开展 EB 炉熔炼大规格铸态扁锭轧制工艺研究,是直接轧制大规格钛合金铸锭的前提。因此,有必要研究EB炉熔炼TC4钛合金的热变形行为。本文对EB炉熔炼的TC4钛合金进行高温热模拟压缩实验,研究变形温度为850~1100℃、应变速率为0.01~10 s-1条件下的热变形行为并绘制热加工图。
1 实验方法
用EB炉熔炼TC4钛合金,用连续升温金相法测定相转变温度约为995±5℃。在Gleeble-3800实验机上进行热模拟压缩实验,试样的直径为8 mm长度为12 mm。热模拟压缩实验温度为850,900,950,1000,1050,1100℃;应变速率为0.01,0.1,1.0,10 s-1;变形量为50%。加热到设定温度后保温3 min,压缩变形后水冷。用金相显微镜和扫描电子显微镜观察的不同条件变形后的显微组织。
2 实验结果
2.1 真应力-真应变曲线
图1
图1
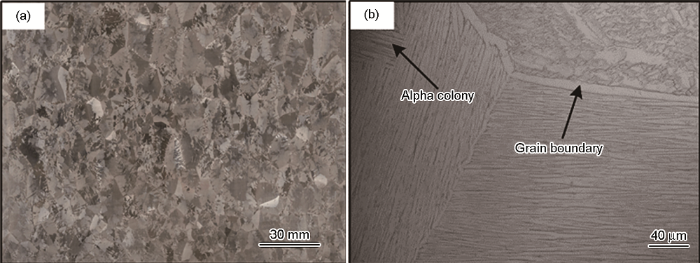
TC4钛合金原始铸锭的低倍组织和原始显微组织
Fig.1
Macroscopic structure (a) and original structure (b) of TC4钛合金
图2
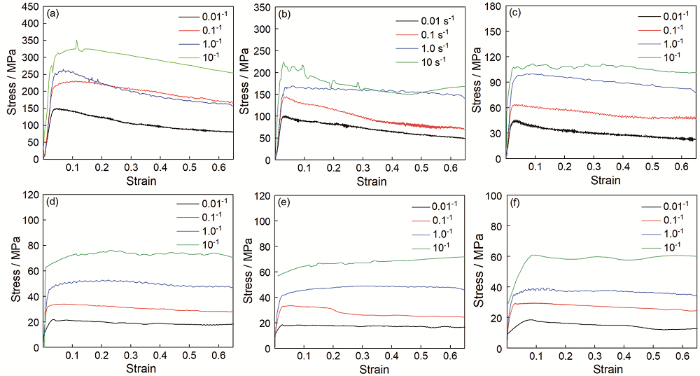
图2
在不同温度和应变速率条件下的真应力真应变曲线
Fig.2
True stress and true strain curves (a) 850℃, (b) 900℃, (c) 950℃, (d) 1000℃, (e) 1050℃, (f) 1100℃
图3
图3
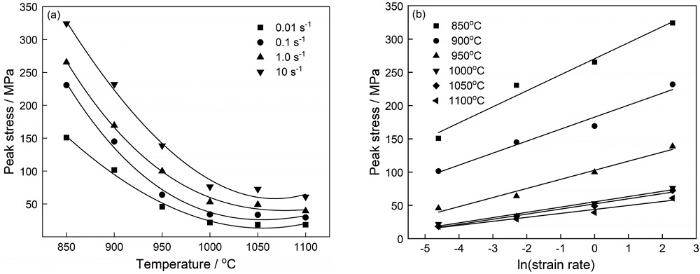
高温压缩变形峰值应力与变形温度和应变速率的关系
Fig.3
Dependence of peak stress on temperature and strain rate (a) T-
2.2 本构关系和变形激活能
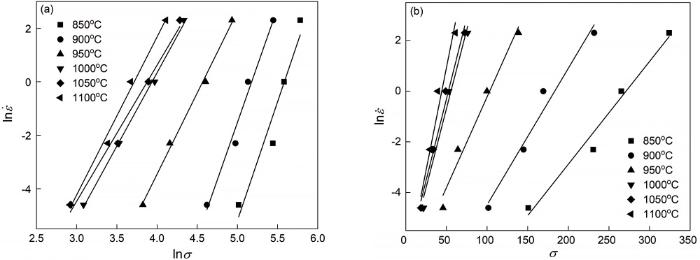
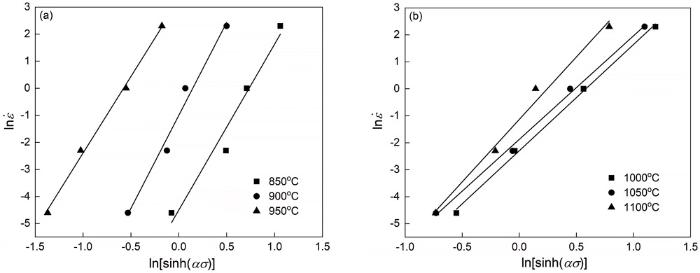
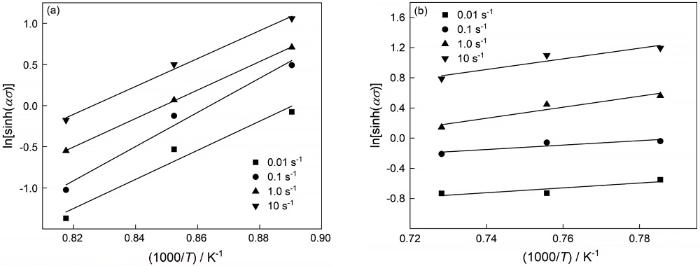
Arrhenius方程也称为材料的力学本构关系,是对多种回归模型总结改进的结果,能准确反映热变形过程中变形参数与流变应力的关系[15]。Arrhenius方程有三种表达形式:在低应力下应变速率与应力呈幂函数关系,如
其中
对
图4
图5
图6
图6
高温压缩变形峰值应力与变形温度的关系
Fig.6
Relationship between hot compression deformation peak stress and deformation temperature
图7
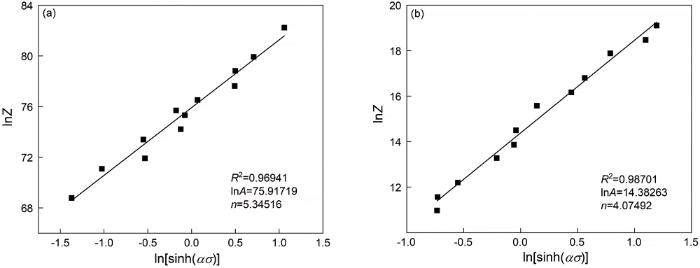
将上述所求参数代入双曲正弦型本构方程,即可得到(α+β)两相区和β单相区的本构模型。
(α+β)两相区:
β单相区:
2.3 本构模型的误差
