1 实验方法
1.1 rGO/Fe3O4 的制备
用水热法制备Fe3O4碳基复合材料。将0.27 g六水合氯化铁、0.26 g聚乙二醇和0.9 g乙酸钠置于30 mL的乙二醇中,用磁力搅拌器充分搅拌后加入10 mg氧化石墨烯,超声搅拌0.5 h使其充分分散。将得到的溶液倒入100 mL水热反应釜中,在200℃反应8h。将得到的试样标记为S10。在其它条件不变的情况下分别将氧化石墨烯添加量改变为30、50、70 mg,将得到的试样分别标记为S30、S50、S70;为了对比,制备不添加氧化石墨烯的试样并标记为S0。
1.2 rGO/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料的制备
将环氧树脂加热到110℃使其全部熔融,然后加入rGO/Fe3O4复合物,搅拌均匀后加入酸酐固化剂(添加量是环氧树脂质量的40%)继续搅拌均匀。将得到的共混物浇注到(已在110℃预热)模具中,抽真空脱泡1 h,升温到150℃固化8 h后关闭烘箱,使其自然冷却至室温。得到的试样用于测试吸波性能(180 mm×180 mm×3 mm)和力学性能的(ASTM D 5942-96)。
1.3 性能测试
用MiniFlex600 X射线衍射仪分析测试氧化石墨烯、Fe3O4的晶体结构,用Tecnai F30 透射电镜和Su8010扫描电镜测试试样的晶面间距、微观结构和形貌以及纳米粒子分布。用矢量网络分析仪(Agilent 8720ET)的弓形法测试方法测试氧化石墨烯/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料的吸波性能,用XJJ-50摆锤式简支梁冲击机测试氧化石墨烯/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料的冲击强度。
2 结果和讨论
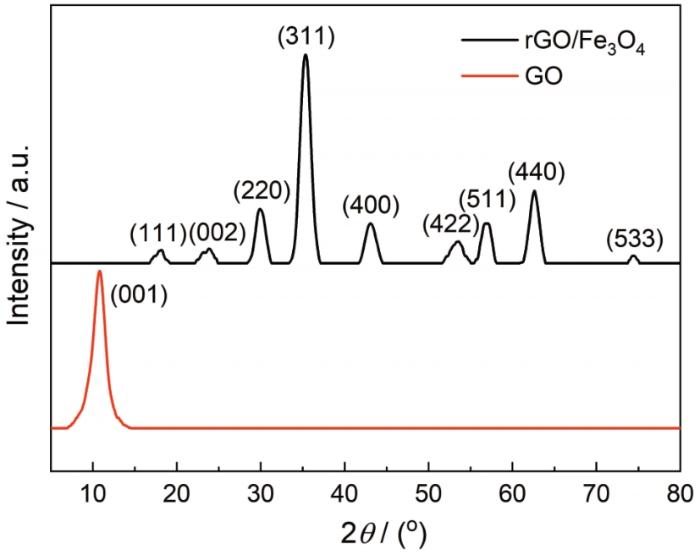
图1给出了氧化石墨烯和S30试样的晶面结构。可以看出,氧化石墨烯的XRD图谱中10.8°处出现一个尖峰,属于氧化石墨烯的(001)峰。使用Bragg方程nλ=2dsinθ计算出氧化石墨烯的层间间距为0.92 nm。在S30的XRD谱图中25.4°处出现一个宽峰,是一个非晶态的峰,而在10.8°处没有出峰。其原因是,在高温下氧化石墨烯的部分含氧官能团被脱除,氧化石墨烯被还原。同时,在S30的XRD谱中的18.3°、30.1°、35.4°、43.1°、53.4°、56.9°、62.5°和74.0°处出现了衍射峰,分别对应Fe3O4的(111)、(220)、(311)、(222)、(400)、(422)、(511)、(440)和(533)晶面。这些结果,与Fe3O4的标准XRD卡(JCPDSNO.65-3107)完全相符。X射线衍射分析结果表明,氯化铁在高温水热反应后得到了Fe3O4颗粒,而氧化石墨烯在高温下部分还原变成了还原氧化石墨烯。
图1
图2
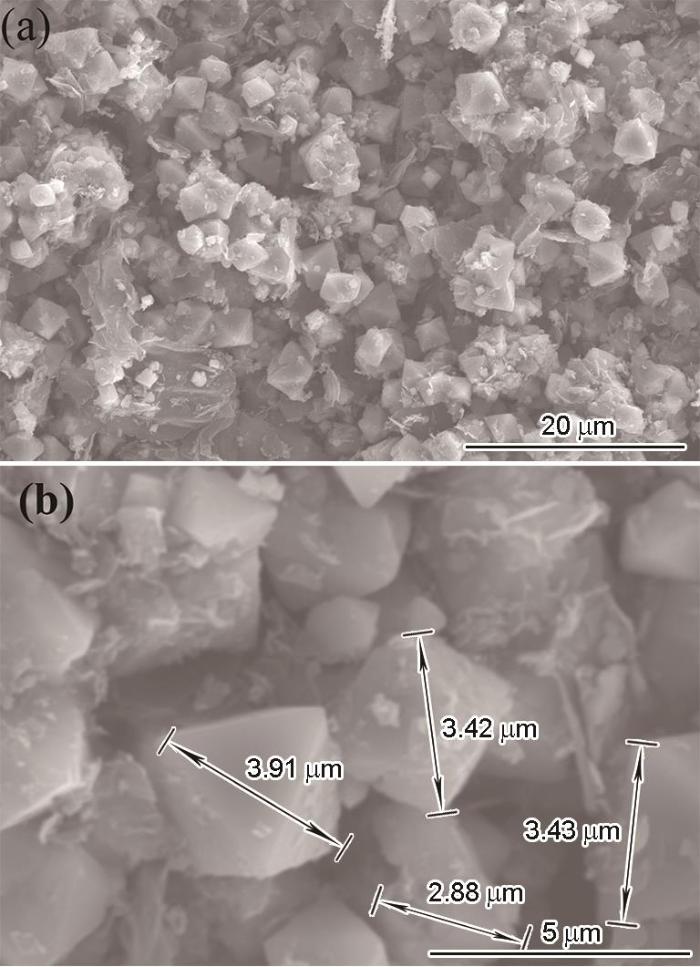
图3给出了S30试样的扫描电镜照片。可以看出,Fe3O4颗粒呈正八面体的形貌,是反尖晶石结构Fe3O4的一种典型形貌,其表面覆盖有还原氧化石墨烯,Fe3O4颗粒的尺寸为2~4 μm。
图3
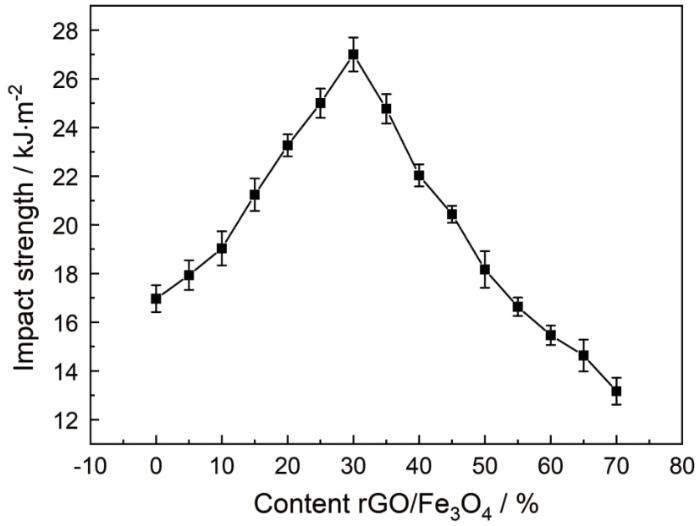
