20Cr1Mo1VTiB耐热钢具有良好的综合性能,是制造火力发电厂高温螺栓和工作在570℃以下的超高压机制螺栓或阀杆的材料。添加碳化物稳定元素V、Ti和晶界强化元素B,可提高这种钢的持久强度[1,2]。龚雪婷等[2]研究了热处理工艺对20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢组织和性能的影响,发现1030℃淬火+720℃回火处理使具有较好强韧性匹配。A.Zieliński[3,4]研究了9% Cr钢和7CrMoVTiB10-10钢在高温长期服役下的组织和性能,发现9% Cr钢中的Laves相使其冲击韧性恶化。在7CrMoVTiB10-10钢的高温时效过程中基体发生回复,板条贝氏体组织消失并析出M23C6、M2C及M6C碳化物,使其力学性能降低。Guo[5]研究了20Cr32Ni1Nb钢,发现在时效过程中NbC和M23C6的粗化和NbC在枝晶边界向G相转变降低了材料的力学性能。Chen等[6]认为,含Ti、Mo的钢更容易在铁素体基体中产生纳米级碳化物,使材料的强度提高。
1 实验方法
20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢的化学成分列于表1。用真空炉冶炼50 kg钢锭,开坯后锻成直径为18 mm的棒材,锻后缓冷退火。用线切割切取拉伸和冲击试样并对其进行热处理:在1030℃保温1 h后油冷;在720℃保温2 h空冷,然后在500℃分别时效0 h、50 h、100 h、300 h、500 h、1000 h、2000 h。
表1 20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢的化学成分(%,质量分数)
Table 1
| C | Cr | Mo | V | Ti | B | Si | Mn | S | P | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.22 | 1.17 | 1.02 | 0.91 | 0.056 | 0.004 | 0.042 | 0.28 | 0.0015 | 0.0049 | 0.0092 | 0.0053 |
在WE-300型拉伸试验机上进行拉伸实验,采用d0=5 mm的标准试样。在JBN-300B型冲击试验机上进行冲击试验,采用10 mm×10 mm×55 mm的V型缺口试样。将长期时效后的试样研磨抛光后用4%硝酸酒精溶液侵蚀,用Olympus GX51图像分析仪观察金相组织,用Zeiss SUPRATM场发射扫描电子显微镜观察析出相形貌,用PHILIPS APD-10型X射线衍射仪分析相结构。将从时效处理后的试样上切取0.3 mm厚的样品磨成50 μm厚的薄片,用6%的高氯酸酒精溶液电解双喷、低温减薄,用JEM-2100透射电子显微镜观察板条贝氏体和析出相形貌,操作电压为200 kV。
2 实验结果
2.1 微观组织
图1
图1
20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢热处理后的组织
