制备铁氧体的方法有液相法、气相法和固相法。用液相法制备的铁氧体,有纯度高、均匀性好和化学组成可控等优点。液相法包括溶胶-凝胶法、水热法和化学共沉淀法等[11]。用溶胶凝胶法制备吸波材料,组分易控、流变特性好。谈尚华等[12]用水热法制备的单一离子掺杂的ZnFe2O4吸波材料,吸收层厚度为2.00 mm时反射损耗值达到-10.00 dB。云月厚等[13]用化学共沉淀法制备的Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4吸波材料,在1.00~18.00 GHz波段在8.70、10.20、11.30 GHz处出现的反射峰,反射损耗依次为-11.50、-8.90、-10.40 dB。用水热法和化学共沉淀法制备的铁氧体材料,晶粒团聚严重和密度过高[14]。Wenhui L等[15]用溶胶-凝胶法制备的NiFe2O4@C@PPy吸波材料,吸收层厚度1.75 mm时有效吸收频带(< -10.00 dB)达到5.50 GHz (11.75~17.25 GHz),反射损耗最小值-38.69 dB。张晏清等[16]用溶胶-凝胶法分别制备了NiFe2O4、CoFe2O4吸波材料。CoFe2O4在C波段(5.00 ~6.40 GHz)和X波段内(8.50~12.00 GHz)的反射损耗最小值为-16.58、-8.54 dB;NiFe2O4在C波段和Ku波段内的反射损耗最小值为-15.62、-8.03 dB。本文用溶胶-凝胶法制备镍钴铁氧体Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4,研究镍、钴离子比例对其吸波性能的影响。
1 实验方法
1.1 样品的制备
(1) 将含金属离子的硝酸镍(Ni(NO3)2·6H2O)、硝酸钴(Co(NO3)2·6H2O)和硝酸铁(Fe(NO3)3·9H2O)与柠檬酸按照物质的量1∶1(其中Ni2+、Co2+在铁氧体中掺杂的比例为Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4 (x = 0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9)混合后置于50 mL蒸馏水中。(2)将其超声处理10 min后用玻璃棒搅拌,然后再超声处理10 min。(3)将得到的混合溶液倒入四口烧瓶中进行80 ℃恒温水浴搅拌10 min,以3 s/滴的速率滴加氨水将pH值调节到7,再以120 r/min的转速恒温水浴搅拌4 h。(4)将得到的溶胶放入120 ℃真空干燥箱中真空干燥4 h,将得到的凝胶在室温下冷却15 min。(5)将凝胶置于马弗炉中,以15 ℃/min的速率升温至200 ℃保温5 min。(6)将得到的产物充分研磨后放入马弗炉中,以5 ℃/min速率升温至950 ℃,保温180 min后随炉冷却,得到纳米镍钴铁氧体。
1.2 性能表征
用D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪(XRD)测试样品的物相组成,条件为:Cu靶Kα 射线,波长0.15406 nm,工作电压40 kV,管电流30 mA,扫描速度10 (°)/min,扫描范围5°~80°。用JEM-2010型透射电子显微镜(TEM)分析晶体的形貌和粒径,分辨率为0.1~0.2 nm,加速电压为200 kV。用HP8722ES矢量网络分析仪(VNA)和同轴线测试法测试样品在0~18 GHz频率范围的复介电常数和复磁导率。样品粉体与石蜡按按7∶3的比例混合,搅拌均匀后用模具压制成厚度为2 mm的圆环状试样,用矢量网络分析仪测定其电磁参数。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 铁氧体的物相组成
图1给出了不同Ni2+∶Co2+比例铁氧体的XRD谱。可以看出,不同掺杂比例铁氧体其衍射峰强度大致相同,表明用溶胶-凝胶法制备的铁氧体晶化效果较好。衍射角2θ为18.4°、30.3°、35.7°、37.3°、43.4°、53.8°、57.4°、63.0°、71.5°、74.6°、75.6°处的峰分别对应(111)、(220)、(311)、(222)、(400)、(422)、(511)、(440)、(620)、(533)、(622)晶面。将样品的衍射峰与PDF#86-2267标准卡的比较表明,谱中没有出现杂峰[17],表明制备出了纯相尖晶石型镍钴铁氧体。图1中的XRD谱中最强的衍射峰对应(311)晶面,表明晶体的优先晶化取向为(311)。根据Bragg公式和Scherrer公式
图1
图1
不同Ni2+、Co2+掺杂比例的镍钴铁氧体的XRD谱
Fig.1
XRD plot of different doping ratios of Ni2+, Co2+
可计算样品的晶面间距(d)、平均粒径(D)和晶格常数(ɑ)。式中λ为波长(取0.154056);n为反射级数(取1);β为主衍射峰的半峰宽;θ为衍射角;h、k、l为晶面指数。计算出的结构参数列于表1。晶粒尺寸为66~70 nm,表明达到了纳米级。晶格常数从0.8361逐渐降低到0.8315,表明在尖晶石结构中Ni2+逐步取代了Co2+,与掺杂Ni2+∶Co2+比例的增大吻合。结果表明,掺杂Ni2+、Co2+的比例不同,影响铁氧体的结构参数。
表1 镍钴铁氧体的结构参数
Table 1