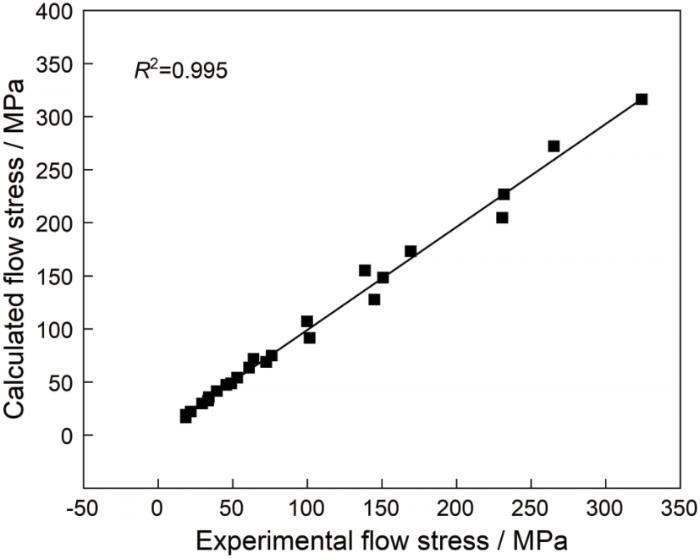
式中σe为流变应力的实验值,σp为利用本构方程计算得出的预测值,N为实验分析得数据点个数(N=24)。可计算出AARE=5.04%。以上分析均表明,所建立的本构模型预测电子束冷床熔炼TC4钛合金的流变应力具有较高的精度,可用于预测其热变形流变应力。
图8
图8
根据本构关系流变应力的预测值与实验值的相关性
Fig.8
Correlation between the experimental and predicted flow stress data by the constitutive equation
2.4 加工图和显微组织
基于动态材料模型(DMM)的热加工图由功率耗散图和失稳图叠加而成,反映变形参数对加工性能的影响[20]。在材料的成形过程中显微组织演变消耗的能量J与线性耗散能量Jm的比例关系,可用功率耗散指数表示。定义为
其中m为应变速率敏感指数,Jm为线性耗散能量。
在动态材料模型中,加工失稳的判据
是根据Prasad失稳判据建立的。由
图9
图9
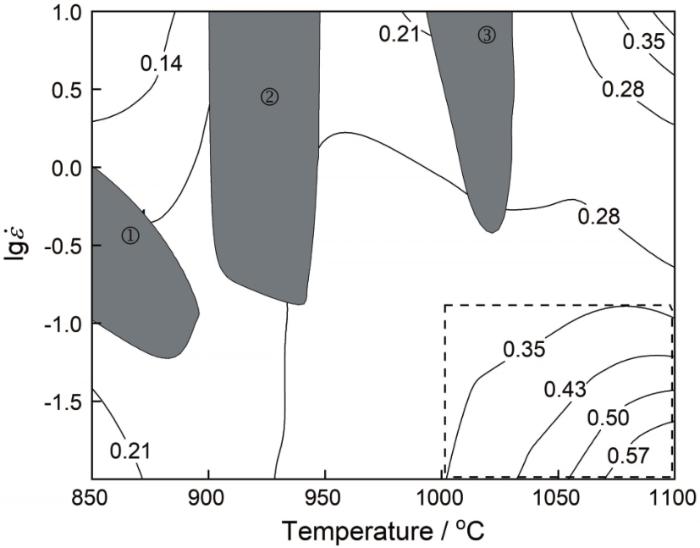
EB炉熔炼TC4钛合金的开坯轧制加工图
Fig.9
Processing maps for primary rolling of TC4 titanium alloy by EBCHM
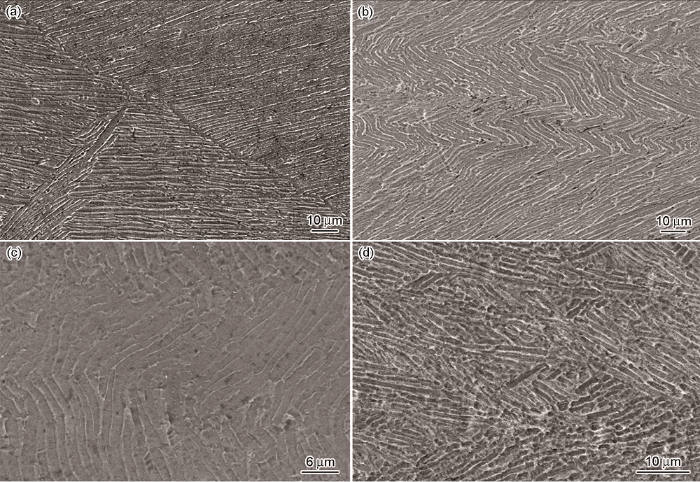
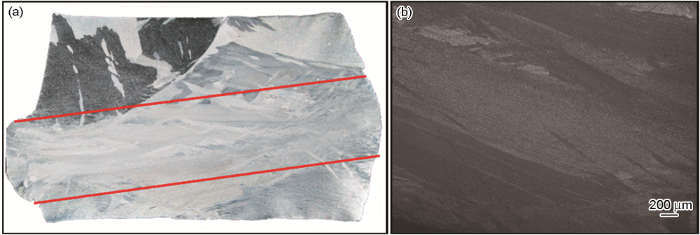
在电子束冷床熔炼TC4钛合金的热加工图中,灰色部分为塑性失稳区①、②、③,在该区域内不适宜加工变形。图10a给出了变形条件为850℃、0.1s-1时的显微组织。可以看出,原始连续的片层组织出现了断裂分离的现象;图10b给出了变形条件为850℃、1.0 s-1时显微组织对应的失稳区域①。可以看出:在此变形条件下片层组织发生了大面积的弯折;随着变形温度的升高,薄片状的扭折趋势相对减弱。图10c给出了变形条件为950℃、1.0 s-1时显微组织对应的失稳区域②。可以看出,部分片层α相发生了弯折,是变形的不均匀和组织的均匀性较低所致。图11给出了变形条件为950℃、10 s-1时的宏观照片。可以看出,在此条件下试样变形后出现了45°剪切,是变形不均匀而产生了局部流动。加工图中的红色虚线区域为适宜的加工区,功率耗散因子值为0.35-0.57,大部分能量用于显微组织的转变。图10d给出了变形条件为1100℃、0.01 s-1对应的显微组织。因其变形温度高,应变速率小,显微组织为片层组织和等轴组织的混合组织,使合金具有良好的综合性能。
图10
图10
不同变形条件下TC4钛合金的微观组织
Fig.10
Microstructures of TC4 titanium alloy under different deformation (a) 850℃, 0.1 s-1; (b) 850℃, 1.0 s-1; (c) 950℃, 1.0 s-1 (d) 1100℃, 0.01 s-1
