石油的溢漏以及工业生产和日常生活中含油污水的排放,使环境受到严重的污染。生物降解法、直接燃烧法、化学试剂分散法以及物理吸附法,可用于治理含油污水,但是其效率低、成本高并可能造成二次污染。近年来,具有特殊润湿性的油水分离材料(如海绵、织物、金属网、凝胶和固体颗粒等)受到了极大的重视[1~11]。超疏水海绵具有优异的吸附性能、良好的重复使用性能,但是制备方法复杂、原料昂贵,且其循环使用性能尚需提高[1~4]。廉价易得的聚氰胺甲醛海绵(MS),具有较高的孔隙率、良好的亲水亲油能力和优异的力学性能。聚氰胺甲醛海绵表面丰富的NH-和N原子基团,可与表面改性物质生成氢键,使其与表面改性结构间具有良好的粘附性[12]。
可用低表面自由能物质修饰,以构建超疏水表面。常用的低表面能改性材料,有含氟原料、聚硅氧烷和含长碳链物质[18~20]。近年来,用苯并噁嗪制备超疏水表面受到了极大的关注[5,12,13,21~25]。苯并噁嗪是一种新型酚醛树脂,开环聚合后得到的聚苯并噁嗪具有良好的热、机械性能和优异的耐化学腐蚀性,丰富的分子内和分子间氢键使其表面能降低[5,12,13,21~25]。同时,聚苯并噁嗪结构中的酚羟基和N原子可与MS中的NH、N等生成氢键,还能与ZnO中的Zn2+及其表面羟基形成配位键和氢键。可用酚、伯胺和甲醛进行Mannich反应制得苯并噁嗪,且有灵活的分子设计性。研究表明,引入长碳链结构可使材料具有较高的疏水性,还能提高聚苯并噁嗪的韧性[24]。良好的韧性,使改性海绵表面的聚苯并噁嗪受到挤压、摩擦时不易破碎和脱落。鉴于此,本文用ZnO对MS进行表面改性,使用腰果酚和十二胺等可再生原料制备腰果酚/十二胺型苯并噁嗪(Cd-D),并以其作为低表面能物质和粘合剂对MS进行超疏水改性,研究其吸油性能、油水分离性能、重复使用和耐酸碱性能。
1 实验方法
1.1 实验用原料
实验用材料有:无水乙醇、甲醇、甲苯、二氯甲烷、三氯甲烷、正己烷、二水合醋酸锌、六次甲基四胺(HMTA)、氢氧化钠、六水合硝酸锌、十二胺、腰果酚、三聚氰胺甲醛海绵、豆油以及润滑油。
1.2 腰果酚-十二胺型苯并噁嗪(Cd-D)的制备
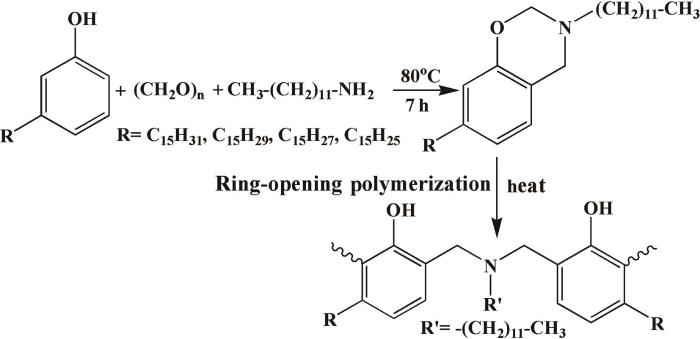
图1
图1
Cd-D的合成路线及其固化物(PCd-D)结构
Fig.1
Synthetic route of Cd-D and structure of the cured Cd-D (PCd-D)
FT-IR(KBr压片测试):2927、2855 cm-1(CH3-、CH2-吸收峰),1617、1578、1462 cm-1(苯环骨架振动吸收峰),1237 cm-1(C-O-C不对称伸缩振动吸收峰), 1117 cm-1(C-N吸收峰),962 cm-1(噁嗪环特征峰)。1H NMR(TMS做内标,CDCl3为溶剂,300 MHz,δ ppm):0.92~2.80(腰果酚侧链和十二胺碳链上的H原子),3.96、4.92(噁嗪环Ar-CH2-N-和-O-CH2-N-中的H),5.45、5.85(腰果酚侧链上-CH2=CH上的H),6.65~6.90(苯环上的H)。
1.3 超疏水海绵的制备
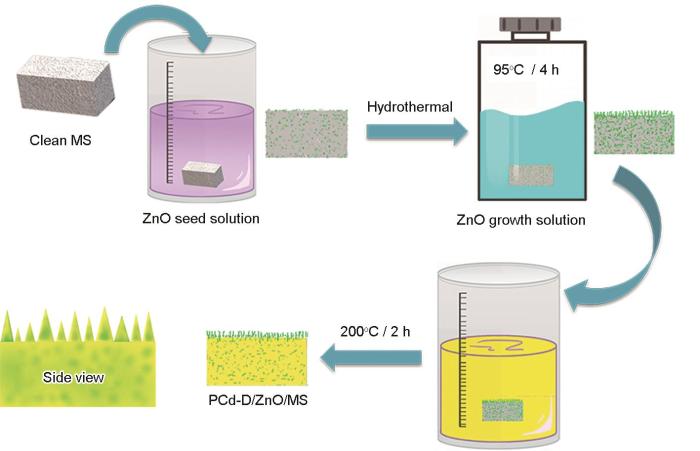
