纤维素是天然可再生高分子材料,且无毒、可降解和价格低廉。因为化石能源短缺和化石燃料环境污染,开发和应用纤维素可再生材料极为重要。纤维素的结构中含有大量的羟基,具有一定的吸附能力但是吸附容量很低。对纤维素进行化学改性引入新的官能团,可显著提高其吸附性能[1~4]。将纤维素的尺寸降低到纳米级,也称为纳米纤维素(NC),可增大其长径比和比表面积,使其吸附性能提高[5,6]。对纤维素进行化学或物理处理,可得到纳米纤维素(至少有一维尺寸达到纳米级)。与传统的纤维素相比,纳米纤维素具有高强度、高比表面积、高杨氏模量和长径比大等性能,是目前纤维素科学和技术领域中最具发展潜力的材料之一[7,8]。目前对纤维素吸附剂的研究比较多,但是对纳米纤维素吸附剂的研究比较少[9]。
制备纳米纤维素的常用方法,有机械法、酸解法和酶解法。其中机械法能耗大,成本高;酸水解法对设备的要求苛刻,残留物难以回收和后处理;酶解法的效率不高,反应条件尚需优化。因此开发绿色高效的纳米纤维素制备方法,是该领域的研究热点。
1 实验方法
1.1 实验用原料
脱脂棉纤维素;离子液体为1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑硫酸氢盐([Bmim]HSO4)(熔点为28℃,纯度99%);丙烯酸、过硫酸钾、丙酰胺和无水乙醇,纯度99%以上。
1.2 纳米纤维素和纳米纤维吸附剂(AA/AM-g-NC)的制备
NC的制备:将1 g脱脂棉纤维和20 g离子液体 [Bmim]HSO4加入250 mL三口烧瓶中,将三口烧瓶置于100℃油浴锅中加热且均匀搅拌以使脱脂棉纤维完全溶胀、分散并水解,反应2 h后将纤维素溶液在温水浴中超声30 min,然后用无水乙醇和蒸馏水反复离心(2000 r/min)洗涤至中性。将洗涤后的纤维素均匀分散在超纯水(浓度在1%左右)中,放入高压细胞均质机中使其进一步超微细化。为了防止高压过程中的温度过高,实验在5℃的冷却水循环机中进行。高压均质后,取上清液分析备用。
AA/AM-g-NC的制备:将1 g脱脂棉纤维和适量的离子液体1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑硫酸氢盐([Bmim]HSO4)加入250 mL三口烧瓶中,将三口烧瓶置于100℃油浴锅中加热且均匀搅拌以使脱脂棉纤维完全溶胀并分散;将分散后的纤维素离子液体溶液的温度降至40~50℃,然后在N2保护下按比例加入一定质量的引发剂过硫酸钾,继续通N2并在匀速搅拌下加入一定比例的单体丙烯酰胺(AM)、80%中和度的丙烯酸(AA)和交联剂N,N-亚甲基双丙烯酰胺,继续反应3 h。反应结束后在离心机中用蒸馏水和无水乙醇或丙酮反复离心洗涤,并用丙酮作为溶剂索氏抽提去除均聚物;随后将抽提后的纤维素基接枝共聚物(记为AA/AM-g-Ce)均匀分散在超纯水中,形成均匀的水相分散液(浓度在1%~2%左右)。将分散液放入高压细胞均质机中,利用匀质机内的匀质阀突然失压形成的空穴效应和高速冲击,使悬浮液进一步超微细化。为了防止高压过程中温度过高,实验在5℃的冷却水循环机中进行。高压均质后即可得到纳米纤维素基接枝共聚物胶体溶液,将其冷冻干燥后得到纳米纤维素吸附剂,记为AA/AM-g-NC。
1.3 产物的表征
