研究金属柱壳在爆轰加载下的膨胀断裂行为,有十分重要的学术意义和应用价值。爆轰加载下的金属柱壳,其断裂呈现出拉伸断裂、纯剪切断裂、拉剪混合断裂等多种模式。许多学者对其断裂机理开展了研究。G. I. Taylor[1]最早建立了断裂模型,较好地描述了低爆压下柱壳的断裂行为。根据这个模型,拉伸型裂纹从外表起源,沿径向朝内壁方向发展并随着作用于内壁上的爆轰产物压力下降,最终贯穿从环向压应力状态变化到环向拉应力状态的壳壁内层, 形成贯穿断裂。C. R.Hoggatt [2]分析了高爆压下金属壳中的应力状态,认为较高的应变速率使金属柱壳呈现出剪切断裂模式。许多学者观察爆轰后的断裂碎片的宏观特征和用模拟计算等方法分析了金属柱壳的剪切断裂行为[3,4,5,6]以及在高爆压下金属柱壳的剪切断裂行为。但是,金属柱壳膨胀爆轰加载导致其断裂模式改变的因素较多。把其在高爆压下金属柱壳复杂的断裂行为简单地归因于应变速率效应,并不合适。金属材料的断裂,受诸多因素如温度、加载方式、材料性能、材料宏观尺寸以及微观结构等的影响 [7,8,9,10]。而在爆轰加载过程中各种条件又相互影响而发生改变,例如材料在动态加载下受到高压、高速冲击波的作用产生剧烈的动态响应产生孪生、位错及剪切带等变形组织[11,12,13]、以及高压相变结构[14]。这种结构的改变又引起应变率等其它条件的变化,从而影响材料的断裂行为[15]。因此,对比研究金属柱壳不同条件下的膨胀爆轰断裂行为并分析各种影响因素的作用机理,有利于揭示其本征断裂机理。
HR2钢是一种典型的抗氢脆奥氏体不锈钢,具有良好的综合力学性能、高温抗氧化性、良好的抗氢脆性能等,在工业和军事领域得到了广泛的应用[16]。本文选取不同壁厚的HR2钢柱壳进行爆轰加载实验,表征爆轰后断裂碎片的宏观形貌、断口微观形貌以及横截面的变形微观结构,对比研究不同壁厚的金属柱壳的变形结构及断裂模式,以揭示金属柱壳膨胀爆轰加载下的断裂机理、分析壁厚对金属柱壳断裂行为的影响。
1 实验方法
表1 HR2钢的化学成分
Table 1
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.04 | <1.00 | 8.00~10.00 | <0.025 | <0.015 | 5.50~8.00 | 19.00~21.50 | 0.20~0.34 |
图1
图1
HR2钢柱壳芯部和外表面的原始微观结构金相
Fig.1
Microstructure in the internal (a) and near the outer surface (b) of as-annealed HR2 steel cylinder
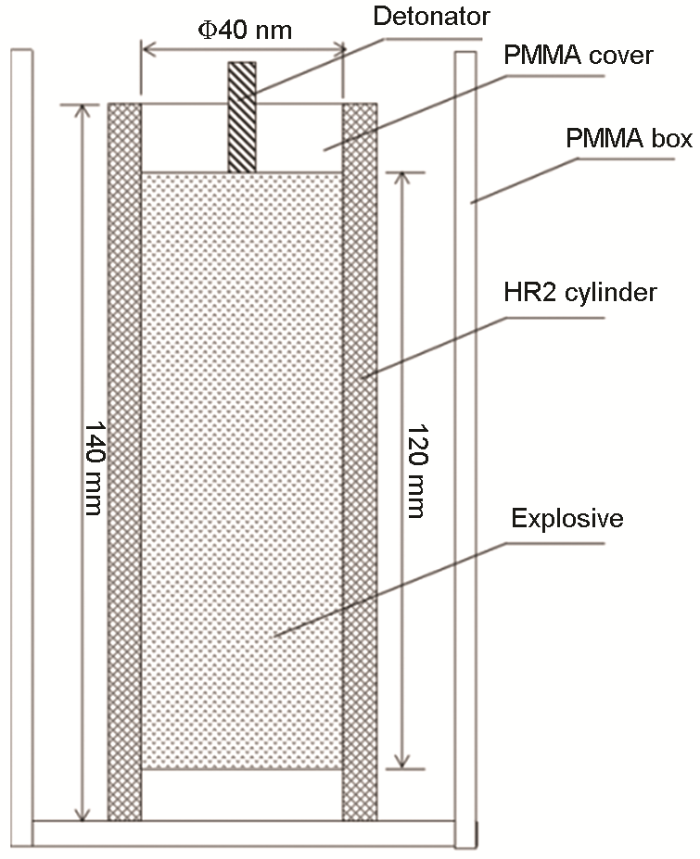
采用单点起爆进行HR2钢柱壳的膨胀爆轰实验,实验装置如图2所示。在炸药的一端插入雷管,然后通过点燃雷管来引爆炸药,炸药爆炸产生的爆轰波从炸药柱的一端传到另一端。不同厚度样品的炸药量相同,使爆压相同。爆轰实验中使用固体炸药TNT,炸药柱尺寸长120 mm,直径40 mm;雷管采用BL21,直径为7 mm;传爆药采用PETN,药柱长为5 mm,直径为20 mm;有机玻璃外套筒内径为82.4 mm,外径为86.4 mm,长为150 mm。为了得到爆轰后完整的断裂残片,在有机玻璃外套筒外用沙围住。HR2柱壳为140 mm,在起爆端有15 mm无TNT炸药,在底端有5 mm无TNT炸药,以区分爆炸后断裂碎片的方向。
图2
用FEI Nova NanoSEM 430场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察断口,用GX71金相显微镜和FEI F20透射电镜(TEM)表征断裂碎片的微观结构。采用电解双喷和离子减薄相结合的方法制备用于TEM分析的试样。使用MVK-H300显微硬度仪测量断裂碎片的硬度,采用维氏金刚石压头。
2 实验结果
