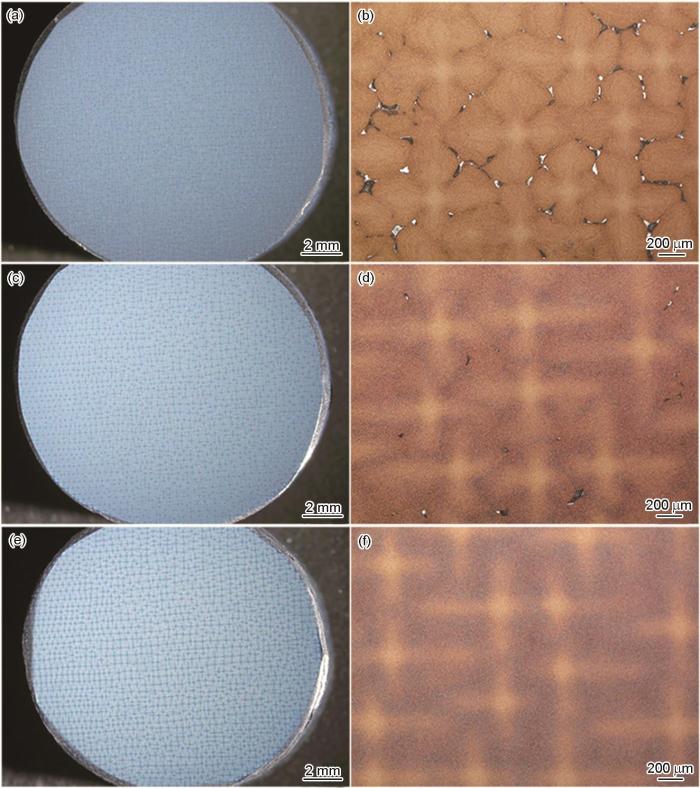
图8给出了标准热处理态和热等静压后续完整热处理态DD33合金其内部微孔的三维特征,可见区域一致均为样品内部中心位置约1 mm3。对比两种状态下样品内部XCT定量结果,标准热处理态合金其内部微孔最大孔的等效直径为36.9 μm,大尺寸微孔的形状大多不规则。而热等静压后续完整热处理态合金其内部微孔的平均尺寸更小且形状更均匀,最大孔的等效直径为14.2 μm。因此,本文实验中所选择DD33单晶高温合金的热等静压及后续热处理制度,能明显消除合金内部的显微孔洞,综合效果较好。
图8
图8
HRS标准热处理态和热等静压后完整热处理态DD33合金内部微孔的三维特征
Fig.8
Three dimensional morphologies of micro-pores inside the SHT DD33 sample by different processing. (a, b, c) HRS, (d, e, f) HIP
2.4 热等静压对合金持久性能的影响
表4列出了DD33合金标准热处理态(简称HRS样品)和热等静压+后续完整热处理态(简称HIP)样品,在中温高应力850℃/650 MPa和高温低应力1100℃/170 MPa两种条件下的持久性能,数据取自2或3组平行试样结果的平均值。可以看出,热等静压样品在两种条件下的持久性能都显著提高,在850℃/650 MPa条件下HRS样品的持久寿命为76.4 h[28],HIP样品的持久寿命为95.3 h,热等静压处理后的样品寿命提高了25%,延伸率从18.3%提高到27.6%;在1100℃/170 MPa条件下,HIP样品的持久寿命为51.9 h,相比未热等静压的HRS样品寿命提高了34%,延伸率也有一定的提高。
表4 热等静压对DD33合金不同条件下持久性能的影响
Table 4
| Test condition | State | Stress rupture lifetime, t/h | Elongation, δ/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 850℃/650 MPa | HRS (SHT) | 76.4 | 18.3 |
| HIP (AHS3HT3) | 95.3 | 27.6 | |
| 1100℃/170 MPa | HRS (SHT) | 38.8 | 27.0 |
| HIP (AHS3HT3) | 51.9 | 33.1 |
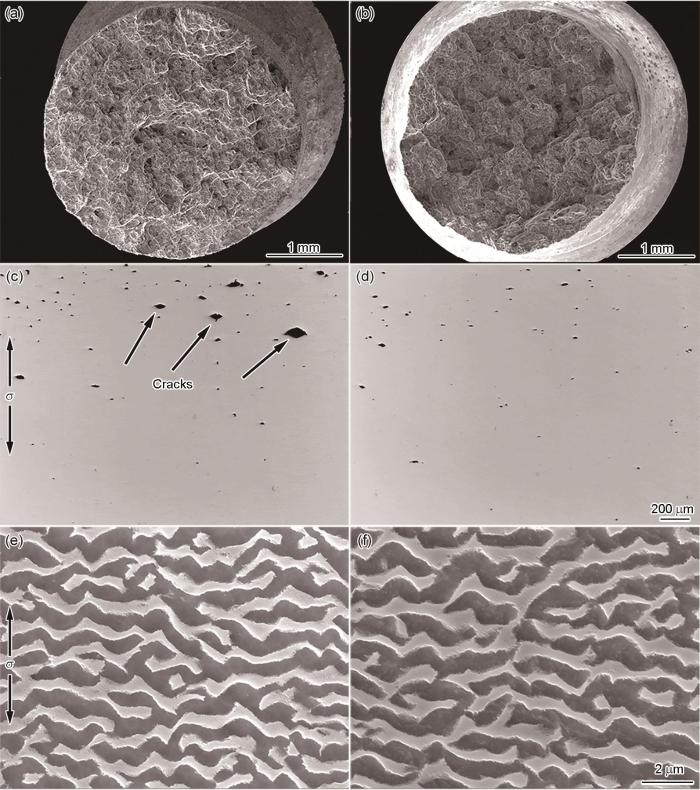
图9给出了在1100℃/170 MPa条件下持久断裂后HRS和HIP样品的组织形貌。从宏观断口形貌(图9a和b)可以看出,两种工艺下的DD33合金断裂特征基本类似,均为微孔聚集型断裂。但是,对比观察两者的低倍金相断口纵剖面可见,HRS样品的断口附近出现更多的裂纹,且其主要在大尺寸孔洞处萌生(图9c);HIP样品在后续热处理和高温持久过程中虽然有一些愈合的孔洞再次长大或成为裂纹源,但是与HRS样品相比其显微孔洞的尺寸更小且数量更少,从而延缓了裂纹的萌生与扩展[32],使蠕变持久断裂寿命延长。同时,本文对DD33合金断口附近组织的高倍观察发现,HRS与HIP样品的γʹ相均出现了筏化,但是两者的γʹ相尺寸和形貌没有明显的不同(图9e和f),也未观察到样品中微孔附近有明显析出TCP析出相。同时,热等静压的高温等静压相当于对合金又进行了一段固溶处理,使合金的组织更加均匀,在一定程度上提高了单晶高温合金的塑性,因此样品的延伸率略有提高。综上所述,适当的热等静压和后续热处理能显著减少DD33单晶高温合金内部的显微孔洞缺陷,使其持久性能提高。
图9
图9
DD33合金HRS和HIP样品在1100℃/170 MPa下持久断口的组织形貌
