晶界对高温合金性能的影响,与晶界取向差有关[7,8]。随着晶界取向差的增加,晶界对高温合金性能的劣化更加显著。李小阳等[9]和Zhu等[10]研究发现,随着晶界取向差的增大高温合金SRR99双晶的塑性不断降低,断裂方式由沿滑移带断裂转变为沿晶界断裂。随着取向差的增加,高温合金晶界的结构发生规律性变化而使其性能降低。Huang等[11]研究发现,随着晶界取向差的增大,DD6单晶高温合金晶界处析出的拓扑密排相(简称TCP相)使其性能降低。Shi等[12]研究发现,随着晶界取向差的增大,高温合金DD5晶界碳化物析出相的密度提高而使其高温高周疲劳性能降低。Li等[13]与秦健朝等[14]研究单晶高温合金蠕变性能时也观察到,晶界取向差达到特定值时单晶高温合金的蠕变性能极快地降低。但是,目前对DD6单晶高温合金的力学性能的研究较少,因此需要研究晶界取向差对DD6单晶高温合金性能的影响。
本文用双籽晶法制备含有特定取向差晶界的DD6高温合金双晶样品,然后对其进行常温(25 ℃)和高温(760 ℃)拉伸实验,研究温度和晶界取向差对DD6高温合金拉伸性能的影响。
1 实验方法
实验用第二代镍基单晶高温合金DD6的化学成分,列于表1。
表1 DD6高温合金的名义成分
Table 1
| Co | Cr | Al | Mo | W | Ta | Re | Nb | Hf | C | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 4.3 | 5.6 | 2 | 8 | 7.5 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.006 | Bal. |
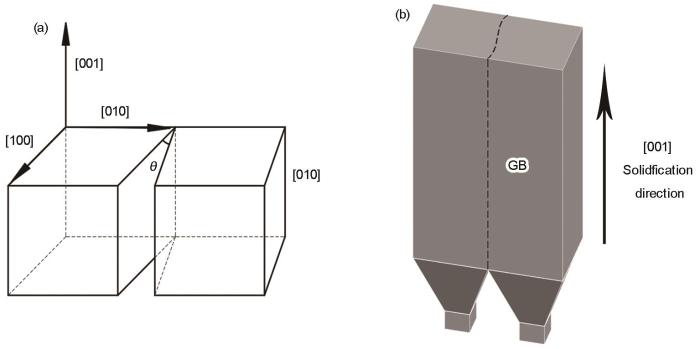
用籽晶法+定向凝固制备高温合金铸态双晶板,制备过程如图1所示。将两个相同高温合金籽晶中的一个按照图1a所示的方法以[001]方向为轴旋转
图1
图1
双晶板样品的籽晶方位和定向凝固示意图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of two crystal seeds method (a) orientations of seeds crystals, (b) directional solidification
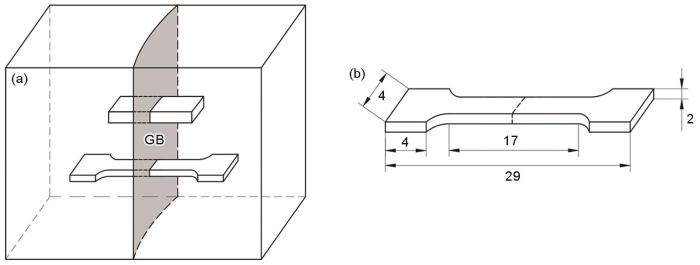
按照图2a所示的方法从DD6双晶板上切取含有晶界的板状拉伸样品和观察组织的块状样品。拉伸样品的尺寸如图2b所示。晶界位于样品平行段中央并垂直于应力加载方向。将块状样品腐蚀后用扫描电镜观察其组织形貌,腐蚀剂的成分为80 mL HCl + 20 g CuSO4 + 100 mL H2O。用4组晶界取向差为0°、4°、8°、12°的双晶样品进行拉伸实验。每组样品在同一温度做3次拉伸实验,取其结果的平均值。拉伸实验机的型号为Instron5982,引伸计为人工装卡类型,标距为12.5 mm,应变加载速率为5
图2
图2
板状拉伸样品和块状金相样品切取过程的示意图和拉伸样品的尺寸
Fig.2
Schematic diagram of tensile sample and metallographic sample (a) sample cutting process, (b) shape and dimension of tensile sample (unit: mm)
2 实验结果
2.1 不同晶界取向差样品的组织结构
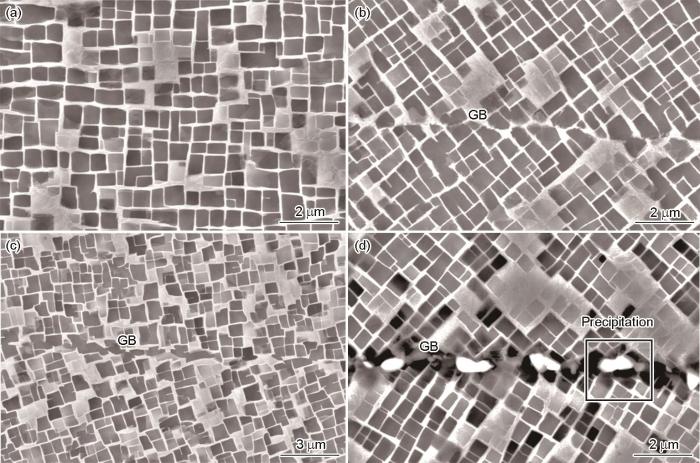
图3
图3
双晶样品的晶界组织结构
Fig.3