可用冲击强度表征材料的韧性。测试了不同环氧树脂含量的S30试样的冲击强度,以研究rGO/Fe3O4复合物对环氧树脂韧性的影响。参照ASTM D 5942-96标准,测试在 XCJ-4 型简支梁冲击试验机上进行,无缺口样条的尺寸为60 mm×6 mm×4 mm,测试结果如图4所示。可以看出,添加了rGO/Fe3O4复合物的环氧树脂的冲击强度都比纯环氧树脂高。S30添加量为30%的rGO/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料,其冲击强度达到27 kJ/m2,比纯环氧树脂冲击强度提高了58.8%。上述结果表明,rGO/Fe3O4使环氧树脂增韧。其原因是,一方面,Fe3O4作为无机刚性粒子能阻止树脂中微裂纹的扩展;另一方面,还原氧化石墨烯表面大量的羟基、环氧基等活性官能团与环氧树脂和固化剂形成化学键,使rGO和环氧树脂界面间的粘结强度提高,进而提高了环氧树脂的冲击强度。但是,添加过多的rGO/Fe3O4复合物使环氧树脂复合材料的冲击强度下降。其原因是,过多的rGO/Fe3O4不容易均匀分散在环氧树脂中,出现的团聚在环氧树脂基体中产生缺陷而使材料的冲击强度降低。
图4
图4
rGO/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料的冲击强度
Fig.4
Impact strength of rGO/Fe3O4/ epoxy resin composites
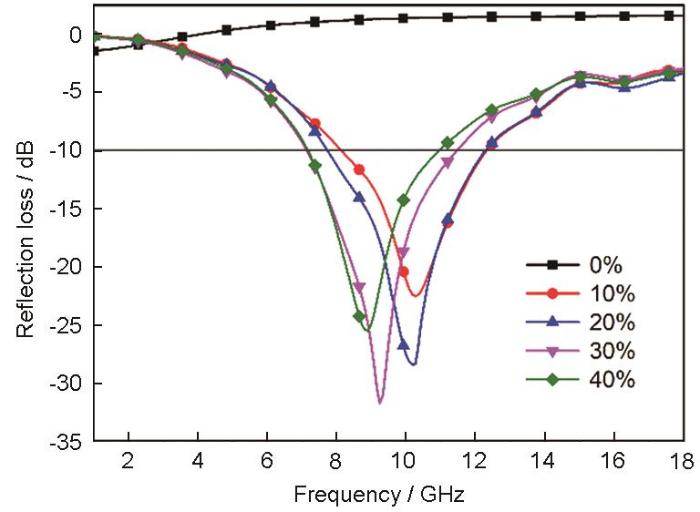
石墨烯、Fe3O4以及它们的复合物都是常用的吸波材料,而纯环氧是一种透波材料。为了研究rGO/Fe3O4复合物对环氧树脂吸波性能的影响,用弓形法测试了rGO/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料的反射率值。图5给出了在环氧树脂中添加不同含量S30试样的反射率。可以看出,未添加rGO/Fe3O4复合物的纯环氧树脂没有吸波性能,添加rGO/Fe3O4复合物使吸波性能显著提高。rGO/Fe3O4复合物添加量为20%时,反射率小于-10 dB的频率范围为7.7~12.3 GHz,有效吸收频宽达4.6 GHz,覆盖了整个X波段。rGO/Fe3O4复合物添加量为30%时,最小反射率达-31.7 dB。表1列出了环氧树脂中添加不同含量S30的吸波性能,包括最小反射率值、反射率小于-10 dB的频率范围和频宽。
图5
图5
S30不同含量复合材料的反射率
Fig.5
Reflectance value with different S30 content in epoxy resin
表1 S30含量不同的复合材料的吸波性能
Table 1
| S30 content in epoxy resin | RLmin/dB | Frequency range/GHz (RL≤-10 dB) | The bandwidth /GHz (RL≤-10 dB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | -1.4 | - | - |
| 10% | -22.5 | 8.1-12.3 | 4.2 |
| 20% | -28.4 | 7.7-12.3 | 4.6 |
| 30% | -31.7 | 7.1-11.5 | 4.4 |
| 40% | -25.5 | 7.2-10.9 | 3.7 |