Fig.9
Fracture morphology of (a, c, e) HRS and (b, d, f) HIP specimens after 1100℃/170 MPa (a, b) the fracture surfaces, (c, d) the longitudinal section OM morphologies, (e, f) the morphology of γ/γʹ microstructure
3 结论
(1) DD33单晶高温合金在经过1310℃/120 MPa/4 h的热等静压处理后,合金显微组织γʹ相立方化程度提高,枝晶干与枝晶间的γʹ相尺寸也有所增大。
(2) 对热等静压后的DD33单晶高温合金进行恰当的后续热处理(1325℃/10 h/AC+1180℃/4 h/AC+870℃/24 h/AC),可得到与标准热处理态合金基本相同的γʹ相尺寸和体积分数。
(3) 热等静压能显著减少DD33单晶高温合金样品内部的显微孔洞数量和尺寸,虽然后续热处理在近表面产生一定数量的小尺寸固溶微孔但是能显著消除样品内部中心位置的微孔。
(4) 热等静压和完整热处理使DD33合金的持久性能显著提高,因为热等静压能显著减少持久蠕变裂纹源的显微孔洞缺陷。
参考文献
Nickel-based superalloys for advanced turbine engines: chemistry, microstructure and properties
[J].
Recent progress in research and development of nickel-based single crystal superalloys
[J].
镍基单晶高温合金的研发进展
[J].
On the origin of sliver defects in single crystal investment castings
[J].
Freckle formation and freckle criterion in superalloy castings
[J].
Synchrotron tomography of porosity in single-crystal nickel-base superalloys
[J].
Ex-situ X-ray tomography characterization of porosity during high-temperature creep in a Ni-based single-crystal superalloy: toward understanding what is damage
[J].
Effect of porosity and eutectics on the high-temperature low-cycle fatigue performance of a nickel-base single-crystal superalloy
[J].
The effect of casting conditions on the high-cycle fatigue properties of the single-crystal nickel-base superalloy PWA 1483
[J].
An overview of hot isostatic pressing
[J].
Effect of hot-isostatic pressing on microstructure and mechanical properties of second generation single crystal superalloy DD6
[J].
热等静压对第二代单晶高温合金DD6显微组织和力学性能的影响
[J].