Microstructure of GBs of bicrystal samples (a) 0°, (b) 4°, (c) 8°, (d) 12°
如图3所示,4°晶界为一条白色折线,几乎完全由
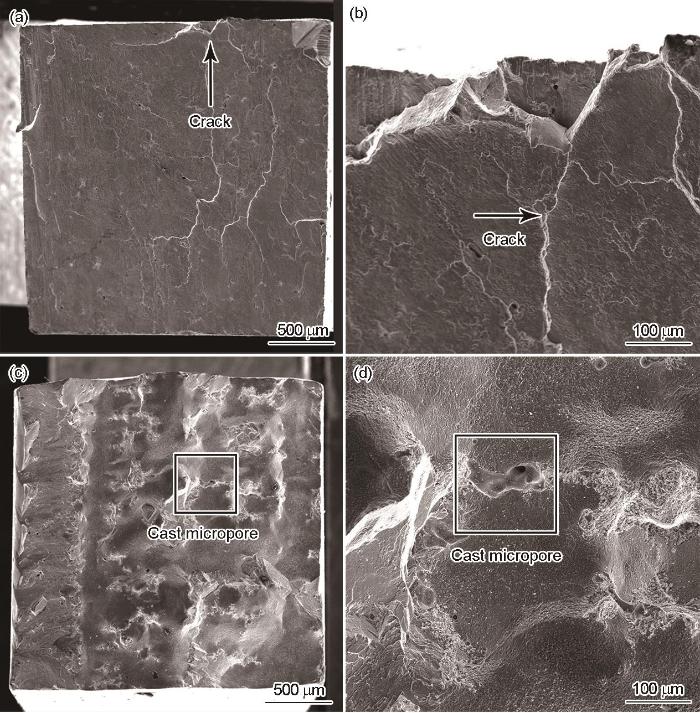
同时,如图4所示,在双晶组织中铸造微孔均匀分布,其尺寸约为80 μm。由于制备工艺完全相同,4组样品的基体组织相同,因此其中铸造微孔的密度和尺寸也大致相同。
图4
图4
双晶样品中铸造缩孔的金相照片和 SEM照片
Fig.4
Metallographic images (a) and SEM images (b) of cast micropores in bicrystal samples
2.2 不同晶界取向差样品的拉伸性能
图5
图5
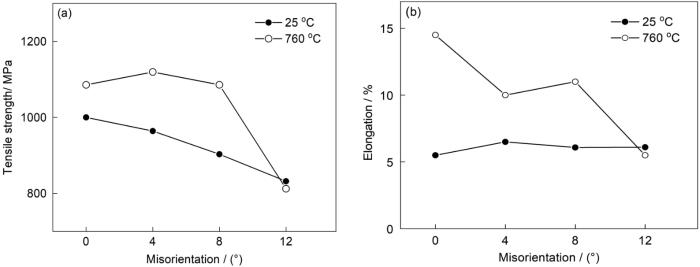
在不同温度下抗拉强度和伸长率与晶界取向差的关系
Fig.5
Tensile strength (a) and elongation to fracture (b) vs. the misorientation at different temperatures
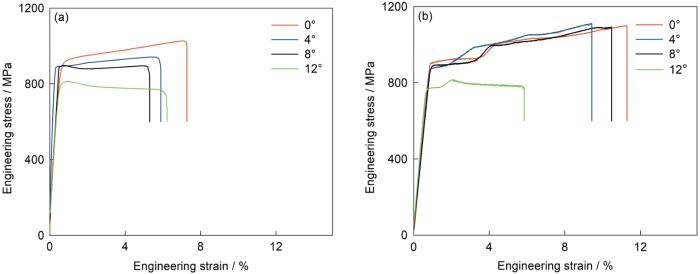
如图5所示,0°样品的常温抗拉强度为1000 MPa,断后伸长率为5.5%。晶界取向差从0°增大到12°,双晶样品的常温抗拉强度连续降低了173 MPa,而断后伸长率几乎不变。
如图5所示,0°样品的760 ℃抗拉强度为1085 MPa,断后伸长率为14.5%。晶界取向差从0°增大到4°抗拉强度几乎不变,断后伸长率降低4%;晶界取向差从4°增大到8°,抗拉强度和断后伸长率都几乎不变;晶界取向差从8°增大到12°抗拉强度和断后伸长率均较速地降低:抗拉强度降低270 MPa,断后伸长率降低5.5%。
图6给出了DD6高温合金双晶的常温和760 ℃工程应力-应变曲线。可以看出,随着晶界取向差的增大屈服后的曲线变化趋势出现差异。晶界取向差小于8°的双晶样品其拉伸应力随着应变的增大持续增大,表现出明显的加工硬化趋势;而当晶界取向差达到12°时,随着应力的增大应变持续减小。
图6
图6
常温和760 ℃的工程应力-应变曲线
Fig.6
Tensile engineering stress-strain curves of tensile test of bicrystal samples with different misorientations tested at (a) ambient temperature, (b) 760 oC
图7
图7
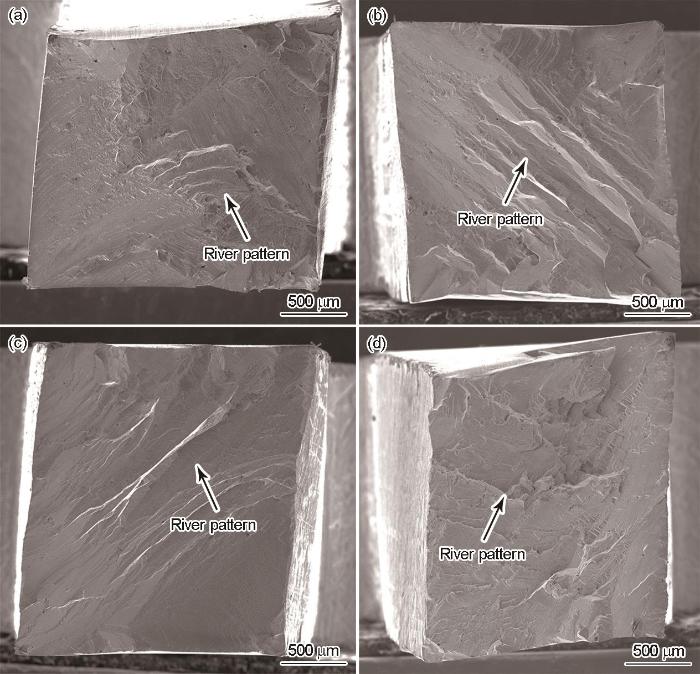
不同晶界取向差样品的常温拉伸断口
Fig.7
Tensile fracture of samples of the different misorientations at ambient temperature (a) 0°, (b) 4°, (c) 8°, (d) 12°
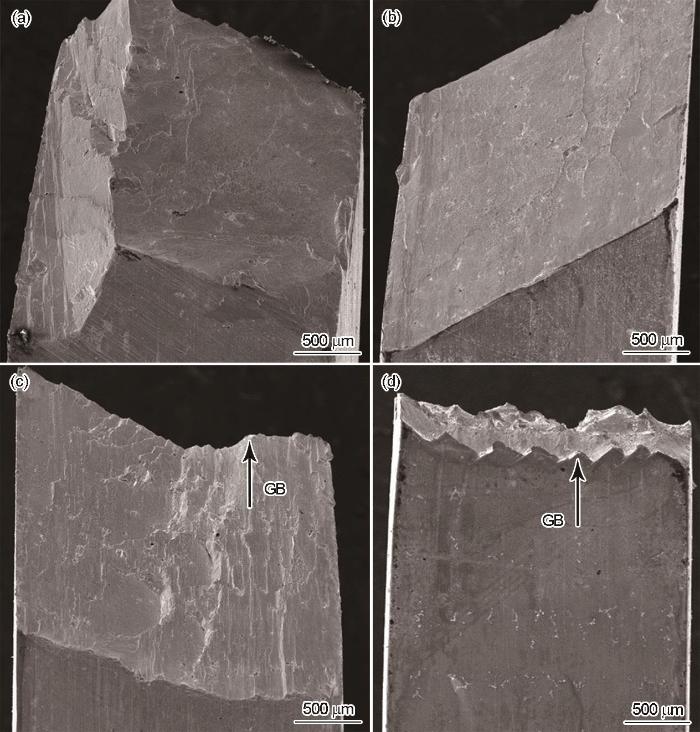
760 ℃拉伸断口由单个或几个较大的平整倾斜面构成,因此用侧视观察断口,其形貌如图8所示。在760 ℃拉伸,4组样品的断口有所不同。其中晶界取向差为0°、4°、8°的样品其断口形貌相似,都由单个或几个较大的平面构成。其原因是,DD6单晶高温合金在760 ℃拉伸时主要滑移方式为八面体滑移。八面体滑移的滑移面为{111},裂纹在{111}平面扩展,最终形成这种断口,断裂方式为沿 {111}晶面的类解理断口[20]。随着晶界取向差的增大,断口显示出沿晶开裂特征。晶界取向差为8°的样品呈现沿晶开裂与类解理断裂的混合特征。晶界取向差增大到12°时拉伸样品完全沿晶界开裂,断口从侧面观察为锯齿形,与晶界取向差为0°、4°、8°样品的断口形貌完全不同。