HR2钢柱壳在爆轰加载后,对断裂碎片进行回收、称质量,与爆轰前柱壳的质量对比计算出HR2钢断裂碎片的回收率。薄壁柱壳的断裂碎片回收率为85%,厚壁柱壳的回收率为89%。轰加载后薄壁柱壳(6 mm)和厚壁柱壳(12 mm)分别减小为3.8 mm和7.5 mm,沿径向的压缩变形量分别为38%和37%,应变量近似相同。
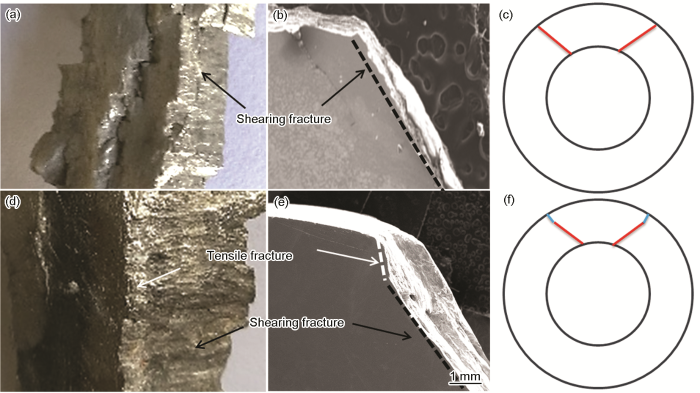
对HR2柱壳的断裂碎片宏观形貌的观察发现,薄壁柱壳的断裂碎片(图3a)窄而薄,宽度约为8~15 mm,断面较为平直,沿着与柱壳表面相倾斜的方向扩展。厚壁柱壳的断裂碎片(图3d)宽而厚,宽度约为20~30 mm,断面在内表面一侧与薄壁柱壳近似较为平直,沿与柱壳表面相倾斜的方向扩展,但是在近外表面处端口方向有明显的偏折。对断裂碎片的截面SEM形貌的(低倍)观察发现,薄壁柱壳(图3b)断裂碎片断面与表面呈近似45°夹角(图3b中的黑色虚线),为纯剪切断口。厚壁柱壳断裂碎片中(图3e)靠近外表面约1 mm的断口方向近似与柱壳表面垂直(图3e白色虚线),在柱壳内断口方向改变,与表面呈近似45°夹角(图3e黑色虚线),呈现出拉剪混合断口。在图3c和3f的示意图中,分别画出了薄壁柱壳与厚壁柱壳断口在金属柱壳壳壁中的扩展方向。
图3
图3
HR2钢柱薄壁和厚壁壳断裂碎片的宏观形貌、断口形貌和断裂模式示意图。
Fig.3
Macroscopic morphology (a), (d), fracture morphology (b), (e) of fracture fragments and the schematic diagram of fracture mode (c), (f) in thin-walled and thick-walled HR2 steel cylinder respectively
图4a给出了薄壁柱壳断裂碎片的横截面微观组织的典型形貌,可见晶粒发生了沿径向压缩变形,并且沿平行样品表面的方向拉长。在一些晶粒中出现了高密度的条带状变形组织,样品内部出现了贯穿多个晶粒的剪切带,并且在剪切带上形成了微裂纹(图4a黑色箭头)。大量观察结果表明,柱壳碎片内表面附近塑性变形更为严重,剪切带密度较高。在薄壁和厚壁柱壳碎片外表面均察到有表面裂纹形成,如图4b和4c所示,在薄壁样品的外表面裂纹沿剪切带方向扩展(图4b中的黑色箭头)。厚壁样品的变形微观结构与薄壁样品的类似,裂纹也是沿剪切带形核扩展(图4c黑色箭头),但是在其外表面出现了与样品表面近似垂直的拉伸裂纹,并且观察到裂纹两端呈现由拉伸断裂导致的颈缩形貌(图4c白色箭头)。这些结果表明,样品最外层发生了拉伸断裂,但是拉伸裂纹的扩展至样品内部转为沿剪切方向扩展,呈现出明显的外表拉伸裂纹,内侧剪切裂纹的拉剪混合形貌。
图4
图4
HR2钢柱壳爆轰加载后横截面的金相组织
Fig.4
Cross sectional observation of microscopic morphology inside the HR2 steel cylinder (a), near the outer surface (b) of thin-wall shell fragments and near the outer surface of thick-walled cylinder fragments after exploding
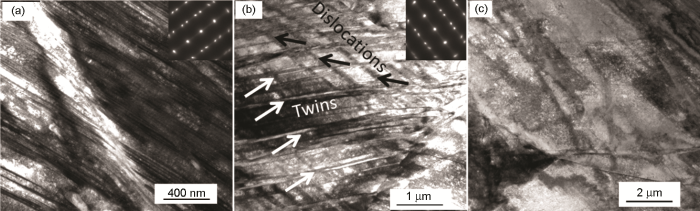
图5
图5
HR2钢薄壁柱壳爆轰加载后横截面微观结构。
Fig.5
Cross-section TEM images of nanoscaled twins (a), coarse twins (b) and dislocation structures (c) in the thin-walled HR2 steel cylinder after exploding
3 分析和讨论
3.1 断裂碎片横截面中的应变分布