Effects of hot isostatic pressure on microdefects and stress rupture life of second-generation nickel-based single crystal superalloy in as-cast and as-solid-solution states
[J].Due to the excellent high temperature comprehensive performance and cost effective, the second-generation nickel-based single crystal superalloy has been widely used in the high-pressure turbine blades of advanced aero-engines. Microdefects such as micropores and interdendritic eutectic are seriously harmful to the high temperature mechanical properties of nickel-based single crystal superalloys. Hot isostatic pressure (HIP) technology, which has been widely used in powder and casting superalloys, can effectively reduce the micropores, interdendritic eutectic and other structural defects formed in the turbine blades during manufacturing, and improve the service reliability of turbine blades. However, the effect of HIP process on the high temperature stress rupture life of nickel-based single crystal superalloys is still controversial, especially with regard to the initial microstructure state of the nickel-based single crystal superalloys, i.e. the as-cast microstructure state or the as-solid-solution state. In this work, a kind of second-generation nickel-based single crystal superalloy with as-cast state or as-solid-solution state was selected as the research object. Through two-stage heat/booster type heat treatment process, in combination with microdefects quantitative analysis, quantitative characterization of alloying element segregation and high temperature stress rupture tests at 980 ℃ and 250 MPa, the effects of HIP process on the microdefects and high temperature stress rupture life of the used superalloy with different initial microstructures were studied. The results indicated that the solid-solution treatment can significantly promote the diffusion of alloying elements, such as Re, W, Al, and Ta, reduce the area fraction of interdendritic eutectic, but significantly increase the average area fraction and size of micropores in the used alloy with as-cast state. While, HIP process can effectively reduce the average area fraction and size of microspores in the used alloy with as-cast state or as-solid-solution state, but cannot eliminate the interdendritic eutectic as remarkable as the solid-solution treatment. By HIP process of the used alloy with as-solid-solution state, the area fraction of micropores is reduced to 0.005%, the eutectic structure is basically eliminated, and the dendrite segregation of Re, W, Al, Ta and other elements is significantly alleviated, resulting in the higher stress ruputure life of the used alloy, about 40% over that of the used alloy with the standard heat treatment state. Performing HIP process on nickel-based single crystal superalloy alloy with as-solid-solution state is of benefit to the high temperature stress rupture life due to the reduction of microdefects and the homogenization of alloying elements, in comparison with performing HIP process directly on the alloy with as-cast sate.
热等静压对铸态及固溶态第二代镍基单晶高温合金显微缺陷及持久性能的影响
[J].以初始组织分别为铸态组织和固溶态组织的第二代镍基单晶高温合金为研究对象,通过进行1300 ℃、30 MPa、2 h+1300 ℃、100 MPa、3 h两阶段的热等静压处理,对比热等静压前后显微缺陷及微观组织的变化,并在980 ℃、250 MPa条件下进行高温持久性能实验,明确了热等静压处理对不同初始组织状态下镍基单晶合金组织状态及持久性能改善的影响机制。结果表明:固溶处理显著促进Re、W、Al、Ta等合金元素的扩散,降低铸态组织共晶面积分数但显著提高显微孔洞平均面积分数及平均尺寸。热等静压处理可以显著降低显微孔洞平均面积分数及平均尺寸且对固溶态组织的作用更为显著,但热等静压对共晶组织的消除作用不如固溶处理明显。固溶态组织经热等静压处理后,显微孔洞面积分数降低至0.005%;共晶组织基本消除;Re、W、Al、Ta等元素枝晶偏析程度显著缓解;其980 ℃、250 MPa高温持久寿命相比未经热等静压处理的标准热处理态合金提高了40%左右。对固溶态组织进行热等静压处理的工序安排有利于提高显微孔洞闭合作用,促进成分均匀化并显著提高合金高温持久寿命。
Development of microstructure and mechanical properties of a Ni-base single-crystal superalloy by hot-isostatic pressing
[J].
Synchrotron 3D μ-Tomography of Porosity during Hot Isostatic Pressing of a Single-Crystal Nickel-Base Superalloy
[J].
On the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Creep Life of a Single Crystal Superalloys
[J].
Very high cycle fatigue of Ni-based single-crystal superalloys at high temperature
[J].
Damage accumulation during creep deformation of a single crystal superalloy at 1150 C
[J].
Influence of temperature, pressure, and cooling rate during hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure of an SX Ni-base superalloy
[J].
Effect of carbon on the microstructure and creep property of a third generation single crystal nickle-based superalloy
[D].
碳对第三代镍基单晶高温合金组织和蠕变持久性能的影响
[D].
Compositional design considerations for microsegregation in single crystal superalloy systems
[J].
Strain accumulation and fatigue crack initiation at pores and carbides in a SX superalloy at room temperature
[J].