用超高分辨率场发射扫描电镜(XL-30,Philips-FEI公司)和场发射透射电子显微镜(Tecnai G2 F20对S-TWIN 200kV,Philips-FEI公司)分析产物的微观形貌和尺寸;将干燥的Ce、NC、AA/AM-g-NC分别与KBr按一定比例混合,在玛瑙研钵中精细研磨后挤压成圆盘状。在分析前,将其置于70℃烤箱中干燥10 min。用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Nicolet is5,赛默飞公司)分析产物的官能团,设定扫描范围为400~4000 cm -1;用元素分析仪(2400系列II型CHNS/O)定量测定NC、AA/AM-g-NC样品中C、H、N和O各元素的含量;使用X射线粉末光衍射仪(X'Pert Pro MPD)对样品进行扫描分析;用X-射线光电子能谱(Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250 X,Thermo Fisher Scientific 公司)测定样品表面的化学组分。
1.4 纳米纤维素吸附剂吸附性能的表征
以亚甲基蓝溶液为吸附质,用静态吸附试验测定AA/AM -g-NC的吸附性能。将50 mL浓度为20 mg/L的亚甲基蓝溶液放入锥形瓶中,投加0.02 g吸附剂AA/AM-g-NC后置于恒温振荡床中在一定温度和转速条件下震荡一段时间。反应结束后取适量的上清液用紫外可见分光光度计测定亚甲基蓝吸光度(λ=664 nm),用亚甲基蓝的工作曲线计算其浓度并计算吸附剂的吸附容量。
去除率为:
平衡吸附容量为:
式中Ce为吸附前亚甲基蓝的质量浓度(mg/L),C0为吸附后亚甲基蓝的质量浓度(mg/L),V为亚甲基蓝溶液的体积(L),X为AA/AM-g-NC的用量(g)。
2 实验结果和分析
2.1 纳米纤维素吸附剂的形貌和组成
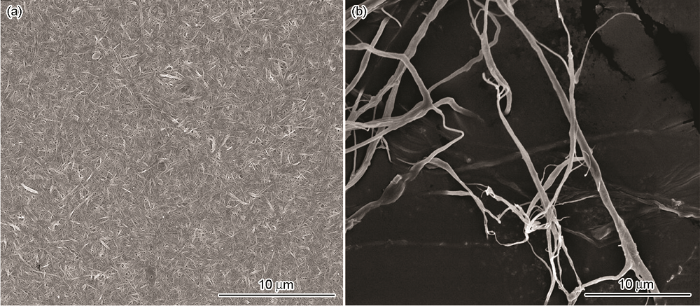
图1
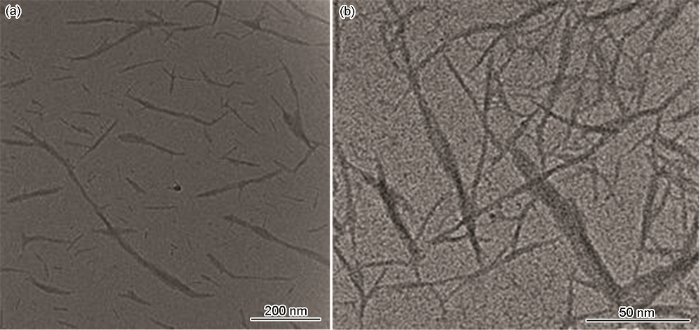
图2
图3
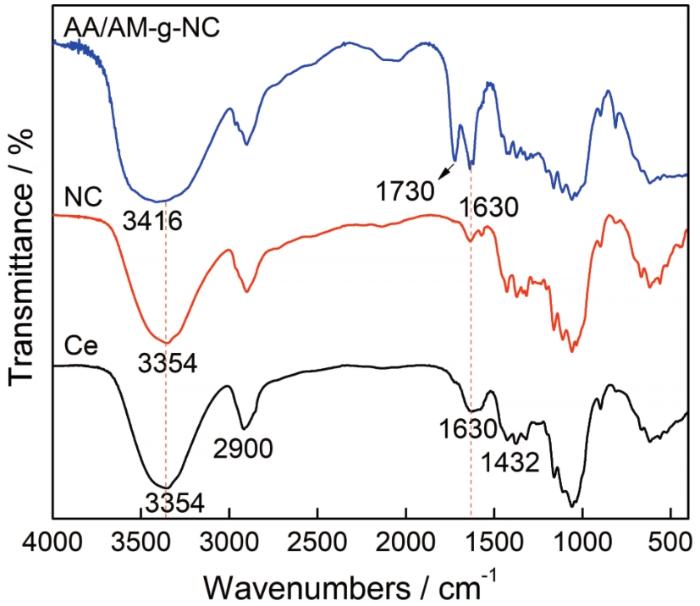
图4
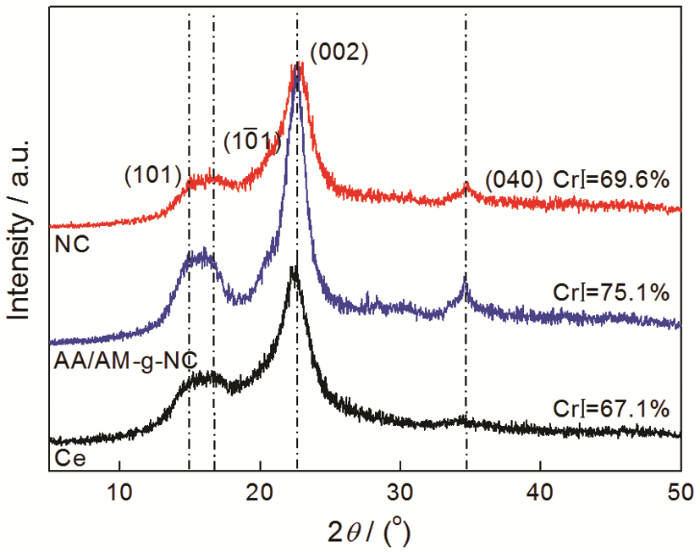
图5
图5
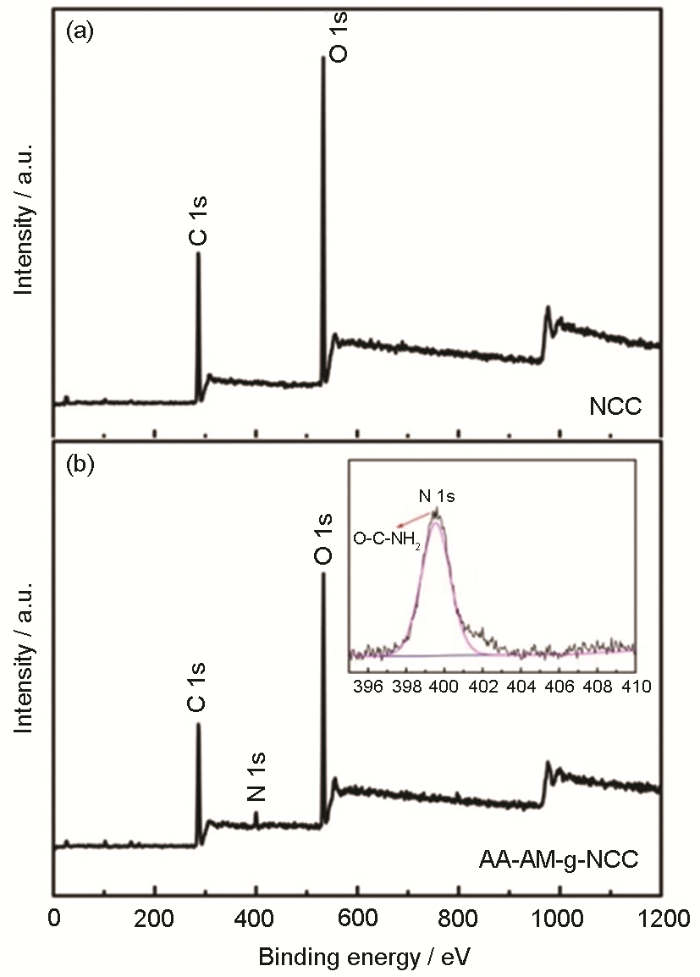
纳米纤维素NC和AA/AM -g-NC的XPS图谱以及N1s的高分辨图谱
Fig.5
XPS survey spectra of NC (a) and AA/AM-g-NC (b) and XPS survey scan of N1s core level (b inserted)
图6
图6
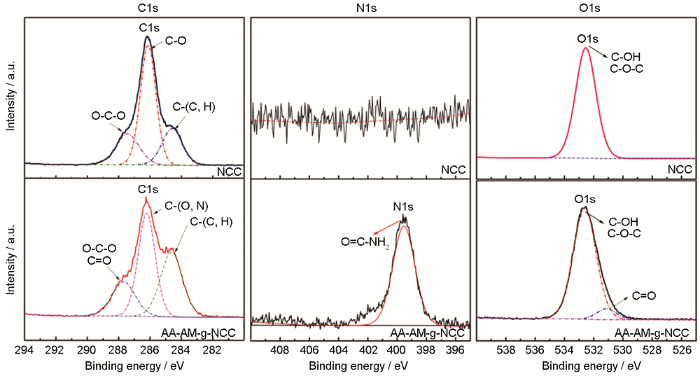
NC和AA/AM-g-NC处理后C1s、N1s和O1s的XPS图谱
Fig.6
XPS survey of C1s, N1s and O1s of NC and AA/AM-g-NC
图6给出了 C1s、O1s及N1s的高分辨图谱。NC及吸附剂上的C有三种类型[15]:一种是与C或H连接的C,即C-(C,H),其电子结合能为284.6 eV;第二种为与O或N连接的C,即C-O或C-N,其电子结合能为286 eV;第三种是连接两个O的C,即O-C-O或C=O,其电子结合能为287.7 eV。在O1s的高分辨图谱中,NC中的O主要来自C-O单键,即HO-C和C-O-C,其结合能为532.6 eV;而吸附剂AA/AM-g-NC中的O有两种类型:1) C-O单键,结合能为532.6 eV;2) C=O双键,结合能为531.2 eV,主要来自丙烯酸及丙烯酰胺的酯基。吸附剂AA/AM-g-NC表面的N元素,主要来源于接枝的单体丙烯酰胺中的氨基(-NH2),其结合能为399.6 eV。XPS结果表明,吸附剂表面有羧基及氨基基团。
表1 NC和 AA/AM -g-NC元素含量
Table 1