图11
图11
在950℃、10 s-1条件下变形后合金的宏观和微观照片
Fig.11
Macro photos and microstructures of the specimens under 950℃、10 s-1
综上结果,可得电子束冷床熔炼TC4钛合金的热加工变形条件。塑性失稳区:变形温度850~900℃、应变速率0.1~1 s-1;900~950℃、0.13~10 s-1;1000~1025℃、0.3~10 s-1;适宜的加工区域:变形温度1000℃⁓1100℃、应变速率0.01⁓0.1 s-1。
3 分析和讨论
表1 用不同熔炼方式制备的TC4钛合金的热变形激活能
Table 1
用EB炉熔炼与VAR熔炼制备的TC4钛合金铸锭有以下不同:(1)EB炉具有很好地精炼除杂效果,可去除高低密度夹杂物,得到细晶均质铸锭;(2)可省去VAR熔炼后的开坯锻造,直接进行扁锭轧制。其他研究得到的VAR熔炼TC4钛合金的铸态开坯热加工图表明,VAR熔炼TC4钛合金铸态开坯的塑性失稳区域集中分布在高温大应变量或高应变速率。其原因是,过高的变形温度产生热效应,使中心区域温度急剧升高从而出现魏氏组织;应变速率过高时金属流动较快,合金内部散热较慢,使显微组织过热。因此,在高温高应变速率下合金容易产生裂纹、绝热剪切带和局部金属流动等缺陷[10]。方刚等[23]提出,在低应变速率条件下功率耗散效率较高适宜加工,或在近β区进行高应变速率变形,在1000~1050℃、0.01 s-1区域为超塑性成形区;白娇娇等[10]提出,TC4钛合金的最佳加工范围为900~950℃、0.01~0.1 s-1,开坯锻造在两相区内进行;岳远旺等[24]由BP神经网络预测,TC4钛合金的热加工图指出最佳的加工区为1125~1260 K、0.01~0.06 s-1。EB炉熔炼TC4钛合金的塑性失稳区域为变形温度850~900℃、应变速率0.1-1 s-1,900~950℃、0.13~10 s-1,1000~1025℃、0.3~10 s-1,塑性失稳区集中在相对较高的应变速率。从显微组织可以看出,合金发生了片层弯折、片层折断以及局部流动。同时,低于相变温度时合金的功率耗散效率
4 结论
(1) 随着应变的增大TC4钛合金的流变应力迅速增大并达到峰值,随后逐渐降低并进入稳态阶段,真应力-真应变曲线呈现明显的动态回复形式。
(2) 基于Arrhenius模型和Z参数,分别计算出用电子束冷床熔炼的TC4钛合金在(α+β)两相区的热变形激活能Q(α+β)=746.334 kJ/mol和在β单相区的热变形激活能Qβ=177.841 kJ/mol。所建立的用EB炉熔炼的TC4钛合金在高温变形过程中的流变应力模型预测精度高,预测值与实验值的平均相对误差为5.04%,表明这个模型能很好地预测EB炉熔炼TC4钛合金在高温变形过程中的热变形行为。
(3) 用EB炉熔炼的TC4钛合金的适宜开坯轧制加工区域为:变形温度1000℃⁓1100℃、应变速率0.01⁓0.1 s-1。EB炉熔炼TC4钛合金应该在高于相变温度进行开坯轧制变形,并且其变形速率不能过高,在此区域加工后的组织为片层α和等轴α的混合组织。