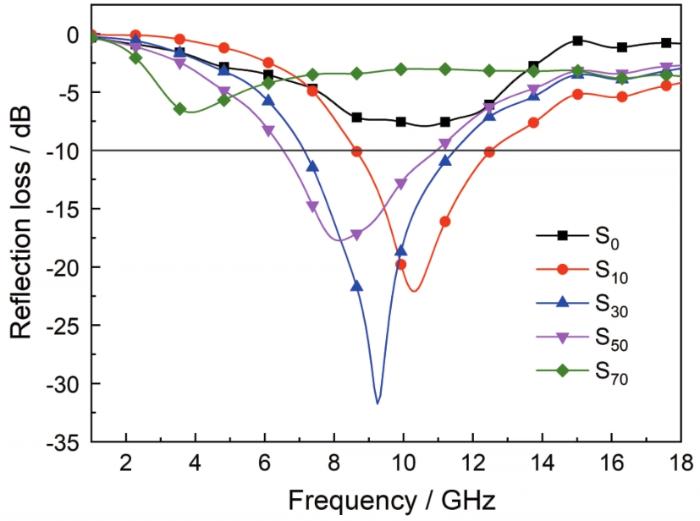
为了研究rGO和Fe3O4颗粒的配比对复合材料吸波性能的影响,分别在环氧树脂中添加30%的S0、S10、S30、S50、S70制备出五组对比样,用弓形法测试其吸波性能。图6表明,只添加Fe3O4颗粒虽然对环氧树脂的吸波性能有提高,但反射率值都大于-10 dB,并且其吸收频段在高频区间,S70样品改性后的环氧树脂吸收频段在低频区间,并且反射率值都大于-10 dB。表2列出了添加S0、S10、S30、S50、S70的环氧树脂复合材料的吸波性能,包括最小反射率值及其对应的频率、反射率小于-10 dB的频率范围和频宽。结果表明,磁性Fe3O4颗粒有利于高频电磁波吸收,介电材料rGO有利于低频电磁波吸收,并且磁性材料和介电性材料有合理的配比。对比S0、S10、S30、S50、S70五个试样改性后环氧树脂复合材料最小反射值出现的频率位置发现,随着石墨烯含量的提高试样达到最小反射率的位置向低频位置移动。其原因是,复合物中石墨烯相对含量提高使Fe3O4的相对含量降低,结果是rGO/Fe3O4复合物的介电常数明显上升,磁导率降低;但是,磁导率与介电常数的乘积呈现升高的趋势。根据四分之一波长公式,磁导率和介电常数的乘积升高,材料的谐振频率降低。因此,随着石墨烯含量的提高试样达到最小反射率的位置向低频位置移动。这表明,控制石墨烯和Fe3O4的相对含量可调控环氧树脂复合材料的吸波性能,使其用于吸收不同频率的电磁波。
图6
图6
添加S0、S10、S30、S50、S70的环氧树脂复合材料的反射率
Fig.6
Reflectance values of epoxy resins composite materials which added S0, S10, S30, S50 and S70
表2 添加有S0、S10、S30、S50、S70的环氧树脂复合材料吸波性能
Table 2
| Samples | The ratio of Fe to rGO | RLmin/dB | Frequency/GHz | Frequency range /GHz(RL≤-10 dB) | The bandwidth /GHz(RL≤-10 dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 56 : 0 | -7.9 | 10.6 | - | - |
| S10 | 56 : 10 | -22.1 | 10.35 | 8.7~12.5 | 3.8 |
| S30 | 56 : 30 | -31.7 | 9.2 | 7.1~11.5 | 4.4 |
| S50 | 56 : 50 | -17.7 | 8.1 | 6.5~10.9 | 4.4 |
| S70 | 56 : 70 | -6.7 | 4.0 | - | - |
3 结论
(1) 以氧化石墨烯、三氯化铁为原料用高温水热法制备的还原氧化石墨烯/Fe3O4复合物,Fe3O4颗粒呈正八面体的形貌,尺寸为2~4 μm,还原氧化石墨烯覆盖在Fe3O4颗粒表面。
(2) 在环氧树脂中添加rGO/Fe3O4复合物制备的复合材料,其冲击强度都比纯环氧树脂高,S30添加量为30%的rGO/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料其冲击强度达到27 kJ/m2,比纯环氧树脂的冲击强度提高了58.8%。