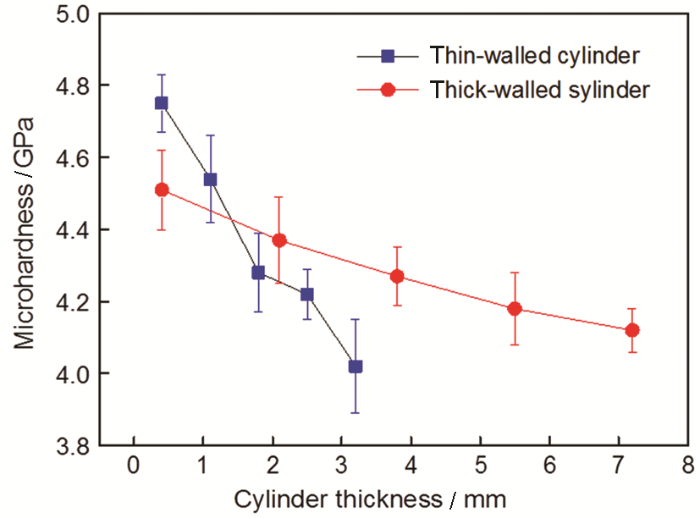
对断裂碎片的变形结构观察发现,碎片内表面附近的应变明显高于外表面附近。变形样品的硬度反映样品的塑性形变程度,为了得到样品中应变分布的定量信息,测量了断裂碎片截面沿径向的硬度。图6给出了薄壁柱壳和厚壁柱壳断裂碎片中硬度沿柱壳壁厚的分布曲线。可以看出,薄壁样品内表面附近的硬度高达4.74 GPa,厚壁样品的硬度4.54 GPa,低于薄壁样品。由内而外的硬度随着壁厚线性减小,薄壁样品的硬度减小得更快,厚壁样品硬度的变化较为平缓。外表面附近薄壁样品的硬度为4.09 GPa;厚壁样品的硬度为4.14 GPa,高于薄壁样品。对硬度的分析结果表明,爆轰加载后柱壳内的应变分布由内表面向外侧线性减小,应变的梯度随着壁厚的增大而降低。
图6
图6
HR2柱壳爆轰加载后硬度沿柱壳壁厚的分布
Fig.6
Hardness variation of the fracture fragments along radial direction
柱壳内壁外壁附近的压缩应变有明显的差别,两种样品的总压缩应变量相同,壳壁越薄应变梯度越大,因此薄壁样品内侧压缩应变大于厚壁样品,因此外侧的应变必然小于厚壁样品。导致这种应变的差的主要原因,是柱壳壳壁内各处的受力状态不同。在柱壳沿径向膨胀过程中,在整个壁厚范围内径向应力处于压缩状态,但是内侧样品受到外侧样品的约束沿径向的压应力更大,由内而外压应力逐渐减小,压应力沿柱壳径向线性减小。
3.2 HR2柱壳膨胀爆轰的断裂机理和厚度对断裂行为的影响
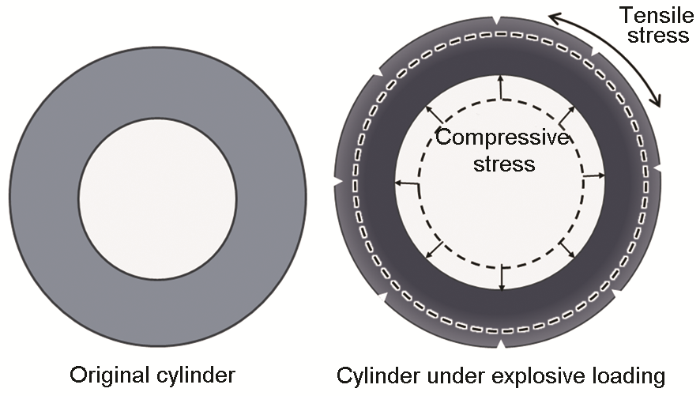
柱壳在膨胀过程中沿径向受到压应力(图7),沿径向发生剧烈的压缩变形。对断裂碎片微观结构的观察表明,不同的晶粒变形程度不同。剪切带出现在发生剧烈孪生变形并产生了高密度孪晶片层的晶粒中,纳米尺度的孪晶片层严重抑制了晶粒中的位错滑移,进一步的塑性变形不能由位错及孪生承担,因此沿应力最大的方向及剪切方向形成了剪切带。进一步的塑性变形主要由剪切带的继续变形和扩展承担,导致沿剪切带的应变集中,样品内部的微裂纹沿剪切带形核。因此,不论薄壁还是厚壁柱壳,在样品内部均观察到了大量沿剪切带分布的微裂纹。
图7
图7
柱壳膨胀爆轰加载下所受应力的示意图
Fig.7
The schematic diagram of compressive stress and tensile stress in an expansion cylinder
除受到径向的压应力外,柱壳的膨胀变形使其同时受到环向拉应力(图7)。在环向拉应力的作用下,在外表面形成拉伸裂纹。柱壳的断裂,实际上是剪切裂纹从样品内部剪切带形核并扩展和拉伸裂纹沿柱壳外表面的形核扩展的共同作用并竞争的结果。
柱壳的壁厚不同其应变分布不同,壁厚越大应变梯度越小。薄壁柱壳内侧的压缩应变明显大于厚壁柱壳,变形更为严重,高密度的剪切带及剪切裂纹迅速在样品内形核。薄壁的柱壳厚度更小,也有利于裂纹迅速扩展至外表面而断裂。因此,薄壁样品的膨胀断裂由样品内大量裂纹沿剪切带萌生主导,最终发生剪切断裂并且断裂碎片更多、更细小。
壁厚较大的柱壳在膨胀过程中,样品内部仍然会在径向压应力的作用下生成剪切裂纹。但是,由于厚度较大应变梯度较小,内侧应变比薄壁柱壳小,样品内部剪切带及剪切裂纹较少,形成较晚,并且样品较厚也延缓了剪切裂纹的扩展。而与样品内侧的情况相反,柱壳外侧样品的应变大于薄壁样品,其外表面拉伸断裂失稳的发生比薄壁样品更早,与柱壳内裂纹沿剪切带的形核同时发生,因此观察到了外表拉伸裂纹引起的拉伸断裂,使样品呈现出拉剪混合的断裂模式。
4 结论
(1) HR2钢爆轰加载后在柱壳内部生成了大量的剪切带,裂纹沿剪切带形核,而柱壳外侧既有沿剪切带形核的裂纹,又有沿样品外表面形核的拉伸裂纹。柱壳的断裂实际上是剪切裂纹从样品内部剪切带形核并扩展和裂纹沿柱壳外表面的形核扩展的共同作用并竞争的结果。