参考文献
Failure and formability studies in warm deep drawing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
[J].
Discussion on economic analysis and decreasing cost process of titanium and titanium alloys
[J].
钛及钛合金材料经济性及低成本方法论述
[J].
Understanding the properties of low-cost iron-containing powder metallurgy titanium alloys
[J].
Development and application of aerial titanium and its alloys
[J].
航空用钛及钛合金的发展及应用
[J].
Status quo and development tendency on the research of low cost titanium alloy
[J].
低成本钛合金研究现状与发展趋势
[J].
High temperature deformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy and its flows stress model
[J].
TC4钛合金高温变形行为及其流动应力模型
[J].
Study on high temperature deformation behavior of HIP TC4 titanium alloy
[J].
热等静压态TC4钛合金高温变形行为研究
[J].
Hot working of commercial Ti-6Al-4V with an equiaxed α-β microstructure: Materials modeling considerations
[J].
Hot compressive deformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy
[J].
TC4钛合金热压变形行为的研究
[J].
High temperature compressive deformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy
[J].
TC4钛合金的高温压缩变形行为
[J].
Hot deformation behavior and low temperature superplasticity of rolled TC4 titanium alloy in the α+β phase field
[D].
轧制态TC4钛合金α+β两相区热变形行为及其低温超塑性研究
[D].