| Sample | O/% | C/% | H/% | N/% |
| NC | 51.24 | 42.65 | 6.02 | 0.37 |
| AA/AM-g-NC | 46.21 | 44.07 | 6.09 | 3.13 |
表2 Ce、NC和AA/AM-g-NC的吸附参数
Table 2
| Sample | Parameters of pore structure | ||
| Surface area/m2·g-1 | Pore volume /cm3·g-1 | Average pore size /nm | |
| Ce | 3.390 | 0.0036 | 6.047 |
| NC | 13.04 | 0.013 | 4.010 |
| AA/AM-g-NC | 12.95 | 0.019 | 5.834 |
2.2 纳米纤维素吸附剂AA/AM -g-NC的吸附性能
2.2.1 AA/AM-g-NC对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能
图7
图7
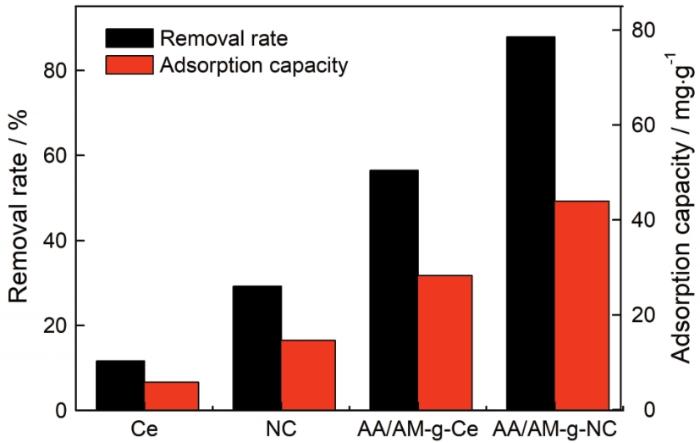
Ce、NC、AA/AM-g-Ce和AA/AM-g-NC对亚甲基蓝的去除率和吸附容量对比
Fig.7
Comparison of remove rate and adsorption capacity of methylene blue on Ce, NC, AA/AM-g-Ce and AA/AM-g-NC. Adsorption conditions: pH,10; MB initial concentration, 20 mg/L; adsorption time, 2 h; adsorption temperature, room temperature
此外,与文献中的纳米纤维素吸附剂相比(表3),改性后的AA/AM-g-NC对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能也表现出一定的优势。
表3 与文献中纳米纤维素吸附剂对亚甲基蓝吸附性能的比较
Table 3
2.2.2 溶液pH值对吸附性能的影响
图8
图8
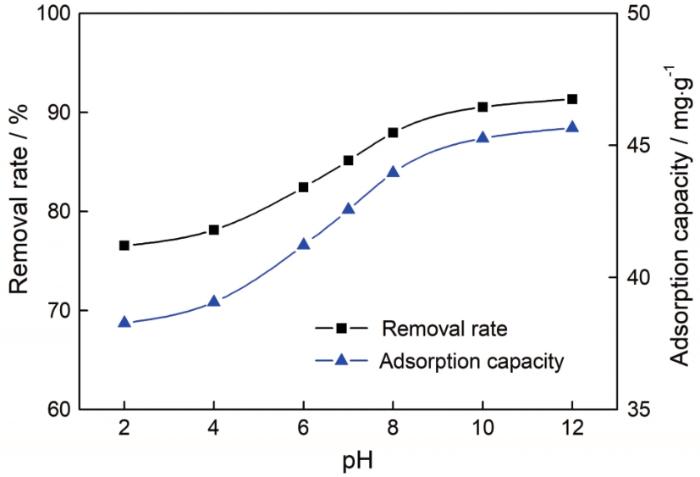
pH值对AA/AM-g-NC吸附性能的影响
Fig.8
Effect of pH on the adsorption properties of AA/AM-g-NC. Adsorption conditions: MB initial con-centration, 20 mg/L; adsorption time, 2 h; adsorption temperature, room temperature
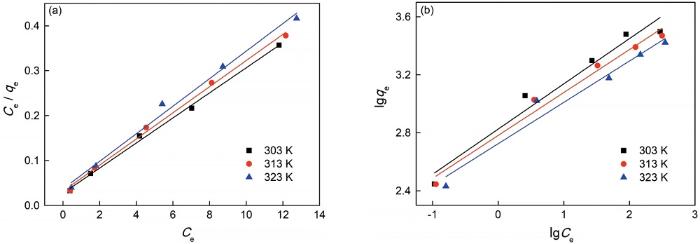
2.2.3 Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温式 使用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温式[19]
图9
图9
Langmuir及Freundlich方程拟合图
Fig.9
Langumuir (a) and Freundlich (b) equation fitting
表4 拟合的Langmuir和Freundlich参数
Table 4
| Temperature/K | Langmuir parameters | Freundlich parameters | ||||