Fatigue crack initiation behavior at intermediate temperature under high stress amplitude for single crystal superalloy DD413
[J].The fatigue crack initiation behavior of a single crystal superalloy DD413 was investigated under high stress amplitude at intermediate temperature. The fracture surfaces and longitudinal section morphologies of the test specimens were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM). It was found that fatigue cracks mostly initiate from the cracked blocky carbides on the surface as well as the cracked skeleton-like carbides at subsurface. All the carbides on the surface of testing specimen crack due to the combined effect of oxidation and cyclic loading. Besides, at the subsurface of testing specimen, the carbides located on the propagation path of a micro-crack can crack as a result of oxidation and cyclic loading. The micro-crack connected to the surface in the specimen is the transportation channel of oxygen for the oxidation of the carbides at the subsurface. Carbides cracked and the micro-crack initiated at the early stage of fatigue, which induced the final failure.
第一代单晶高温合金中温高应力幅下的疲劳裂纹萌生行为
[J].通过应力控制的疲劳实验探究第一代镍基单晶高温合金DD413在中温(760℃)高应力幅下的疲劳裂纹萌生行为,并使用扫描电子显微镜观察和表征了疲劳样品的断口形貌和纵截面的显微组织。结果表明:在高应力幅条件下,疲劳裂纹主要萌生于表面开裂的块状碳化物和次表面开裂的骨架状碳化物。在疲劳过程中,氧化和循环加载的共同作用使样品表面的碳化物都发生了开裂。在样品的次表面,只有位于表面微裂纹扩展路径上的碳化物发生开裂,其原因也与氧化和循环加载有关。样品表面产生的微裂纹,是次表面碳化物发生氧化所需氧气的运输通道。在疲劳的早期阶段碳化物即发生开裂并产生微裂纹,最终使样品发生疲劳断裂。
On the role of carbides during the recrystallization of a directionally solidified nickel-base superalloy
[J].
Model for the porosity growth in single-crystal nickel-base superalloys during homogenization
[J].
Effect of section size and solution treatment on micropore of a third-generation single crystal superalloy DD33
[J].The effect of section size and solution treatment process on micropore of a nickel-based single crystal superalloy DD33 was investigated by optical microscope (OM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that the primary dendrite arm spacing and the volume fraction of eutectics increase with the increasing of section size in the as-cast alloys. Solidification micropores occur at locations near the eutectic. The volume fraction of solidification micropores increases slightly with the increasing of section size. After the same solution treatment for alloys, the volume fractions of residual eutectics and micropores increase with the increasing of section size. Under the condition of the same section size, the volume fraction of micropores increases with the increasing of solution temperature. The formation of internal micropores is due to the Kirkendall effect induced by imbalanced diffusion of the elements during solution treatment. The different section sizes of castings lead to the different segregation degrees, which results in the different volume fractions of the homogenization micropores. According to the evolution of microstructure of the blade, the appropriate solution treatment process was designed and then verified experimentally.
截面尺寸和固溶制度对单晶高温合金DD33中显微孔洞的影响
[J].研究了截面尺寸和固溶制度对DD33单晶高温合金中显微孔洞的影响。结果表明:随着截面尺寸的增大铸态合金的枝晶间距增大,共晶的含量提高。合金中的铸态微孔存在于共晶附近,其体积分数随着截面尺寸的增大稍有提高。在固溶制度相同的条件下,随着截面尺寸的增大残余共晶的含量和微孔的体积分数增加。当截面尺寸相同时,随着固溶温度的升高微孔体积分数增加。在固溶处理过程中各元素的不平衡扩散产生的Kirkendall效应导致合金内部固溶微孔的产生,不同截面尺寸造成组织偏析程度的不同是截面尺寸影响固溶微孔体积分数的主要原因。根据叶片的组织演化规律,给出了叶片固溶制度的设计方案并进行了实验验证。
Formation of solidification and homogenisation micropores in two single crystal superalloys produced by HRS and LMC processes
[J].
HRS和LMC工艺制备的两种镍基单晶高温合金铸态及固溶微孔的形成
[J].
Pore annihilation in a single-crystal nickel-base superalloy during hot isostatic pressing: Experiment and modelling
[J].
Creep anisotropy of a 3rd generation nickel-base single crystal superalloy at 850℃
[J].
Microstructural parameters controlling high-temperature creep life of the nickel-base single-crystal superalloy MC2
[J].
In situ 3D quantification of the evolution of creep cavity size, shape, and spatial orientation using synchrotron X-ray tomography
[J].
Effect of hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure and stress rupture properties of single crystal superalloy
[J].
热等静压对单晶高温合金组织和持久性能的影响
[J].
The influence of high thermal gradient casting, hot isostatic pressing and alternate heat treatment on the structure and properties of a single crystal nickel base superalloy
[A].