依次用无水乙醇和去离子水将海绵(尺寸为1 cm × 1 cm × 1.5 cm)超声清洗,然后在60℃真空干燥4 h后得到干净的海绵。将0.03 mol/L NaOH-甲醇溶液缓慢滴入0.01 mol/L Zn(CH3COO)2-甲醇溶液中,然后在60℃恒温搅拌2 h得到种子溶液。将干净海绵置于种子溶液中搅拌10 min,取出后在175℃烘10 min,重复3次得到ZnO种子海绵。接着将六次甲基四胺溶液缓慢滴入0.03 mol/L Zn(NO3)2溶液中,然后将其与ZnO种子海绵置于95℃的反应釜中恒温反应4 h,用去离子水与无水乙醇冲洗产物后,将其在120℃干燥3 h,得到ZnO/MS海绵。最后将ZnO/MS海绵在Cd-D溶液中浸泡30 min,取出后在200℃固化2 h,得到ZnO和PCd-D改性的超疏水海绵(PCd-D/ZnO/MS)。
实验中苯并噁嗪溶液中Cd-D的质量为海绵的15%。制备流程如图2所示。
图2
1.4 性能表征
用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察海绵改性前后的表面形貌,样品抽真空后进行喷金处理。用型号为Bruker D8 ADVANCE X射线衍射仪测试XRD谱,测试条件为Cu Kα(λ = 0.15418 nm)射线,步长0.01°。用型号为ESCALAB 250Xi的X光电子能谱仪测试海绵表面的化学成分。用接触角测量仪(JC2000C1)测量海绵表面的接触角,测三块海绵6个以上不同部位,取其结果的平均值,测试水滴的大小为5 μL。将干净海绵(Ma)浸泡在油类或有机溶剂中至饱和吸附后,取出后置于不锈钢网上至无液体自由滴落时进行称重(Mb),每种样品重复三次取结果的平均值。吸油量(K)为
PCd-D/ZnO/MS吸油至饱和后,用500 g砝码将吸收的油挤出以模拟实际油水分离中的吸收-挤压操作,重复操作100次,以评定改性海绵的循环使用性能。将PCd-D/ZnO/MS置于HCl (pH = 1)、NaOH (pH = 13)和3.5% (质量分数) NaCl溶液中,测试改性MS在不同时间段内的接触角,研究其耐酸、碱、盐性能。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 ZnO的制备方法对改性MS疏水性的影响
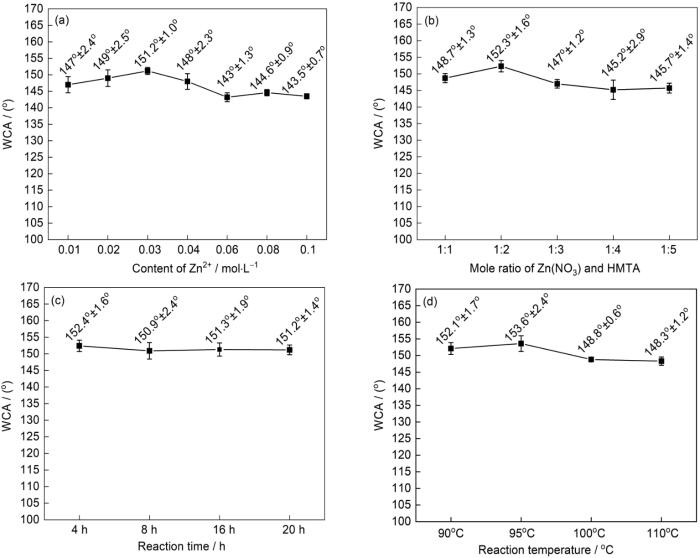
图3
图3
Zn(NO3)2、Zn(NO3)2与HMTA摩尔比、反应时间以及反应温度对PCd-D/ZnO/MS水接触角(WCA)的影响
Fig.3
Effect of Zn(NO3)2 concentration (a), mole ratio to Zn(NO3)2 and HMTA (b), reaction time (c) and reaction temperature (d) on the water contact angle (WCA) of PCd-D/ZnO/MS
图3a给出了Zn(NO3)2浓度变化(0.01~0.1 mol/L)对改性海绵WCA的影响。Zn(NO3)2与HMTA的摩尔比为1∶2、反应温度为95℃、反应时间为4 h及苯并噁嗪溶液中溶质的质量为MS的15%。可以看出,随着Zn(NO3)2浓度的提高PCd-D/ZnO/MS的WCA呈先增大后减小的趋势,Zn(NO3)2浓度为0.03 mol/L时WCA达到最大值(151.2°)。Zn(NO3)2浓度为0.03 mol/L、反应温度为95℃、时间为4 h,改变Zn(NO3)2与HMTA的比例时,所得改性海绵的WCA如图3b所示。可以看出,PCd-D/ZnO/MS的WCA随着HMTA浓度先增大后减小,Zn(NO3)2与HMTA的摩尔比为1∶2时WCA最大(152.3°)。