| Q0/mg·g-1 | b/L·mg-1 | R2 | K | 1/n | R2 | |
| 303 | 35.84 | 0.982 | 0.996 | 16.87 | 0.311 | 0.981 |
| 313 | 34.36 | 0.915 | 0.995 | 16.15 | 0.296 | 0.990 |
| 323 | 32.57 | 0.829 | 0.988 | 15.25 | 0.284 | 0.981 |
可以看出,Langmuir吸附等温模型在三个温度的相关系数R2均高于Freundlich吸附等温模型,且根据Langmuir等温吸附模型计算出的最大吸附量Q0与实验测得的最大吸附容量qe的一致性很好。这表明,纳米纤维素吸附剂对亚甲基蓝的吸附符合Langmuir等温吸附模型,对亚甲基蓝在吸附剂表面发生的是单分子层吸附。
式中,b为Langmuir参数(L/mol),ΔH为焓变(kJ/mol),R为气体参数(8.314 J/(mol·K)),T为吸附温度(K),ΔG为自由能的变化(kJ/mol),ΔS为熵变(kJ/(mol·K))。
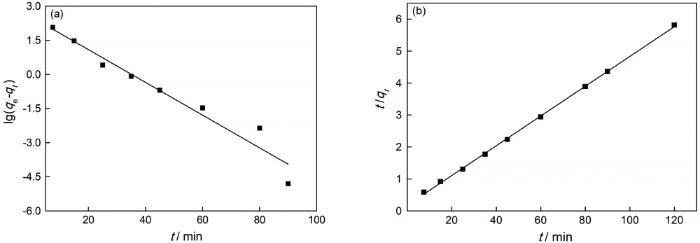
使用准一级动力学方程
和准二级动力学方程
表5 热力学参数
Table 5
| Temperature/K | △G/kJ·mol-1 | △S/J·(mol·K)-1 | △H/kJ·mol-1 |
| 303 | -0.0459 | -0.0225 | -6.876 |
| 313 | -0.232 | -0.0212 | |
| 323 | -0.505 | -0.0197 |
2.2.5 吸附动力学
图10
图10
准一级动力学和准二级动力学拟合曲线
Fig.10
Fitting curves of Pseudo-first-order (a) and Pseudo-second-order (b)
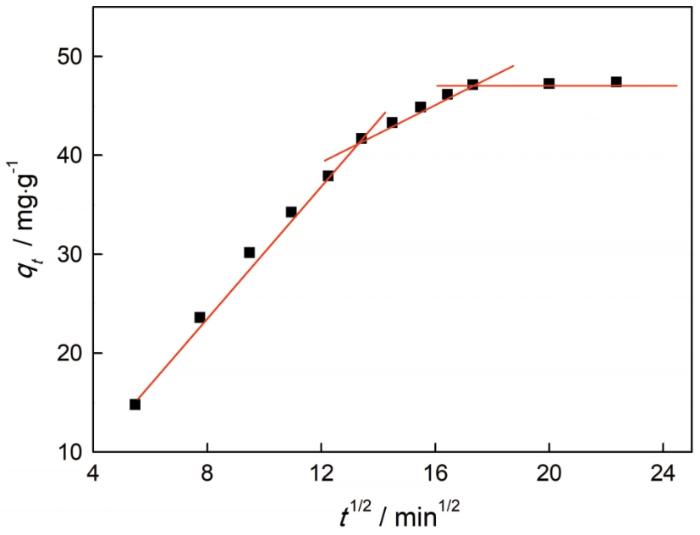
图11
表6 吸附过程的动力学参数
Table 6
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic model | Pseudo-second-order kinetic model | ||||
| k1 | qe | R2 | k2 | qe | R2 |
| 0.030 | 56.02 | 0.935 | 0.0012 | 48.92 | 0.999 |
3 结论
(1) 以脱脂棉纤维素为原料、以丙烯酸AA和丙烯酰胺AM为接枝单体,在离子液体[Bmim]HSO4中对纤维素进行水解及接枝改性,然后对其进行高压均质处理,可制备出纳米纤维素吸附剂AA/AM-g-NC。对脱脂棉进行离子液体辅助高压均质处理后得到纤丝网状结构的纳米纤维素吸附剂AA/AM-g-NC,其表面接有AM及AA的官能团,纤维素的晶型没有改变,结晶度有所提高。
(2) 纳米纤维素吸附剂AA/AM-g-NC对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能受pH值的影响,碱性条件有利于吸附剂的吸附;对亚甲基蓝的吸附符合Langmuir吸附等温式,为单分子层吸附;吸附过程为放热反应,升温不利于AA/AM-g-NC对亚甲基蓝的吸附。吸附在自发有利的条件下进行,吸附过程为固/液相界面的分子运动趋于稳定的熵减少过程;吸附过程符合准二级动力学模型。对亚甲基蓝的吸附,受控于颗粒内扩散和表面扩散。
参考文献
Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review
[J].A number of industries currently produce varying concentrations of heavy metal laden waste streams with significant consequences for any receiving environmental compartment. In recent years, increasing emphasis has been placed on environmental impact minimisation and resulting from this the range and capability of natural and prepared materials capable of heavy metal removal has seen steady development. In particular considerable work has been carried out on the use of both natural materials and their modifications. These natural materials, in many instances are relatively cheap, abundant in supply and have significant potential for modification and ultimately enhancement of their adsorption capabilities. This review paper reviews the current state of research on the use of the naturally occurring material cellulose, its modified forms and their efficacy as adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from waste streams. Adsorbents based on direct modification of cellulose are evaluated initially and subsequently modifications resulting from the grafting of selected monomers to the cellulose backbone with subsequent functionalisation are assessed. The heavy metal adsorption capacities for these modified cellulose materials were found to be significant and levels of uptake were comparable, in many instances, to both other naturally occurring adsorbent materials and commercial ion exchange type resins. Many of the modified cellulose adsorbents proved regenerable and re-usable over a number of adsorption/desorption cycles allowing recovery of the adsorbed heavy metal in a more concentrated form.
A modified cellulose adsorbent for the removal of nickel(II) from aqueous solutions
[J].
Removal of organic pollutants from water by modified cellulose fibres
[J].
Surface modification of cellulose by PCL grafts
[J].
Adhesion and surface issues in cellulose and nanocellulose
[J].
Cellulose nanocrystals and related Nanocomposites: Review of some properties and challenges
[J].
Research progress in stimuli-responsive functional materials based on cellulose nanocrystals
[J].
基于纤维素纳米晶体的刺激响应功能材料的研究进展
[J].
Preparation of nanocellulose: a review
[J].
Functionalization of nanocrystalline cellulose for decontamination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous system: computational modeling approach
[J].
Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids
[J].We report here initial results that demonstrate that cellulose can be dissolved without activation or pretreatment in, and regenerated from, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and other hydrophilic ionic liquids. This may enable the application of ionic liquids as alternatives to environmentally undesirable solvents currently used for dissolution of this important bioresource.
Dissolution and regeneration of cellulose and development in processing cellulose-based materials with ionic liquids
[J].
离子液体中的纤维素溶解、再生及材料制备研究进展
[J].
Effect of surface modification and hybridization of uhmwpe fibers on performance of their composites with epoxy resin
[J].