(3) 在环氧树脂中添加rGO/Fe3O4复合物使复合材料吸波性能显著提高,rGO/Fe3O4复合物添加量为20%的复合材料其反射率在小于-10 dB的频率范围为7.7~12.3 GHz,有效吸收频宽达4.6 GHz,覆盖了整个X波段,rGO/Fe3O4复合物添加量为30%时,最小反射率达-31.7 dB。
(4) 随着石墨烯含量的提高,rGO/Fe3O4/环氧树脂复合材料达到最小反射率的位置向低频位置移动。这表明,控制石墨烯和Fe3O4的相对含量可调控环氧树脂复合材料的吸波性能。
参考文献
Modification of epoxy resin with epoxidized hydroxyl terminated polybutadiene liquid rubber
[J].
EHTPB液体橡胶改性环氧树脂研究
[J].
Effects of liquid polysulfide rubber on dielectric properties of epoxy resin
[J].
液态聚硫橡胶对环氧树脂介电性能的影响
[J].
Effect of free volume on cryogenic mechanical properties of epoxy resin reinforced by hyperbranched polymers
[J].
Highly toughened and heat-resistant poly(lactic acid) with balanced strength using an unsaturated liquid crystalline polyester via dynamic vulcanization
[J].
Novel epoxy resin adhesives toughened by functionalized poly (ether ether ketone)s
[J].
Effects of hydrolyzed cyclic carbonate toughener on properties of epoxy resin
[J].
水解环状碳酸酯增韧剂对环氧树脂性能的影响
[J].
Tuning the interface in epoxy-based composites and laminates through epoxy grafted graphene oxide enhances mechanical properties
[J].
Low loading of tannic acid-functionalized WS30 nanosheets for robust epoxy nanocomposites
[J].
A dual approach in direct ink writing of thermally cured shape memory rubber toughened epoxy
[J].
Toughening epoxy asphalt binder using core-shell rubber nanoparticles
[J].
A nano-TiO2/regenerated cellulose biohybrid enables simultaneously improved strength and toughness of solid epoxy resins
[J].
Study on mechanical property of SiO2-ESBS/EP
[J].