(2) 柱壳的塑形变形不均匀,由内壁至外沿柱壳厚度线性减少,壁厚增加应变梯度减小。
(3) 薄壁柱壳内侧压缩变形剧烈,断裂由样品内裂纹沿剪切带的形核及扩展主导,发生剪切断裂;而厚壁柱壳中内侧与薄壁柱壳类似,裂纹沿剪切带形核扩展,但是最外侧则为环向拉应力主导,发生拉伸断裂而表现出拉剪结合的断裂模式。
参考文献
The Fragmentation of Tubular Bombs
[A].
Fracture behavior of tubular bombs
[J].
Expansion of cylindrical shells subjected to internal explosive detonations
[J].Two explosively loaded cylindrical shell experiments were conducted to provide experimental data for benchmarking numerical codes. Each shell was subjected to internal high-explosive detonations, which caused it to expand outwardly at strain rates on the order of 104 s–1. At approximately 150 percent strain, multiple plastic instabilities appeared on the surface of these shells in a quasi-periodic pattem. These instabilities continued to develop into bands of localized shear and eventually formed cracks before causing the shell to fragment. Diagnostic equipment on these experiments included a Fabry-Perot interferometer and a fast-framing camera. The experiments and the data obtained from the diagnostic equipment are discussed and illustrated.]]>
Dynamic Fracture and Fragmentation
[J].
A numerical model for adiabatic shear bands with application to a thick-walled cylinder in 304 stainless steel
[J].
Strain-rate effects of expanding fracture of 45 steel cylinder shells driven by detonation, Expl
45钢柱壳膨胀断裂的应变率效应
[J].
Impact fracture behavior of X80 pipeline steel
[J].Pipeline steels have been widely used in a long-distance transportation of large amounts of crude oil or natural gas under high pressure due to their high transportation efficiency, low energy loss and production cost. For high pressure gas transmission pipelines made from high-strength steels an important problem is