表面改性和混杂对超高分子量聚乙烯纤维/环氧树脂复合材料性能的影响
[J].
Preparation and water absorption/retention properties of coconut husk powders/ poly (acrylic acid-co-acryl amide) hybrid superabsorbent
[J].
椰糠粉/聚丙烯酸-丙烯酰胺复合吸水材料的制备及其吸保水性能
[J].
Homogeneous isolation of nanocellulose from cotton cellulose by high pressure homogenization
[J].
An experimental investigation of modified and unmodified flax fibres with XPS, ToF-SIMS and ATR-FTIR
[J].
Study of adsorption of Janus Green B and methylene blue on nanocrystalline cellulose
[J].
Cellulose nanocrystal-alginate hydrogel beads as novel adsorbents for organic dyes in aqueous solutions
[J].
Novel cellulose nanowhiskers-based polyurethane foam for rapid and persistent removal of methylene blue from its aqueous solutions
[J].
Uranium sorption by glutamate glucall: A modified chitosan part I: Equilibrium studies
[J].
Adsorption of trivalent chromium from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon
[J].
Removal of phenols from effluents by fly ash
[J].
Biosorption of copper(II) and lead(II) from aqueous solution by chaff in a fixed-bed column
[J].In this article, the ability of chaff to adsorb heavy metal ions from aqueous solution was investigated in a fixed-bed column. The effect of important parameters, such as the value of pH, the flow rate, the influent concentration of solution and the effect of coexistence ions, was studied. Also the adsorption/desorption recycles of chaff were shown, and the results indicated that chaff could be recycled to remove heavy metal ions. The Thomas model was applied to adsorption of copper and lead at different flow rate and different influent concentration to predict the breakthrough curves and to determine the characteristic parameters of the column useful for process design. The model was found suitable for describing the biosorption process of the dynamic behavior of the chaff column. All the results suggested that chaff as adsorbent to removal heavy metal ions from solution prove efficient, and the rate of biosorption process is speedy. Furthermore, the efficiency of adsorption is high. When the flow rate was 3.6 ml min(-1) and the influent concentration of copper and lead was 14.82 mg l(-1) and 50.12 mg l(-1) respectively, the equilibrium adsorption biomass reached 1.98 mg g(-1) and 6.72 mg g(-1), respectively. The competitive adsorption for lead and copper was studied. Moreover the total adsorbing capability of chaff did not decrease when there were both copper(II) and lead(II) in solution.
Removal of Fe(II) ions from aqueous solution by Calabrian pine bark wastes
[J].The ability of Calabrian pine bark wastes (Pinus brutia Ten) for the removal of Fe(II) ions from aqueous solution at different concentrations and temperatures at a fixed pH was investigated. While the amounts of Fe(II) ions adsorbed onto the bark increased with increasing concentration, it increased slightly with increasing the temperature. Kinetics studies showed that adsorption process followed the first-order kinetic model as well as intra-particle diffusion kinetics. Adsorption isotherm followed both Langmuir and Freundlich models. And it was determined that the adsorption was favorable from a dimensionless factor, R(L). Furthermore, the thermodynamic parameters demonstrated that the removal of Fe(II) by the bark was a physical process.
Removal of copper from aqueous solution by aminated and protonated mesoporous aluminas: kinetics and equilibrium
[J].A novel adsorbent, aminated and protonated mesoporous alumina, was prepared and employed for the removal of copper from aqueous solution at concentrations between 5 and 30 mg/l, in batch equilibrium experiments, in order to determine its adsorption properties. The removal of copper by the adsorbents increases with increasing adsorbent dosages. The adsorption mechanism is assumed to be an ion exchange between copper and the hydrogen ions present on the surface of the mesoporous alumina. The adsorbent was characterized by XRD, TEM, SEM, and BET methods. The sorption data have been analyzed and fitted to linearized adsorption isotherm of the Freundlich, Langmuir, and Redlich-Peterson models. The batch sorption kinetics have been tested for first-order, pseudo-first-order, and pseudo-second-order kinetic reaction models. The rate constants of adsorption for all these kinetic models have been calculated. Results also showed that the intraparticle diffusion of Cu(II) on the mesoporous catalyst was the main rate-limiting step.
Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) onto a grafted silica: isotherms and kinetic model
[J].
Transition from bioinert to bioactive material by tailoring the biological cell response to carboxylated nanocellulose
[J].
Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk
[J].