| Structural formula | 2θ / (°) | d / nm | ɑ / nm | (311) Priority crystallization diffraction peak | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM / (°) | D / nm | ||||
| Ni0.1Co0.9Fe2O4 | 35.57 | 0.2521 | 0.8361 | 0.00216 | 66.7 |
| Ni0.3Co0.7Fe2O4 | 35.64 | 0.2517 | 0.8348 | 0.00206 | 69.9 |
| Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 | 35.67 | 0.2515 | 0.8341 | 0.00213 | 67.6 |
| Ni0.7Co0.3Fe2O4 | 35.77 | 0.2508 | 0.8318 | 0.00206 | 68.1 |
| Ni0.9Co0.1Fe2O4 | 35.78 | 0.2507 | 0.8315 | 0.00208 | 69.3 |
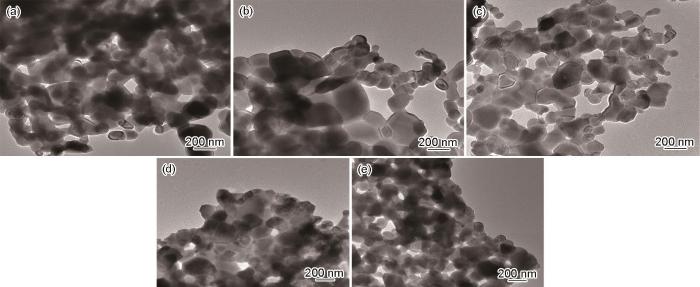
2.2 镍钴铁氧体的形貌
图2
图2
不同Ni2+、Co2+掺杂比的镍钴铁氧体的TEM照片
Fig.2
TEM plot of different doping ratios of Ni2+ and Co2+(a) Ni0.1Co0.9Fe2O4, (b) Ni0.3Co0.7Fe2O4, (c) Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4, (d)Ni0.7Co0.3Fe2O4, (e) Ni0.9Co0.1Fe2O4
2.3 镍钴铁氧体的吸波性能
可计算吸波反射率与频率的关系。式中
图3
图3
不同掺杂比Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4样品的反射损耗、频率和厚度曲线
Fig.3
Curve of reflection loss and frequency and thickness of Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4 samples with different doping ratios
(a) Ni0.1Co0.9Fe2O4, (b) Ni0.3Co0.7Fe2O4, (c) Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4, (d) Ni0.7Co0.3Fe2O4, (e) Ni0.9Co0.1Fe2O4
从图3可以看出,随着Ni2+∶Co2+比列的提高吸波性能呈先降低后提高的趋势。掺杂比例Ni2+∶Co2+ = 0.5∶0.5的铁氧体,其吸波效果最好,且低于-10.00 dB的有效频带宽度为2.21 GHz (15.79~18.00 GHz)。Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4吸波性能较好的原因是,在纳米Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4中Ni2+和Co2+优先占据每个晶胞中的八面体位置(即B位)。随着Ni2+∶Co2+比例提高晶格常数减小,晶向界减少引起退磁能减小和磁矩增大,磁滞损耗随之提高。在掺杂比例过高的铁氧体的八面体(B位)出现Ni3+,产生Ni3+、Ni2+电子交换而Fe3+、Fe2+之间的电子交换消失,使交换电子减少和导电性减弱,使介电损耗减小[20]。这表明,掺杂的比例适当能提高纳米Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4的吸波性能。
表2 镍钴铁氧体、镍铁氧体和钴铁氧体的晶粒尺寸
Table 2
| Structural formula | Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 | NiFe2O4 | CoFe2O4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| D / nm | 67.6 | 56.0 | 36.0 |
表3 镍钴铁氧体、镍铁氧体和钴铁氧体的吸波性能
Table 3
| Structural formula | Min. reflection loss / dB | Frequency / GHz | Bandwidth / GHz (≤ -10 dB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 | -16.15 | 17.32 | 2.21(15.79~18.00) |
| NiFe2O4 | -16.58 | 6.20 | 1.40(5.00~6.40) |
| CoFe2O4 | -15.62 | 6.20 | 1.00(5.40~6.40) |
Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4的晶粒尺寸比单一的NiFe2O4、CoFe2O4的大,反射损耗的最小值没有显著提高且变化范围较小,但有效吸波频带拓宽为0.81~1.21 GHz,有效吸波频带右移到Ku波段内,成为高频吸波材料。