图8
图8
不同晶界取向差样品的760 ℃拉伸断口
Fig.8
Tensile fracture of samples of the different misorientations at 760 ℃ (a) 0°, (b) 4°, (c) 8°, (d) 12°
熊新红等[21]研究DD6单晶高温合金拉伸行为时也发现类似的现象:在常温和650 ℃拉伸试样表面出现滑移线,断裂方式为类解理断裂。在650 ℃拉伸出现类解离断裂特征,是动态应变时效与不均匀变形所致。随着拉伸温度进一步提高到1020 ℃,样品表现为韧窝断裂。
图9
3 讨论
3.1 晶界结构对拉伸性能的影响
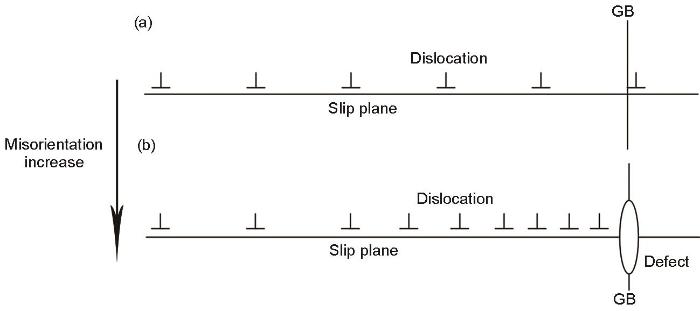
如图5a所示,晶界取向差小于8°时,单晶高温合金的强度受晶界的影响较小,更多地取决于单晶基体的强度。高温合金的屈服效应反常,在一定温度范围内其屈服强度随着温度的升高而提高[17]。因此,晶界取向差小于8°的样品,其760 ℃抗拉强度高于常温抗拉强度,且随着取向差的变化趋势较为平缓。随着晶界取向差的增大,晶界取向差大于8°的DD6双晶样品,其760 ℃拉伸断裂为沿晶断裂,即拉伸断裂过程转变为晶界主导,使抗拉强度大幅度降低。DD6双晶抗拉强度的大幅度降低,与其晶界结构有关。DD6高温合金晶界取向差从8°增大到12°,在晶界处析出大量
图10
图11
图11
晶界取向差对DD6双晶样品拉伸断裂机制的影响
Fig.11
Effect of GB misorientation on tensile fracture mechanism of DD6 bicrystal samples
(a) cleavage-like fracture, (b) intergranular fracture
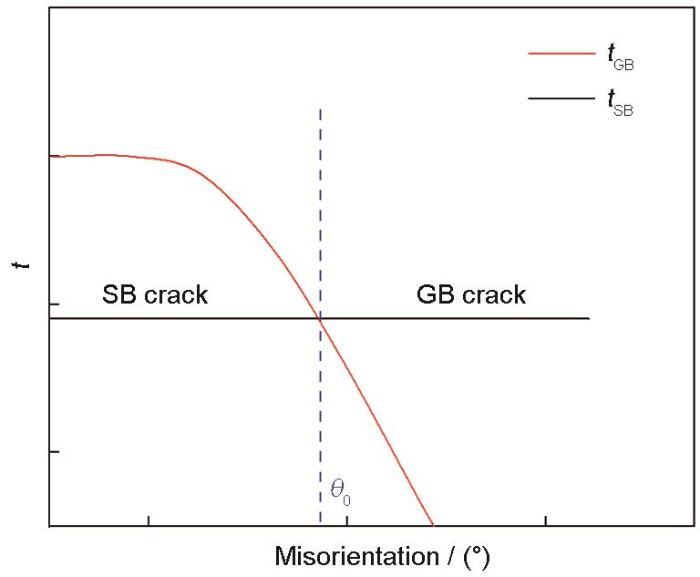
3.2 拉伸断裂机制的转变
其中
于是
由于双晶取向差不同样品是同一种金属材料,拉伸过程中的弹性能相同。因此,在两种拉伸断裂机制竞争过程中可忽略弹性能的变化,即可忽略
其中
其中
其中
其中
随着取向差的增大
图12
图12
Fig.12
A qualitatively description for variations
4 结论
(1) 双晶样品在760 ℃的拉伸性能优于常温,但是晶界对拉伸性能的影响更加显著。高温合金的晶界取向差从0°增大到12°其断后伸长率不变,但是常温抗拉强度降低了173 MPa;而760 ℃的抗拉强度降低了270 MPa,断后伸长率降低了9%。随着晶界取向差的增大,双晶样品的常温拉伸性能变化更为均匀,而760 ℃拉伸性能大幅度降低。
(2) 双晶样品在常温下的断裂方式为解理断裂。晶界取向差从0°增大到8°,双晶样品的760 ℃拉伸断裂方式为类解理断裂;晶界取向差从8°增大到12°,断裂方式由类解理断裂转变为沿晶断裂。随着晶界取向差的增大DD6高温合金晶界处
(3) 随着晶界取向差的增大晶界结构逐渐复杂。晶界开裂能量门槛的降低和晶界能量积累速度的提高,使拉伸断裂机制由类解理断裂转变为沿晶断裂。
参考文献
Effect of rhenium addition on isothermal oxidation behavior of a nickel-base single crystal superalloy