Study on the hot deformation behavior of TC4-DT alloy with equiaxed α+β starting structure based on processing map
[J].
Study on hot deformation behavior of titanium alloy by modified Arrhennius equation
[J].
基于修正的Arrhennius方程钛合金高温本构方程研究
[J].
A novel computational method of processing map for Ti-6Al-4V alloy and corresponding microstructure study
[J].
Constitutive equations for elevated temperature flow stress of Ti-6Al-4V alloy considering the effect of strain
[J].
Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy subjected to multi-pass warm rolled
[J].
稀有金属材料与工程
Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel
[J].
Hot deformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy with high-oxygen in β phase region
[J].
高氧TC4钛合金β相区变形行为研究
[J].
Predicted constitutive modeling of hot deformation for AZ31 magnesium alloy
[J].
Incoloy 800H高温变形流动应力预测模型
[J].
Hot compression deformation behavior and processing map of TA15 alloy
[J].
TA15钛合金高温热压缩变形行为及热加工图
[J].
Construction of processing maps based on expanded data by BP-ANN and identification of optimal deforming parameters for Ti-6Al-4V alloy
[J].
The study on the application of the improved constituive equation for titanium alloy in high speed milling
[D].
钛合金Ti-6A1-4V修正本构模型在高速铣削中的应用研究
[D].
Processing map of titanium alloy TC4 and its application for plate rolling analyses
[J].
TC4钛合金加工图及其在板材轧制工艺分析中的应用
[J].