图3c、d给出了反应时间和温度对PCd-D/ZnO/MS疏水性的影响,Zn(NO3)2浓度为0.03 mol/L、Zn(NO3)2与HMTA的摩尔比为1∶2。水热反应温度为95℃时,反应时间对PCd-D/ZnO/MS海绵疏水性的影响如图3c所示。可以看出,反应时间为4 h时改性MS的WCA最大(152.4°)。在4~20 h范围内反应时间对改性海绵WCA的影响较小(变化在±1°内),即对海绵表面粗糙度的影响较小。图3d给出了反应时间为4 h时,反应温度(90~110℃)对改性MS疏水性的影响。水热反应反应温度为95℃时PCd-D/ZnO/MS的WCA接触角最大(153.6°)。鉴于此,后续制备超疏水PCd-D/ZnO/MS的实验条件为:Zn(NO3)2浓度为0.03 mol/L、Zn(NO3)2与HMTA的摩尔比为1∶2、反应时间为4 h和温度为95℃。
2.2 超疏水PCd-D/ZnO/MS的表面形貌和成分
2.2.1 超疏水海绵PCd-D/ZnO/MS的形貌
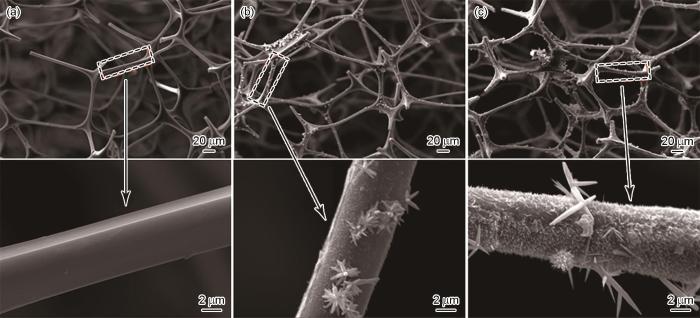
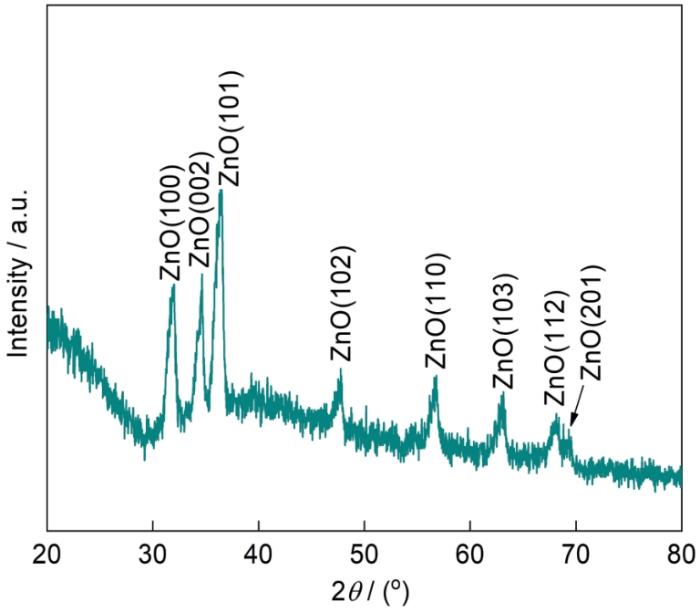
图4给出了原始MS、ZnO改性海绵(ZnO/MS)和超疏水海绵PCd-D/ZnO/MS的SEM照片。从图4a可以看出,原始MS呈三维多孔结构,海绵骨架表面光滑。图4b表明,用水热法制备的ZnO改性MS骨架的表面粗糙,表面均匀覆盖了一层纳米级ZnO纳米线,还有长度为1~4 μm的棒状ZnO。图4c给出了超疏水PCd-D/ZnO/MS的SEM照片。由于ZnO表面覆盖了一层聚苯并噁嗪,可清晰地观察到MS表面生成了一层均匀的ZnO纳米线和ZnO纳米棒。这些结果表明,通过ZnO和Cd-D的改性在海绵表面形成了一层微纳米粗糙结构。还可以看出,反应后MS骨架没有变化,即用水热法和浸涂法制备超疏水MS的过程没有破坏MS的骨架结构。
图4
图4
原始MS、ZnO/MS和PCd-D/ZnO/MS的SEM照片
Fig.4
SEM images of original MS (a), ZnO/MS (b) and PCd-D/ZnO/MS (c)
2.2.2 PCd-D/ZnO/MS的组成
图5
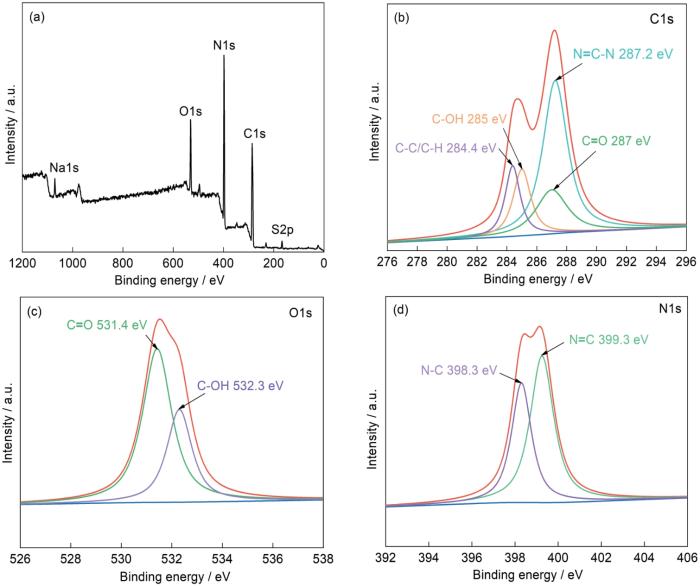
2.2.3 MS改性前后的表面成分
图6和图7给出了用XPS对MS改性前后表面成分的分析。图6a中176.0、290.0、401.9、536.9、1079.9 eV处的峰分别属于S2p、C1s、N1s、O1s、Na1s,其中C、N、O的含量分别为50.38%、38.64%、10.97%,Na、S的含量约为0.01%(来自MS制备过程中添加的含Na、S助剂)。图6b给出了对C1s分峰后的谱图,结合能为284.4、285.0、287.0、287.2 eV的峰分别属于C-C/C-H、C-OH、N-C=N、C=O的C1s。在图6c中,结合能在531.4、532.3 eV处的峰分别属于C=O和C-OH中的O1s。在图6d中,398.3和399.3 eV处的峰分别属于C-N和C=N中的N1s[28]。
图6
图6
原始MS的XPS全图谱、C1s谱图、O1s谱图和、N 1s谱
Fig.6
XPS spectrum (a), C1s high resolution spectrum (b), O1s high resolution spectrum (c) and N 1s high resolution spectrum (d) of original MS
图7
图7
PCd-D/ZnO/MS的XPS全谱图、C1s谱图、O1s谱图和N 1s谱
Fig.7