[J].Effect of rhenium (Re) addition on isothermal oxidation behavior of a nickel-base single crystal superalloy was investigated by means of intermittent measurement of weight change as well as scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffractometer (XRD). It was shown that, a scale composed of a (Cr, Ti)-enriched outer oxide layer, an inner Al2O3 layer and an inner TiN layer was formed for both the Re-containing and Re-free alloys, however, the Al2O3 layer was much more complete and the amount of TiN was much less on the Re-containing alloy rather than those on the Re-free alloy. Re was found to lower the oxidation rate of the alloy and improve the stability of the entire oxide scale during long-term oxidation by increasing the activity of Cr and thus increasing the content of Cr2O3 in the scale. Enhancement of Cr2O3 formation may then accelerate the selective oxidation of Al and thus promote the formation of a continuous Al2O3 layer beneath the outer oxide scale, as a result, which inhibited the formation of the inner nitride.
铼对镍基单晶高温合金恒温氧化行为的影响
[J].采用不连续增重法研究了Re对一种镍基单晶高温合金1000℃恒温氧化行为的影响,采用扫描电镜(SEM)和X射线衍射分析仪(XRD)对样品的组织进行了观察。结果表明,两种合金生成的氧化膜成分相似,都生成了以含Cr、Ti氧化物为主的外氧化层、Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>内氧化层以及含有TiN的内氮化层。但二者氧化速率及氧化层结构存在较大差异,含Re合金的氧化速率较慢,Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>层较完整且TiN数量较少。Re的作用机理在于它提高了合金中Cr的活度,增大氧化膜中Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>的含量,加快Al的选择性氧化,促进合金氧化膜内部连续Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>层的形成,抑制合金内部氮化物的生成,提高长期氧化下氧化膜的稳定性。
Nickel-based superalloys for advanced turbine engines: chemistry, microstructure and properties