to know their fracture behavior in a long running process. In this paper, fracture toughness of X80 pipeline steel was measured by V-notch Charpy impact test at -20 and\linebreak -60 ℃. OM, SEM, EDS and EBSD were used to analyze its fracture mechanism. Experimental results show that the maximum impact load is slightly influenced by temperature, but with the decrease of temperature, crack forming work, crack propagating work and energy absorbed by crack arresting decrease significantly. During fracture process, the intensive tensile stress in the sample would induce the deformation bands formed around the fracture surface and grains elongated along the direction vertical to the main crack, but original austenite grain boundaries are hardly deformed, it would cause stress concentration and then produce intergranular fracture. Generally, brittle second phase particles could act as crack sources under intensive internal stress. In the crack propagation process, grains near the main crack are deformed and elongated tempestuously, resulting in their breaking and new grains with high angle grain boundary (HAGB) formed. Therefore, the grain size decreases and the fraction of HAGB increases in the crack propagation region. Temperature has great influence on the plastic deformation behavior of pipeline steel during facture process. At -20 ℃, the tested steel has good plasticity and the grains are refined during deformation, but at -60 ℃, they are difficult to deform and refine. Consequently, the grain size near crack propagation zones in the sample impacted at -20 ℃ is much smaller than the original grain size, but in -60 ℃ impacted sample the grain sizes has little difference.