XPS spectrum (a), C1s high resolution spectrum (b), O1s high resolution spectrum (c) and N 1s high resolution spectrum (d) of PCd-D/ZnO/MS
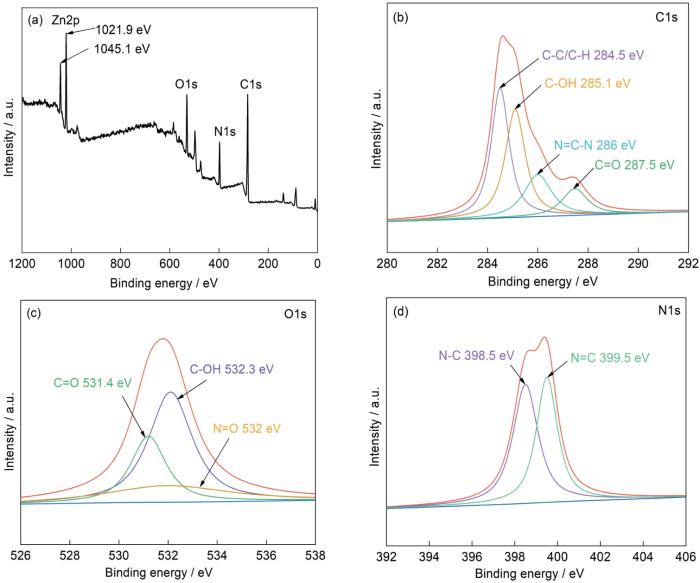
图7给出了超疏水PCd-D/ZnO/MS的XPS测试结果。与图6a相比,除了C1s、N1s和O1s峰外,改性MS在1021.9和1045.1 eV处还出现了属于Zn2p3/2、Zn2p1/2的峰(图7a),进一步证明改性海绵表面有ZnO。此外,PCd-D/ZnO/MS中C、N、O、Zn的含量分别为63.96%、16.12%、15.53%、5.39%。与原始MS相比,改性MS的C和O元素的含量提高,N的含量明显下降。其原因是,PCd-D中C、O、N的含量与MS不同。MS改性前后这些元素含量的变化表明,制备的超疏水海绵表面已经覆盖了一层PCd-D。同时,与初始MS的O1s谱(图6c)相比,在PCd-D/ZnO/MS的532.3 eV处出现了微弱的N=O峰(图7c),这是ZnO生成过程中残留的原料Zn(NO3)2。
表1 MS与PCd-D/ZnO/MS的C1s和N1s解析数据
Table 1
| Samples | Content of C / % | Content of N / % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C/C-H | C-O | N=C-N | C=O | N-C | N=C | |
| MS | 14.98 | 16.37 | 51.02 | 17.63 | 40.45 | 59.55 |
| PCd-D/ZnO/MS | 37.18 | 34.44 | 10.94 | 17.44 | 52.28 | 47.72 |
2.3 分离油水的性能
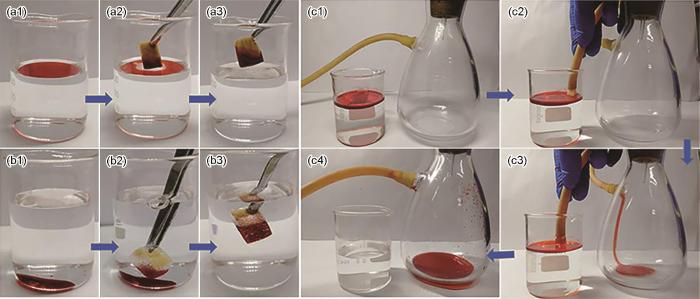
为了检测MS改性前后油水亲和力的改变,先将原始MS和超疏水PCd-D/ZnO/MS分别置于水面,结果如图8a、b所示。由于具有良好的亲水性,原始海绵立即沉入水底(图8a)。浮在水面的PCd-D/ZnO/MS在外力作用下没入水中时,在水与改性MS之间形成了一层致密的空气膜,使其表面出现一层“银镜”现象(图8b)。空气膜阻挡了水向海绵内部的渗透。 将水(亚甲基蓝染色)和大豆油(油红染色)分别滴在原始MS和PCd-D/ZnO/MS表面,以进一步观察海绵改性前后润湿性的转变。结果表明,水滴和原始MS表面接触时,水滴立即被吸收(图8c,WCA为0°);当水滴滴在PCd-D/ZnO/MS表面时,水滴立于其表面且近似球形(图8d,WCA为153.6°),表现出超疏水性。将粘度较大的大豆油滴在海绵表面时,大豆油慢慢渗入原始海绵,而油滴立即被改性海绵所吸收。其原因是,PCd-D结构中的长碳链使改性海绵展现出了超亲油性。这表明,经过ZnO和苯并噁嗪改性后,原始MS不仅由亲水性转变为超疏水性,海绵的亲油性能也明显提高。
图8
图8
MS和PCd-D/ZnO/MS在水中的照片、水和大豆油滴在MS和PCd-D/ZnO/MS的表面状态
Fig.8
Photos of MS (a) and PCd-D/ZnO/MS (b)in water, water droplets and soybean oil droplets on the surface of MS (c) and PCd-D/ZnO/MS (d)