[J].
Creep microstructure damage and influence on re-creep behavior for a nickel-based single crystal superalloy
[J].Creep tests of Nickel-based single crystal superalloy DD413 were carried out by constant loads of 980℃/200 MPa and 870℃/430 MPa, while which then were terminated at plastic strain just reaches 0.2%, 0.5% and 1% respectively, so that to acquire the microstructure of the alloy by different creep damage states. Later on, the pre-strained alloys were further subjected to re-creep test again, so as to acquire their residual creep properties and to establish the relationship between different degraded microstructure and creep properties. Meanwhile the microstructure damage characteristics of DD413 alloy under thermal-mechanical coupling were simulated and quantitatively characterized. The results show that the degradated damage of DD413 alloy structure mainly includes the decrease of γ' phase volume fraction and the increase of γ' phase rafting degree. The higher the creep temperature, the more serious the microstructure damage, and the worse the alloy's re-creep performance. Compared with γ' phase rafting, the decrease of γ' phase volume fraction has little effect on the creep properties of the alloy.
一种镍基单晶高温合金的蠕变组织损伤对再蠕变行为的影响
[J].
The convergence-fault mechanism for low-angle boundary formation in single-crystal castings
[J].
Grain boundary character correlated carbide precipitation and mechanical properties of Ni-20Cr-18W-1Mo superalloy
[J].
Engineering failure of single crystal blades based on failure cases
[J].
从典型失效案例探讨单晶叶片的工程失效问题
[J].