X80厚规格X80 管线钢低温断裂行为研究
[J].采用金相显微镜和扫描电子显微镜对厚规格X80管线钢微观组织和-25℃落锤撕裂试验断口形貌进行观察,研究了X80管线钢的断裂行为与组织之间的关系。研究发现,钢板从表面到厚度中心,针状铁素体体积分数逐渐降低,并出现较多的粒状贝氏体、多边形和准多边形铁素体。具有较高针状铁素体体积分数的钢板,其落锤撕裂剪切面积也越高,多边形和准多边形铁素体以及大尺寸MA岛的存在能够导致解理断裂的产生,不利于钢板的低温断裂韧性。在裂纹扩展的过程中,主裂纹附近组织出现变形,导致脆硬性的MA岛周围出现微孔,微孔与微孔之间随着组织变形相互连接而形成微裂纹。二次裂纹通常在针状铁素体周围出现转折或停滞,说明针状铁素体有利于阻碍裂纹的扩展,提高钢板的断裂韧性。
Electro-magnetic collapse of thick-walled cylinders to investigate spontaneous shear localization
[J].We present an electro-magnetic (EM) setup in order to collapse thick-walled cylinders, for the investigation of spontaneous formation of multiple adiabatic shear bands. The EM setup is based on a pulsed current generator using a capacitor bank system. The cylindrical specimen is part of an assembly of coaxial cylinders, where the inner and outer cylinders, each attached to an opposite pole, are short-circuited. Upon capacitor discharge, a high current flows through the cylinders, in opposite directions, creating repulsive magnetic forces between them. The outer cylinder is driven outwards and the inner cylinder is driven inwards - in a collapsing manner. This work presents the design procedure of the specimens' geometry using numerical simulations, and some preliminary experimental results for SS304L steel specimens. The spatial distribution of the multiple adiabatic shear bands in these specimens is in good agreement with that reported in the literature for explosively driven experiments with the same material. Our numerical simulations of the collapsing cylinder show good agreement with the experimental results for both global behavior and shear band distribution. (C) 2011 Elsevier Ltd.
Adiabatic shear failure in brittle solids
[J].Recent studies have revealed microscopic amorphous lamella resulting from inelastic deformation in the ballistic impact of boron carbide ceramic. The possibility that these deformation features are a consequence of adiabatic shear deformation in the impact event is explored. An early theory of adiabatic shear that was limited to the response of rigid-plastic deformation is expanded to include elastic strain energy. The study reveals that elastic strain energy is commonly a small, but not negligible, contribution to impact-induced adiabatic shear in metals. Elastic strain energy is paramount in brittle solids. Relations are developed from the theory to predict the nominal width and spacing of adiabatic shear-bands in brittle solids. Comparisons of the theoretical predictions are consistent with observations of impact-induced deformation features in boron carbide. (C) 2011 Elsevier Ltd.
Thickness effect on fracture behavior of columnar-grained Cu with preferentially oriented nanoscale twins
[J].
The deformation and fracture behaviors of 316L stainless steels fabricated by spark plasma sintering technique under uniaxial tension
[J].
{332} twins in shock-loaded pure iron
[J].
冲击加载α-Fe中的{332}孪晶
[J].
Shear localization in dynamic deformation of materials: microstructural evolution and self-organization
[J].
Microstructural fingerprints of phase transitions in shock-loaded iron
[J].The complex structural transformation in crystals under static pressure or shock loading has been a subject of long-standing interest to materials scientists and physicists. The polymorphic transformation is of particular importance for iron (Fe), due to its technological and sociological significance in the development of human civilization, as well as its prominent presence in the earth's core. The martensitic transformation α→ε (bcc→hcp) in iron under shock-loading, due to its reversible and transient nature, requires non-trivial detective work to uncover its occurrence. Here we reveal refined microstructural fingerprints, needle-like colonies and three sets of {112}&lt;111&gt; twins with a threefold symmetry, with tell-tale features that are indicative of two sequential martensitic transformations in the reversible α→ε phase transition, even though no ε is retained in the post-shock samples. The signature orientation relationships are consistent with previously-proposed transformation mechanisms, and the unique microstructural fingerprints enable a quantitative assessment of the volume fraction transformed.
Effects of prestrain on high temperature impact properties of 304L stainless steel
[J].