表4 用不同方法制备的镍钴铁氧体、镍铁氧体和钴铁氧体的吸波性能
Table 4
| Preparation method | Structural formula | Min. reflection loss / dB | Frequency / GHz | Bandwidth / GHz (≤ -5 dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol-gel method | NiFe2O4 | -16.58 | 6.20 | 3.80 |
| Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 | -16.15 | 17.32 | 3.65 | |
| CoFe2O4 | -15.62 | 6.20 | 3.80 | |
| Solvothermal method | NiFe2O4 | -9.10 | 6.00 | 1.37 |
| Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 | -14.00 | 3.45 | 1.70 | |
| CoFe2O4 | -16.90 | 1.66 | 1.44 |
用溶胶-凝胶法制备的铁氧体其最小反射损耗都达到-15 dB以下,而用溶剂热法制备的铁氧体其吸波强度更高。从≤ -5 dB的频带宽度分析,用溶胶-凝胶法制备的铁氧体其频带宽度达到3.65~3.80 GHz,是溶剂热法的2.6倍。这表明,用溶胶-凝胶法制备的铁氧体其吸波性能优于用溶剂热法制备的铁氧体。
2.4 铁氧体的电磁性能
铁氧体的损耗角正切值(tanδ)表征电磁波损耗,包括电损耗角正切值(tanδe)和磁损耗角正切值(tanδm),即[22]
式中复介电常数的虚部
图4
图4
Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4样品的tanδe、tanδm和频率曲线
Fig.4
Curve of the Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4 sample tanδe (a), tanδm (b) and frequency
图5
图5
Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4样品的tanδ、C0和频率曲线
Fig.5
Curve of the Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4 sample tanδ (a), C0 (b) and frequency
画出的纳米Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4的磁损耗C0与频率的关系曲线[23]。可以看出,在低频1.00~10.00 GHz区Ni0.7Co0.3Fe2O4样品的曲线波动范围很大,表明磁损耗是自然共振引起的。自然共振发生在低频段,是形状各向异性和磁晶各向异性引起的[24,25]。在4.00~18.00 GHz频率范围Ni0.1Co0.9Fe2O4、Ni0.3Co0.7Fe2O4和Ni0.9Co0.1Fe2O4样品的曲线波动范围很小,表明磁损耗是涡流损耗引起的[26]。样品Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4在1.00~12.00 GHz频段没有出现明显的共振峰,表明该频段的损耗是涡流损耗。交换共振一般发生在高频段,是由表面各向异性和晶粒间的能量交换引起的[27]。这表明,在该频段Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4的磁损耗形式不是交换共振。由此可见,掺杂比例影响镍钴铁氧体的磁损耗形式。
绘制的Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4样品衰减常数与频率的关系曲线,其中α为衰减常数。可见,样品Ni0.1Co0.9Fe2O4、Ni0.3Co0.7Fe2O4、Ni0.7Co0.3Fe2O4、Ni0.9Co0.1Fe2O4在1.00~18.00 GHz频区尽管出现了波动但是不明显。而样品Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4的衰减常数最高,频率为17.32 GHz处达到了187.62。这表明,Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4的衰减常数较高。
图6
图6
Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4样品的衰减常数和频率曲线
Fig. 6
Curve of the Ni x Co1 - x Fe2O4 sample attenuation constant and frequency
图7
图7
Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4样品的阻抗匹配、反射损耗和频率曲线
Fig.7