Effect of low angle boundary on high cycle fatigue properties of single crystal superalloy
[J].
小角度晶界对单晶高温合金高周疲劳性能的影响
[J].
Effect of grain boundary angle on stress rupture properties on a Ni-based bicrystal superalloy
[J].
晶界角度对一种镍基双晶高温合金持久性能的影响
[J].
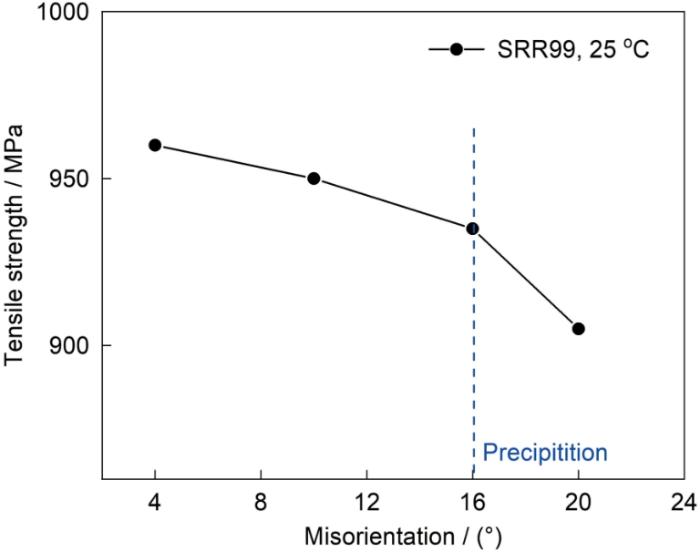
Effect of misorientation on the tensile properties of SRR99 superalloy bicrystals
[J].<p>The tensile deformation behavior, surface morphology, fracture mode and fracture morphology of SRR99 superalloy bicrystals were systematically investigated at room temperature in air. It is shown that the bicrystal with misorientation of 4° has little influence on the tensile properties, however the effect of grain boundary (GB) becomes obvious when the misorientation is 10°, for the bicrystals with misorientations of 16° and 18° the effect of GBs becomes much more serious. It is experimently found that slip is the most important deformation mode in the SRR99 superalloy bicrystals at room temperature. For the bicrystal with misorientation of 4°, slip bands would transfer through GB easily, and finally the specimens fractured along slip bands with typical slip characteristic on their fractography. In the bicrystal with misorientation of 10°,cracks nucleated and propagated either along slip bands or along GBs due to the impingement of slip bands and the strain accumulations, and finally the fracture instability happened along slip bands. The fracture morphology showed not only slip characteristic, but also the features of interdendritic cracks. In the bicrystals with misorientations of 16° and 18°, cracks initiated after yielding, and then propagated along GBs and the fracture surfaces mainly consisted of interdendritic cracks.</p>
取向差对SRR99双晶高温合金拉伸性能的影响
[J].通过对具有不同取向差的SRR99双晶高温合金试样进行室温拉伸实验, 系统比较了取向差对试样拉伸行为、表面形貌、断裂方式和断口形貌的影响. 结果表明: 取向差为4°的晶界对双晶的拉伸性能几乎没有影响; 当取向差达到10°时, 晶界的作用开始明显显现; 而取向差为16°和18°的晶界对双晶的力学性能影响最大. 扫描电镜观察发现: 滑移易于贯穿4°取向差晶界, 最后沿滑移带开裂, 断口呈明显的滑移特征; 取向差为10°的双晶在滑移带撞击下, 裂纹沿滑移带和晶界同时扩展, 最后率先沿滑移带失稳断裂, 断口上除有滑移特征, 还呈现枝晶间开裂特征; 而取向差为16°和18°的双晶, 在屈服初期便萌生晶界裂纹, 最后沿晶界快速发生断裂, 断口枝晶间开裂特征明显.
Tensile deformation behaviors and damage mechanisms of SRR99 superalloy bicrystals with different grain boundary misorientations
[J].
Misorientation related microstructure at the grain boundary in a nickel-based single crystal superalloy
[J].