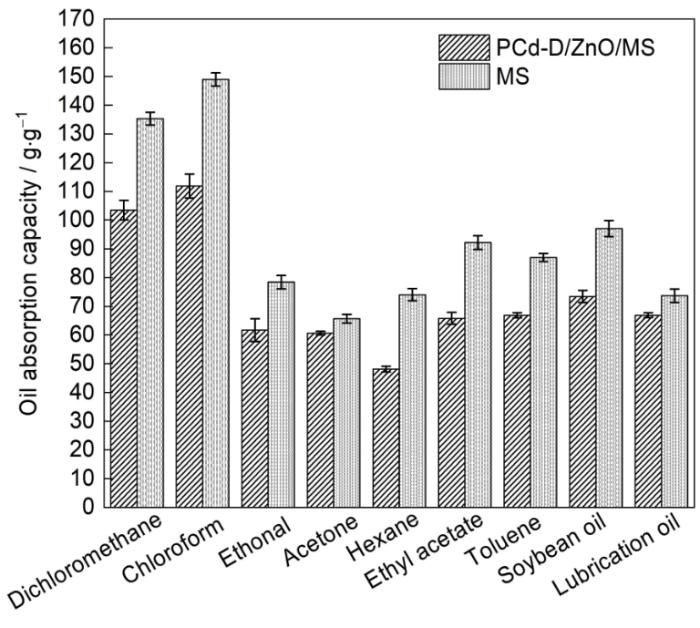
图9给出PCd-D/ZnO/MS对多种有机溶剂和油类的吸附和原始MS的吸油量。可见,PCd-D/ZnO/MS对这些有机溶剂和油类的吸附量均低于原始MS,其原因是PCd-D和ZnO覆盖在MS骨架上使海绵的孔隙率降低。尽管如此,PCd-D/ZnO/MS仍具有较高的吸油量。PCd-D/ZnO/MS对这些有机溶剂或油类的吸油量为48.19~113.44 g/g,对氯仿的吸附量最大(可达113.44 g/g),与近几年来报道的其他超疏水海绵的性能相当[1,2,5,12,29~32]。超疏水海绵对不同油类的吸油量,主要取决于油类的密度和粘度。油类的密度越大、粘度越高,海绵对其吸附量也越大。例如PCd-D/ZnO/MS对氯仿(ρ = 1.5 g/cm3)的吸油量高达113.44 g/g,而对正己烷(ρ = 0.66 g/cm3)的吸油量只有48.19 g/g;对大豆油(粘度为50.10 mm2/s)的吸油量为73.41 g/g,明显高于正己烷(粘度为3.10 mm2/s)。
图9
图9
PCd-D/ZnO/MS对不同有机溶剂和油类的吸附能力
Fig.9
Adsorption capacity of PCd-D/ZnO/MS to different organic solvents and oils
图10
图10
PCd-D/ZnO/MS分离甲苯/水混合物和二氯甲烷/水混合物以及PCd-D/ZnO/MS对大豆油/水混合物的连续分离
Fig.10
Separation of toluene/water mixture (a1~a3) and dichloromethane/water mixture (b1~b3) by PCd-D/ZnO/MS and continuous soybean oil/water separation processes of PCd-D/ZnO/MS (c1~c4)
2.4 机械和化学稳定性
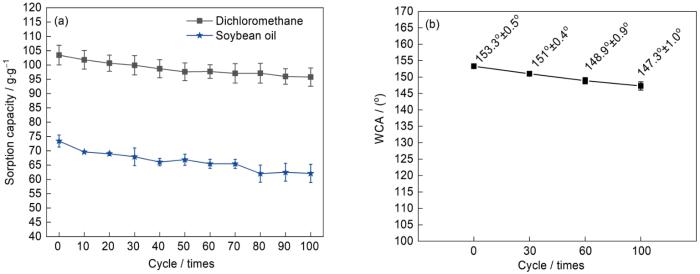
在油水分离过程中,海绵受到挤压、摩擦等各种机械作用,超疏水表面结构逐渐脱落,使改性海绵的疏水性不断下降。以粘度差异较大的大豆油和二氯甲烷(粘度为0.43 mm2/s)为例,通过重复的“吸附-挤压”操作,研究PCd-D/ZnO/MS的机械稳定性,结果如图11所示。图11a表明,随着重复使用次数的增加改性海绵的吸油量缓慢下降。在第30次循环吸油后,对二氯甲烷的吸附量从最初的103.44 g/g下降到99.89 g/g;对豆油的吸附量,从开始的73.41 g/g下降至67.90 g/g。重复使用100次后,对二氯甲烷的吸附量下降了7.40%;对豆油的吸附量下降了15.40%。随着循环使用次数的增加,PCd-D/ZnO/MS对豆油吸附量的下降值明显比二氯甲烷大。其原因是,豆油的粘度较大,用简单的挤压不能充分除去豆油。重复吸附二氯甲烷后的改性海绵的接触角,如图11b所示。可以看出,重复使用30次后仍然保持超疏水状态,循环使用100次后的WCA也高达147.3°±1°,表明PCd-D/ZnO/MS具有优异的循环使用性能,优于或相当于其他超疏水海绵的循环使用性能[1,2,12,29~32]。PCd-D/ZnO/MS优异的可重复使用性,源于其表面改性结构与MS骨架之间的多种化学物理作用。ZnO表面的-OH可与PCd-D中的-OH、N以及MS中的NH、N结构形成氢键,PCd-D与MS之间也能形成大量的氢键;同时,ZnO中的Zn2+还能与PCd-D和MS中的N、O形成配位键,MS中的NH-也能与PCd-D开环聚合过程中形成的中间体发生亲核反应[21,22]。这些作用,使ZnO和PCd-D牢固地粘附在MS表面。