Impedance matching, reflection loss and frequency curves of Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 samples
绘制的Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4样品的阻抗匹配图。可以看出,样品Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4的吸波效果最好且衰减常数最大,因此本文只讨论不同厚度的样品Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4的阻抗匹配图。从图7可见,样品Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4在吸收层厚度3 mm、频率为17.32 GHz时反射损耗值最小为-16.15 dB,此时阻抗匹配值Z为1.34,相比于其它反射损耗最小值时,对应频率下的阻抗匹配值更接近于1。这也验证了Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4在吸波效果最好的频率处不仅衰减常数较大且阻抗匹配更接近1。
3 结论
(1) 在溶液的pH值为7、柠檬酸与金属离子摩尔比为1∶1、晶化温度为950 ℃,晶化时间为3 h的条件下,可制备出晶粒尺寸为66~70 nm的纯相尖晶石型镍钴铁氧体。
(2) Ni2+∶Co2+ = 0.5∶0.5的镍钴铁氧体吸波性能最好。在吸收层厚度为3.0 mm、频率为17.32 GHz处, 反射损耗最小,为-16.15 dB,有效吸收频带为2.21 GHz (15.79 ~18.00 GHz)。
(3) Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4铁氧体在整个频段内的损耗以磁损耗为主,其机制是涡流损耗和交换共振损耗。
参考文献
An optical sensor with wide measurement range for the magnetic field detection
[J].
A sustainable and low-cost route to design FeNi alloy/carbon-decorated coal fly ash with enhanced microwave absorption
[J].
Stealth technology: methods and composite materials—a review
[J].
Comparative study of microwave absorption properties of Ni–Zn ferrites obtained from different synthesis technologies
[J].
Feasibility of as-prepared reticulated porous barium titanate without additional radar-absorbing material coating in potential military applications
[J].
Attapulgite coated polycrystalline iron fibers composites with light weight feature and enhanced microwave absorption properties
[J].
Preparation of FeSiAl–Fe3O4 reinforced graphene/polylactic acid composites and their microwave absorption properties
[J].
EM wave absorption of NiCuCoZn ferrites for use in ultra-high-frequency applications
[J].
Investigation of corrosiveness biodiesel blends using polypyrrole chitosan-cobalt/ferrite nanocomposite
[J].
The impact of Ba substitution on high-temperature transport in lanthanum-strontium ferrite
[J].
Properties and microstructure of oxide dispersion strengthened tungsten alloy prepared by liquid-phase method: a review
[J].
Research progress of hydrothermal preparation and properties for spinel ferrite/titanium dioxide composites
[J].
尖晶石型铁氧体/TiO2复合材料的水热法制备及性能研究进展
[J].
Study on microwave absorption properties of nanometer Ni0.5Zn0.5-Ce x Fe2 - x O4 ferrite by chemistry co-precipitation method
[J].