High-temperature fatigue strength of grain boundaries with different misorientations in nickel-based superalloy bicrystals
[J].Nickel-based single-crystal superalloys are widely used in the manufacture of aeroengine turbine vanes for their excellent high-temperature performance. Low-angle grain boundaries (LAGBs) will be generated inevitably during their manufacture, which are often characterized by grain boundary misorientation (GBM) and will weaken the mechanical properties of superalloys. However, the relationship between GBM and the fatigue properties of superalloys at elevated temperatures has seldom been investigated due to the difficulty in the sample preparation and experiment process. Based on six kinds of bicrystals with different tilt LAGBs made by a second-generation single-crystal superalloy, the effects of misorientation on the grain boundary microstructure and fatigue properties (980 °C) of superalloys were studied systematically in this work. It is found that, with the increase of GBM, the GB precipitates combined with the cast micropores increase monotonically, accordingly both the fatigue life and fatigue strength decrease successively. Fatigue fracture observations show that the cracks of all the bicrystals initiated from the cast micropores at GBs, and then propagated along the GBs. Therefore, the coupling effect of cast micropores and GBM on the fatigue damage mechanisms of the bicrystals are evaluated according to their hindering degrees on the piled-up dislocations. Combining with a hysteresis energy model, a quantitative fatigue strength prediction model of superalloys is established and is well verified by abundant experimental data. This study could provide guidance for fatigue performance prediction and structural design of superalloys.
Effects of low angle boundaries on the mechanical properties of single crystal superalloy DD6
[A]. Proceedings of the Superalloys 2008 [C].
Effect of low angle grain boundaries on mechanical properties of DD5 single crystal Ni-base superalloy
[J].
小角度晶界对DD5镍基单晶高温合金力学性能的影响
[J].采用籽晶法制备了二代镍基单晶高温合金DD5小角度晶界试样,研究小角度晶界对DD5合金力学性能的影响。结果表明:在870 ℃中温拉伸中,晶界角度小于16.1°时,合金抗拉强度和屈服强度无明显变化;晶界角度小于11.4°时,伸长率维持在15%以上;晶界角度大于11.4°后,伸长率开始快速下降;在980 ℃/250 MPa持久条件下,当晶界角度小于5.1°时,持久寿命维持在140 h以上;当晶界角度大于5.1°时,持久寿命随晶界角度增大开始缓慢下降,至14.8°时,持久寿命仍保持为原来的85%;当晶界角度大于14.8°后持久寿命开始快速下降;在1093 ℃/158 MPa持久条件下,当晶界角度小于5.1°时,持久寿命维持在30 h以上;当晶界角度大于5.1°时,持久寿命随晶界角度增大而下降。
Effect of γ′-phase on tensile and stress rupture deformation behavior of high W-containing Ni-based superalloys
[J].
γ′相对高钨镍基高温合金拉伸和持久变形行为的影响
[J].
Effect of hot isostatic pressing on microstructure of a third-generation single crystal superalloy DD33
[J].The third generation DD33 single crystal superalloy was subjected to standard heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing respectively, and then to different post-solution and -aging treatments. Hereafter, the effect of hot isostatic pressing and heat treatment on the microstructure and durability of the alloy were investigated by means of high-temperature endurance tests at 850℃/650 MPa and 1100℃/170 MPa, as well as metallographic microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray three-dimensional imaging (XCT). The results show that after proper hot isostatic pressing and subsequent heat treatment, the as-cast DD33 single crystal superalloys present more or less the same microstructure of (γ' phase size, volume fraction and cubic degree) as those subjected to standard heat treatment. Compared with the standard heat treated alloy, the volume fraction and size of the micropores of the alloy decreased significantly after hot isostatic pressing, from 0.0190% to 0.0005%, and the maximum equivalent diameter of the micropores decreased from 36.9 μm to 14.2 μm. The durable life of the alloy subjected to hot isostatic pressing was significantly prolonged when testing by 850℃/650 MPa and 1100℃/170 MPa. These results show that proper hot isostatic pressing and heat treatment can eliminate the micro voids, therewith, improve the durability of the alloy.
热等静压对第三代单晶高温合金DD33显微组织和持久性能的影响
[J].对第三代DD33单晶高温合金进行标准热处理、热等静压以及不同制度的后续固溶和时效处理,并在850℃/650 MPa和1100℃/170 MPa条件下进行高温持久性能实验,使用金相显微镜(OM)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和X射线三维成像技术(XCT)等手段观察和表征不同状态的样品,研究了热等静压和热处理对这种合金显微组织和持久性能的影响。结果表明:铸态DD33单晶高温合金经过适当的热等静压和后续热处理工艺后,样品的组织形貌(γ′相尺寸、体积分数与立方化程度)与标准热处理态基本相同。与标准热处理态合金相比,热等静压处理后合金显微孔洞的体积分数和尺寸均显著降低,其体积分数从0.0190%降低到0.0005%,最大孔等效直径从36.9 μm减小到14.2 μm。在850℃/650 MPa和1100℃/170 MPa条件下热等静压后的样品持久寿命均显著延长。这表明,适当的热等静压和热处理能消除合金内部的显微孔洞缺陷,使其持久性能显著提高。
Tensile anisotropy of single crystal superalloy DD6
[J].