图11
图11
PCd-D/ZnO/MS循环使用不同次数后的吸油量和水接触角
Fig.11
Oil absorption capacity (a) and WCA (b) of PCd-D/ZnO/MS after different recycle times
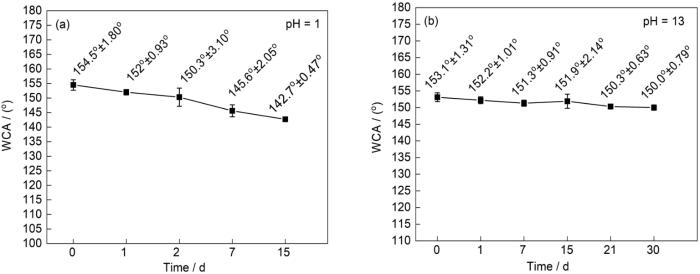
在实际应用中,油水混合物中常处于酸性、碱性或者海水环境中。这些腐蚀性溶液会破坏超疏水材料表面,使其润湿性改变和分离效率的降低。将PCd-D/ZnO/MS分别浸泡在盐酸(pH = 1)和氢氧化钠溶液(pH = 13)中,浸泡不同时间后WCA的耐酸碱腐蚀性能,如图12所示。由图12a可见,在盐酸溶液中浸泡2 d后PCd-D/ZnO/MS的WCA略有下降,仍保持超疏水性(WCA为150.3°);随着浸泡时间的延长其WCA逐渐下降,但是浸泡15 d后仍表现出较高的疏水性(WCA为142.7°)。图12b表明,PCd-D/ZnO/MS在强碱溶液中浸泡30 d后仍保持超疏水状态(WCA为150.0°)。这表明,PCd-D/ZnO/MS具有优异的耐酸碱腐蚀性能,因为表面覆盖的聚苯并噁嗪具有优异的耐酸碱腐蚀性能。改性海绵在NaCl溶液浸泡2 d后仍处于接触角未150°的超疏水状态,在去离子水中浸泡30 d后接触角几乎不变。这些结果表明,PCd-D/ZnO/MS具有优异的耐酸、碱和耐盐性能。
图12
图12
PCd-D/ZnO/MS在HCl和NaOH溶液中浸泡不同时间后的WCA
Fig.12
WCA of PCd-D/ZnO/MS soaked in HCl (a) and NaOH solutions (b) for different time
3 结论
(1) 先用水热法在MS表面构建一层ZnO微-纳米结构,然后用浸涂法将腰果酚-十二胺型苯并噁嗪覆盖在ZnO/MS表面,可制备超疏水海绵PCd-D/ZnO/MS。当水热反应中Zn(NO3)2的浓度为0.03 mol/L、Zn(NO3)2与HMTA的摩尔比为1∶2、反应时间和温度分别为4 h和95℃时,制备出的超疏水MS的WCA最高。
(2) PCd-D/ZnO/MS对有机溶剂和油类有着良好的吸附能力,且其吸油速率极高。
(3) PCd-D/ZnO/MS具有优异的重复使用性能,还具有优异的耐酸、碱和海水腐蚀性能。
参考文献
Facile one-step fabrication of superhydrophobic melamine sponges by poly(phenol-amine) modification method for effective oil-water separation
[J].
Lignin-based superhydrophobic melamine resin sponges and their application in oil/water separation
[J].
Preparation of magnetic, superhydrophobic/superoleophilic polyurethane sponge: separation of oil/water mixture and demulsification
[J].
Fe3O4/PDMS modified collagen sponge and its oil-water separation performance
[J].