SiO2-ESBS/环氧树脂复合材料的力学性能研究
[J].
Research on the toughening mechanism of modified nano-silica and silane molecular cages in the multi-scale microfracture of cement-epoxy composite
[J].
Preparation and performance of liquid crystal polyurethane epoxy resin composites
[J].
液晶聚氨酯/环氧树脂复合材料的制备与性能
[J].
Performance of resin system of E-51 toughened by liquid-crystalline epoxy resin
[J].
液晶环氧树脂增韧改性E-51树脂体系性能研究
[J].
Improvements in thermal, mechanical, and dielectric properties of epoxy resin by chemical modification with a novel amino-terminated liquid-crystalline copoly (ester amide)
[J].
Microwave absorption properties of porous NiZn ferrite powders synthesized by solution combustion method: Effect of fuel contents
[J].
Achievement of superior microwave absorption performance and ultra-wide regulation frequency range in Fe-Co-Nd via tuning the phase constitution and crystallinity
[J].
Investigation of Ku band microwave absorption of three-layer BaFe12O19, carbon-fiber@Fe3O4, and graphene@BaFe12O19@Fe3O4 composite
[J].
Enhanced anti-corrosion and microwave absorption performance with carbonyl iron modified by organic fluorinated chemicals
[J].
Mushroom cap-shaped porous carbon particles with excellent microwave absorption properties
[J].
Chitosan-derived carbon aerogels with multiscale features for efficient microwave absorption
[J].
Tunable microwave absorption performance of carbon fiber-reinforced reaction bonded silicon nitride composites
[J].
Low frequency electromagnetic parameters and absorbing heat generation properties of carbon nanotubes
[J].
碳纳米管材料低频电磁参数及吸波产热特性
[J].
Controlled reduction of graphene oxide laminate and its applications for ultra-wideband microwave absorption
[J].
Cubic-like Co/NC composites derived from ZIF-67 with a dual control strategy of size and graphitization degree for microwave absorption
[J].MOFs with high tunability are considered ideal candidates as microwave-absorbing materials. Strict experimental conditions can ensure the repeatability and maximize the potential of such materials. In this study, cubic ZIF-67 carbides synthesized at different solution temperatures showed an adjustable average size, and then by adjusting the calcination temperature we could control the degree of graphitization, so as to explore the synergistic effect of these two aspects to achieve an in-depth understanding of the electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption properties. The results showed that sample 30-600 (with the former number referring to the synthesis temperature and the latter to the calcination temperature) showed the widest effective absorption bandwidth (5.75 GHz, 1.8 mm) and the optimal reflection loss (-56.92 dB, 2.1 mm). The best matching electromagnetic parameters were obtained under the synergistic action of a smaller particle size and appropriate degree of graphitization, so as to achieve strong attenuation characteristics under low electromagnetic wave reflection. The microwave loss mechanism of the sample mainly involved dielectric losses, such as from conductance loss, dipole polarization, and interface polarization. Starting from the experimental details, this work proposes a dual control strategy for developing microwave-absorbing materials with both simplicity and practicability, which provides a useful reference for other microwave absorbents synthesized at room temperature.
Self-assembly of ternary hollow microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption and controllable microwave absorption properties
[J].In this study, we report a simple and efficient two-step method consisting of water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion technique and subsequent annealing process for synthesizing the hollow reduced graphene oxide microspheres embedded with Co nanoparticles (Air@rGO€Co). The microspheres showed good electromagnetic properties because of the coexistence of magnetic loss and dielectric loss to microwaves. The minimum reflection loss (RL) value of S reaches -68.1 dB at 13.8 GHz with a thickness of 2.2 mm, and the absorption bandwidth (lower than -10 dB) is 7.1 GHz covering from 10.9 GHz to 18.0 GHz. More interestingly, we can easily controll the microwave absorbing properties of the microspheres by changing the ratio of the two components in the composites. The excellent electromagnetic match at the corresponding resonance peaks for dielectric and magnetic loss play an important role in improving microwave absorption property. Our study provides a good potential method for preparation of lightweight microwave absorbing materials.
Silica particles wrapped with poly (aniline-co-pyrrole) and reduced graphene oxide for advanced microwave absorption
[J].
Air@rGO€Fe3O4 microspheres with spongy shells: self-assembly and microwave absorption performance
[J].
Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials
[J].
3D-printed carbon fiber/polyamide-based flexible honeycomb structural absorber for multifunctional broadband microwave absorption
[J].
Influence of serrated edge and rectangular strips of MWCNT bucky paper on the electromagnetic properties of glass fiber/epoxy resin composites
[J].