单晶高温合金DD6拉伸性能各向异性
[J].研究了[001],[011],[111]取向第二代单晶高温合金DD6的拉伸性能与断口组织.结果表明:DD6单晶高温合金存在拉伸各向异性,850℃以上[001]取向DD6单晶高温合金的抗拉强度与屈服强度分别高于[011],[111]取向合金的强度,[001],[011],[111]取向DD6单晶高温合金的拉伸断口具有类解理断裂与韧窝断裂的特征.
Effects of low angle grain boundaries on tensile properties of single crystal superalloy DD6
[J].
小角度晶界对单晶高温合金DD6拉伸性能的影响
[J].采用两个籽晶制备了第二代单晶高温合金DD6小角度晶界试样,在800,850,900,950℃的条件下,进行了拉伸实验研究。结果表明:小角度晶界对合金伸长率有显著影响;在850℃,小角度晶界试样具有最大的伸长率;高于850℃,随着温度的升高小角度晶界试样伸长率具有明显下降倾向。小角度晶界对合金抗拉强度的影响较小;除角度大于约9°的小角度晶界外,相同实验温度条件下小角度晶界试样的抗拉强度大致相当。随着温度的升高和晶界角度的增大,小角度晶界强度降低而成为相对较为薄弱部位,从而导致拉伸性能的降低。
Influence of shot peening on tensile properties of DD6 single crystal superalloy
[J].The influence of cast steel shot-peening on the tensile properties of the second generation single crystal superalloy DD6 under 500, 600,650℃ was investigated by SEM, X-ray and TEM. The results show that the shot-peening has no influence on the tensile strength of DD6 alloy at 500, 600,650℃, and the yield strength is slightly increased, while the elongation and the shrinkage of cross section are remarkably decreased. The shot-peening DD6 alloy is ruptured after the flow stress rising to the highest point, and the cross section of fracture samples presents circle shape. The stress-strain curves of non-shot-peening DD6 alloy exhibit double stages feature, and the cross section of fracture samples presents ellipse shape.
喷丸对DD6单晶高温合金拉伸性能的影响
[J].
Tensile behavior of nickel-base single-crystal superalloy DD6
[J].
Fatigue cracking at twin boundaries: effects of crystallographic orientation and stacking fault energy
[J].
Grain boundary effects on cyclic deformation and fatigue damage
[J].
Investigation on in situ tensile behavior of superalloy bicrystals with different GB misorientations
[J].
Misorientation effect of grain boundary on the formation of discontinuous precipitation in second and third generation single crystal superalloys
[J].
Precipitation behavior of grain boundary M23C6 and its effect on tensile properties of Ni-Cr-W based superalloy
[J].
γ′-cutting as rate-controlling recovery process during high-temperature and low-stress creep of superalloy single crystals
[J].
Microstructure and dislocation structure evolution during creep life of Ni-based single crystal superalloys
[J].The high performance of Ni single crystal superalloys during high temperature low stress creep service, is intrinsically determined by the combined effects of microstructural evolution and the dislocation behaviour. In the field of the evolution of dislocation network, two main recovery mechanism based on dislocation migration dominate the process. One is superdislocations shearing into γ’ rafts through a two-superpartials-assisted approach. Another is the compact dislocations migrating along γ/γ′ interface. These two mechanisms are similarly climb-rate-controlled process. In this work, a model for the minimum creep rate based on thermodynamic and kinetic calculations and using an existing detailed dislocation dynamics model has been built by taking the dislocation migration behaviours as well as the rafted microstructure into consideration, which can well reproduce the ([100] tensile) creep properties of existing Ni superalloy grades, without the need to make the dislocation parameter values composition dependent.
Cyclic plastic strain energy as a damage criterion and environmental effect in Nb-bearing high strength, low alloy steel
[J].
A model of fatigue crack nucleation in single crystal iron and copper
[J].
The impact of misorientation on the grain boundary energy in bi-crystal copper: an atomistic simulation study
[J].Atomistic simulations were performed to investigate the relationships among the misorientation, dislocation density, and grain boundary energy of twist and tilt bi-crystal grain boundaries. In this work, the grain boundary energies were calculated based on the embedded-atom method interatomic potential for Cu. The results show that the dislocation density of the grain boundary changes with the rotation angle, thereby affecting the grain boundary energy. Furthermore, the grain boundary energy of a grain boundary with no dislocations is greater than that of a grain boundary with dislocations, which results from the distribution of the atomic potential energy on the grain boundaries. Additionally, the grain boundary energy increases with the dislocation density of the grain boundary in the case of dislocations on the grain boundary. On this basis, a new relationship is proposed for the misorientation angle and grain boundary energy. We assume that when the driving force of dislocation nucleation breaks through the grain boundary energy barrier, the grain boundary energy declines.© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Grain boundary characterization and energetics of superalloys
[J].