Fe3O4/聚二甲基硅氧烷改性胶原海绵及其油水分离性能
[J].
Fabrication of sustainable and durable bio-polybenzoxazine based superhydrophobic cotton fabric for efficient oil/water separation
[J].
Superhydrophobic cotton fabric based on polydopamine via simple one-pot immersion for oil water separation
[J].Superhydrophobic fabric was fabricated by dipping the cotton fabric into ethanol solution of dopamine, silver nitrate and hexdecyltrimethoxysilane followed by bakingdry, and of which the surface morphology and chemical composition were characterized by scanning electron microscope and x-ray photoelectron spectroscope, respectively. Surface wettability was measured by contact angle meter. Durability was assessed by abrasion or immersion in different aqueous solutions of acid, alkali, or boiling water. Results show that the in-situ-generated Ag particles were retained after abrasion or immersion test due to the high adhesion of polydopamine; thus, the so-obtained superhydrophobic fabric possessed good durability. Moreover, the superhydrophobic fabric showed good oil-water separation performance with oil-water separation efficiency up to 97% and oil flow up to 15.93 m3·m-2·h-1.
基于聚多巴胺的超疏水棉织物的一锅法制备及其油水分离性能
[J].将棉织物浸入多巴胺、硝酸银、十六烷基三甲氧基硅烷的乙醇溶液中,取出烘干制备出超疏水棉织物。用扫描电子显微镜和X射线光电子能谱表征其表面形貌和元素,用接触角测量仪测量其接触角并进行摩擦或液体浸泡(如酸、碱、沸水)实验检测其耐用性。结果表明,聚多巴胺的强附着性使原位生成的银纳米粒子能经受摩擦或不同液体的浸泡,从而使超疏水织物具有良好的耐用性。超疏水棉织物还具有良好的油水分离性能,其油水分离效率高达97%,油流量最高可达15.93 m<sup>3</sup>·m<sup>-2</sup>·h<sup>-1</sup>。
Dual-functional underliquid superhydrophobic and superoleophobic stainless steel mesh decorated with Ni3S2 nanorods for continuous oil/water separation
[J].
Facile construction and fabrication of a superhydrophobic copper mesh for ultraefficient oil/water separation
[J].
Fabrication of superhydrophobic/oleophilic starch cryogel via a simple sol-gel immersion process for removing oil from water
[J].
Biochar adsorbents with enhanced hydrophobicity for oil spill removal
[J].
Preparation and properties of superhydrophobic-superoleophilic sand for oil-water separation
[J].
用于油水分离的超疏水-超亲油沙子的制备及其性能
[J].
A sustainable strategy for remediation of oily sewage: Clean and safe
[J].
A robust polybenzoxazine/SiO2 fabric with superhydrophobicity for high-flux oil/water separation
[J].
Chemically stable superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge coated with ZnO/epoxy resin coating for effective oil/water separation
[J].
A compound of ZnO/PDMS with photocatalytic, self-cleaning and antibacterial properties prepared via two-step method
[J].
One-pot synthesis of fluorine functionalized Zr-MOFs and their in situ growth on sponge for oil absorption
[J].
Facile surface treatment and decoration of graphene-based 3D polymeric sponges for high performance separation of heavy oil-in-water emulsions
[J].
Chitosan/sodium polyborate based micro-nano coating with high flame retardancy and superhydrophobicity for cotton fabric
[J].In this work, a sustainable flame retardant and superhydrophobic cotton fabric was prepared by a two-step process: the cotton fabric was firstly treated with a chitosan/sodium polyborate polyelectrolyte complex water solution to obtain a flame retardant layer, and then treated with a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) tetrahydrofuran solution to construct a superhydrophobic layer. The phase-separated chitosan with a micro-nano roughness structure was covered by PDMS, which synergistically improved the hydrophobicity of the cotton fabric. The flammability evaluation indicated that the limiting oxygen index value of the treated fabric was increased to 40.0% from 18.2%, the peak of heat release rate was reduced by 63.8%, and the total heat release was reduced by 57.6% compared with that of the control sample. The enhanced flame retardancy was attributed to the excellent charring ability in the condensed phase. The treated fabric also showed anti-sticking, self-cleaning, and oil/water-separating properties. This coating treatment without any F, Cl, Br, P elements involved is regarded as a clean methodology for producing flame retardant and superhydrophobic cotton fabrics.Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
One-step dipping fabrication of Fe3O4/PVDF-HFP composite 3D porous sponge for magnetically controllable oil-water separation
[J].
Preparation and properties of sepiolite superhydrophobic composite coatings
[J].The suspension of sepiolite powder in the mixture of anhydrous ethanol, ammonia and ethyl orthosilicate was first prepared and then coupling modified with surfactant in varying process conditions. Further, the modified sepiolite powder was acquired from the prepared suspension by means of ultrasonic assisted stirring, centrifugal dehydration, washing, drying and grinding successively. The modified sepiolite powder was dispersed in anhydrous ethanol and applied on the surface of glass slide to prepare a thin superhydrophobic coating. The contact angle (CA) and rolling angle (SA) of the coating with water were measured by using OCA 20 contact angle tester, the structure of functional groups on the surface of powders before and after modification was analyzed by Bruker-80V Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, the changes of elements on the surface of powders before and after modification were analyzed by Escalab 250XI X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, the micromorphology of the powders before and after modification was observed by Nova Nano SEM450 and JEM-1230 transmission electron microscopy, and the properties of sepiolite superhydrophobic composite coating were investigatied. The results show that: when the modification is carried out at 0℃ for 3 h, with 1 g of sepiolite powder as raw material and 0.8 mL of cetyltrimethoxy silane as modifier. A coating made of the modified sepiolite powder presents a contact angle of 157.2° with a rolling angle of 10.5°. During modification process SiO2 particles were adsorbed on the surface of sepiolite to create a rough surface, which was grafted with long chain alkyl groups of cetyltrimethoxy silane. The adhesion of water droplets to the coating surface decreases rapidly first and then slowly with the increase of the volume of water droplets. Due to the weak adhesion of water droplets to the coating, the water droplets can easy roll on the coating surface, so that resulted in good self-cleaning performance of the coating.