化学共沉淀法制备的纳米Ni0.5Zn0.5Ce x -Fe2 - x O4铁氧体微波吸收特性研究
[J].采用化学共沉淀法制备了纳米Ni<sub>0.5</sub>Zn<sub>0.5</sub>Ce<sub>x</sub>Fe<sub>2-x</sub>O<sub>4</sub>(x=0,0.005,0.01,0.015)铁氧体吸波材料,用AV3618型微波矢量网络分析仪测试了样品在8.2~12.5GHz范围内的微波吸收特性,实验结果表明:稀土元素铈的含量影响材料的吸波性能,当x=0.01时,纳米Ni<sub>0.5</sub>Zn<sub>0.5</sub>Ce<sub>x</sub>Fe<sub>2-x</sub>O<sub>4</sub>铁氧体的吸波性能最佳.对于Ni<sub>0.5</sub>Zn<sub>0.5</sub>Ce<sub>0.01</sub>Fe<sub>1.99</sub>O<sub>4</sub>铁氧体吸波材料,当涂层厚度为1mm时,在测试频段内有三个吸收峰,在8.8GHz处,其最大吸收衰减量为15.4dB,10 dB以上带宽达3.8GHz,适量掺杂稀土元素铈是提高镍锌铁氧体吸波材料性能的一种有效途径.
Ultralight coral-like hierarchical Fe/CNTs/Porous carbon composite derived from biomass with tunable microwave absorption performance
[J].
Fabrication of core-shell NiFe2O4@C@PPy composite microspheres with efficient microwave absorption properties
[J].
Preparation and microwave absorbing property of cobalt and nickel ferrite nanopowders
[J].
纳米钴、镍铁氧体的制备与吸波性能
[J].
Dielectric behavior of Zr4+ doped MgFe2O4 spinel ferrite synthesized by solid-state reaction method
[J].
Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Gd-Co ferrite@carbon core-shell structure composites
[J].
Design of ultralight and stable Ti3C2T x /SiCnw hybrid aerogel with hierarchical structure and heterogeneous interface for electromagnetic wave absorption
[J].
Influence of doping with metal ions Co2+, Mn2+ and Cu2+ on absorbability of nano Ni-Zn ferrite
[J].
三种金属离子掺杂对纳米镍锌铁氧体吸波性能的影响
[J].应用水热法将Co<sup>2+</sup>、Mn<sup>2+</sup>和Cu<sup>2+</sup> 掺杂到纳米镍锌铁氧体粉末中,使用XRD、TEM和VNA等手段对其进行表征和分析,研究了掺杂不同金属离子对样品的粒度、形貌、电磁损耗性能以及吸收性能的影响。采用水热法制备纳米钴镍锌铁氧体纯相,以提高Co<sup>2+</sup>的含量。结果表明:掺杂后纳米镍锌铁氧体颗粒的结构由球形转变为不规则四边形,平均粒径增加到35~60 mn。掺杂Co<sup>2+</sup>后,晶格常数由0.8352增加到0.8404。掺杂Co<sup>2+</sup>改变了反射率与频率的关系曲线中吸收峰的位置,增大了吸收器的带宽,提高了材料的低频吸波性能。Mn<sup>2+</sup>的掺杂比例影响晶格常数的大小,但是纳米晶粒容易团聚,并且没有提高电磁损耗吸波性能反而降低。掺杂Cu<sup>2+</sup>仍然出现团聚,当掺杂量为0.15(原子分数)时吸波性能较为优异。
Preparation and properties of nickel substituted cobalt ferrite hollow microspheres
[J].
纳米镍钴铁氧体空心微球的制备与性能
[J].
Structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of aluminum substituted Co-Cu-Zn nano-crystalline ferrites
[J].
CNTs-improved electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Sr-doped Fe3O4/CNTs nanocomposites and physical mechanism
[J].
Effect of Mn substitution on structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Co2Y hexagonal ferrite
[J].
Exceeding natural resonance frequency limit and enhanced microwave absorption performance of Fe3O4 nanorods coated with SiO2 layer
[J].
Preparation and soft magnetic properties of FeNi@Al2O3 composites
[J].
Efficient electromagnetic wave absorption performances dominated by exchanged resonance of lightweight PC/Fe3O4@PDA hybrid nanocomposite
[J].
Investigating the synergistic impedance match and attenuation effect of Co@C composite through adjusting the permittivity and permeability
[J].
Heterostructured C@Fe3O4@FeSiCr composite absorbing material derived from MIL-88(Fe)@FeSiCr
[J].
First-principles investigations on MXene-blue phosphorene and MXene-MoS2 transistors
[J].
ZnFe2O4@SiO2@Polypyrrole nanocomposites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties in the K and Ka band regions
[J].