海泡石超疏水复合涂层的制备和性能
[J].
Preparation of a main-chain-type polybenzoxazine-modified melamine sponge via non-solvent-induced phase inversion for oil absorption and very-high-flux separation of water-in-oil emulsions
[J].
Durable superhydrophobic melamine sponge based on polybenzoxazine and Fe3O4 for oil/water separation
[J].
Preparation and anticorrosion properties of bio-based polybenzoxazine/cellulose nanocrystals superhydrophobic coating
[J].A bio-based benzoxazine monomer was synthesized by using cardanol, stearylamine and paraformaldehyde as raw materials. Differential scanning calorimetry and infrared spectroscopy were employed to investigate the thermal curing behavior of benzoxazine with tannic acid acting as the curing agent. The results show that tannic acid can effectively reduce the ring-opening curing temperature of benzoxazine. The polybenzoxazine primer was prepared on the surface of carbon steel sheet, and then the topcoat was obtained by adding amino-modified cellulose nanocrystalline. The bio-based superhydrophobic coating (PBTC) was constructed with static water contact angle of 161.1°±2.9°. The superhydrophobic coating exhibits good temperature resistance and scratch resistance. Moreover, the electrochemical measurement results indicated that the PBTC coating could still exhibit excellent corrosion resistance after immersion in NaCl aqueous solution for 30 days.
生物基聚苯并噁嗪/纤维素纳米晶超疏水防腐蚀涂层的制备及性能
[J].以腰果酚、十八胺和多聚甲醛为原料合成出生物基苯并嗪单体,以单宁酸为固化剂,采用差示扫描量热分析技术和红外光谱考察了苯并嗪单体的热固化行为,结果表明单宁酸可以有效降低苯并嗪的开环固化温度。在钢片表面首先制备聚苯并嗪涂层作为底漆,再通过在涂层中掺杂氨基修饰纤维素纳米晶制备面漆,构建出静态水接触角为161.1°±2.9°的生物基超疏水防腐蚀涂层(PBTC)。该超疏水涂层表现出良好的耐高低温性能和耐刮擦性。电化学测试结果表明PBTC涂层在NaCl水溶液中浸泡30天后仍然具有良好的防腐蚀性能。
Eco-friendly stable cardanol-based benzoxazine modified superhydrophobic cotton fabrics for oil-water separation
[J].
Fluorine free bio-based polybenzoxazine coated substrates for oil-water separation and anti-icing applications
[J].
Nylon fibers as template for the controlled growth of highly oriented single crystalline ZnO nanowires
[J].
Sustainable superhydrophobic branched hierarchical ZnO nanowires: stability and wettability phase diagram
[J].
Superhydrophobic MS@CuO@SA sponge for oil/water separation with excellent durability and reusability
[J].
Fluorine-free superhydrophobic covalent-organic-polymer nanosheet coating for selective dye and emulsion separation
[J].Covalent organic polymer nanosheets (COPNs) endowed with porous networks and large surface areas in their structures offer great advantages over other materials in addressing environmental problems. In this study, fluorine-free superhydrophobic COPNs were designed and applied to selective dye absorption. Notably, COPNs selectively adsorb dyes with a high hydrophobic index (HI) and reject low HI dyes with maximum adsorption capacities of 361 and 263 mg/g for crystal violet and methylene blue, respectively. The adsorption isotherm model showed that the COPNs follow the Langmuir adsorption isotherm model and pseudo-second-order kinetics. Next, we explored the superhydrophobicity of the COPNs by in situ fabrication with melamine sponge (COPNs-MS), which incorporates the superhydrophobicity of COPNs [water contact angle (WCA) of >150°] with the structure and flexibility of the MS skeleton. The COPNs-MS shows various oil-adsorbing properties with good adsorption capacity (from 60 to 120 g/g) and also effectively separates various surfactant-stabilized emulsions with a separation efficiency of over 99%. The as-fabricated COPNs-MS retains its superhydrophobicity in various solvents and hazardous conditions (WCA ≥ 150°) and exhibits good flame retardancy and excellent compression properties with excellent antifouling property due to the superhydrophobic COPN coating. Furthermore, COPNs-MS also demonstrates excellent recyclability because the strong COPN coating in the MS skeleton retains its hydrophobicity. Therefore, our fluorine-free superhydrophobic COPNs are not only capable of selective dye adsorption but also exhibit very good oil adsorption and surfactant-stabilized emulsion separation performance.
Superhydrophobic-superoleophilic biochar-based foam for high-efficiency and repeatable oil-water separation
[J].