Fig.1
The microstructures of 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel after quenching at 1030℃ for 1 h, and then oil cooling (a) 1030℃×1 h quenching and then oil cooling+720℃×2 h tempering and air cooling; (b) 1030℃×1 h quenching and then oil cooling
图2
图2
时效时间对20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢显微组织的影响
Fig.2
Effect of aging time on the microstructures of 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel (a) 500 h; (b) 1000 h; (c) 2000 h
图3
图3
时效不同时间后20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢中板条贝氏体的形貌
Fig.3
Lath bainite morphologies in the 20Cr1Mo1V-TiB bolt steel aged for different times (a) 0 h; (b) 1000 h; (c) 2000 h
2.2 析出相分析
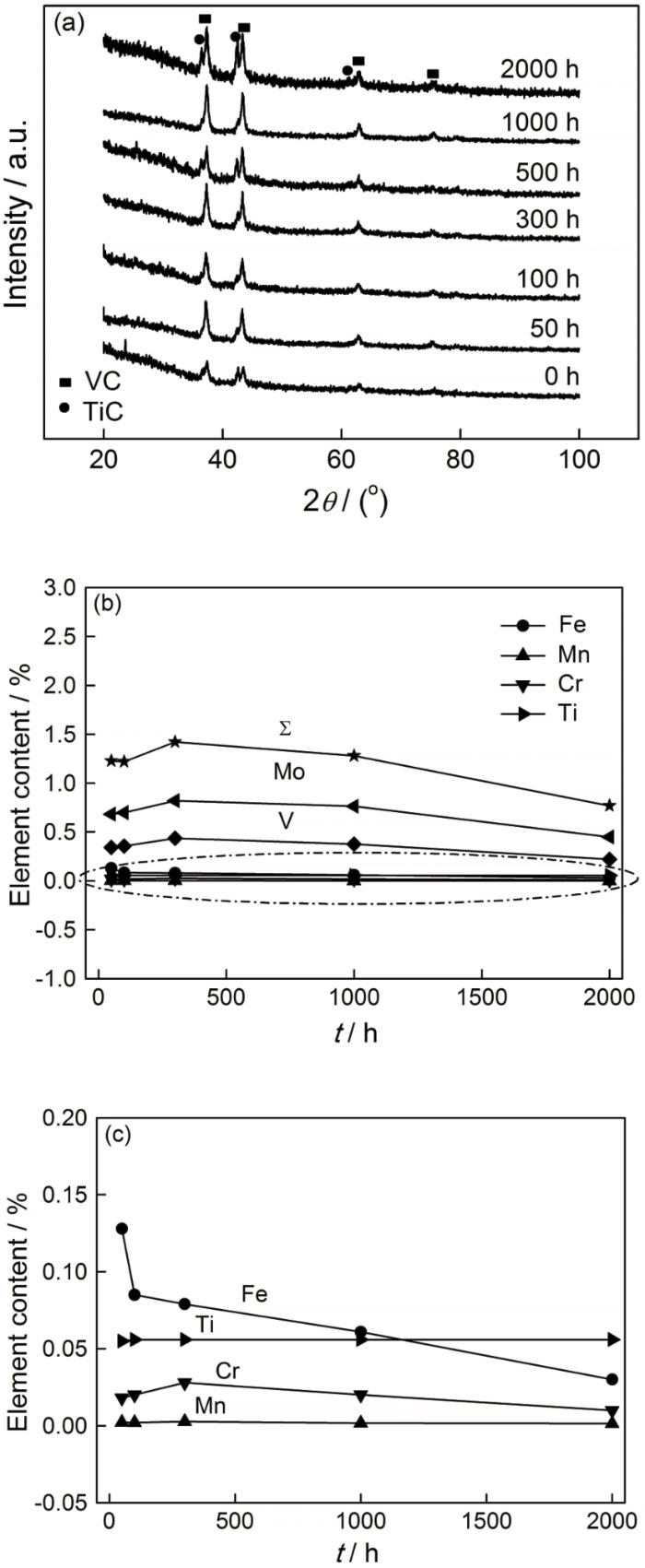
图4
图4
时效不同时间后20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢中的析出相及其含量与时效时间的关系
Fig.4
Analysis of precipitates in the 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel aged for different times. (a) XRD pattern of precipitates; (b) Elements in the precipitates as a function of aging time; (c) An enlarged view of the parts in Figure 4 (b)
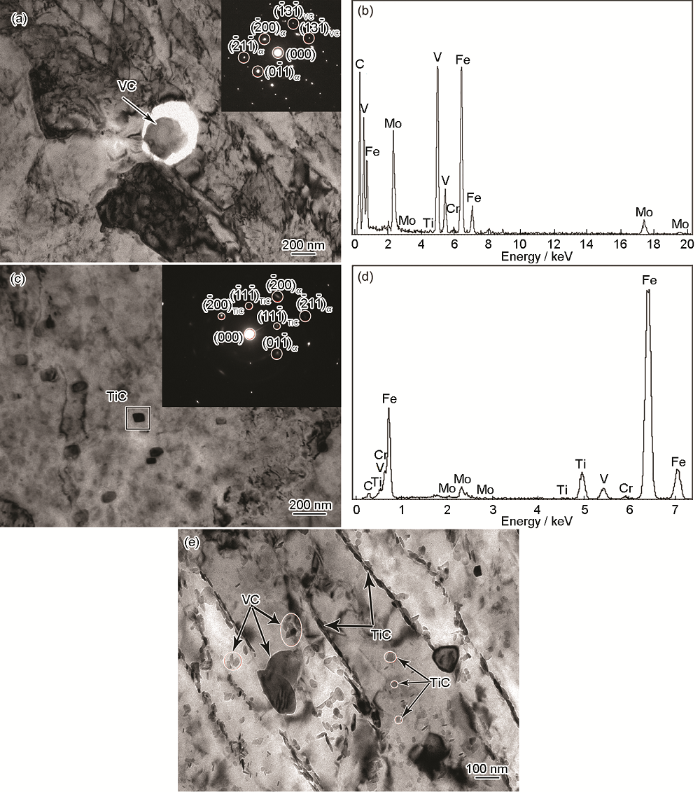
20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢时效2000 h后析出相的形貌和能谱,如图5所示,可见其中的椭球状碳化物为VC(图5a)。能谱分析结果表明:VC中固溶了Mo、Cr等强化元素(图5b),方形碳化物为TiC(图5c),TiC中固溶了Mo、V、Cr等强化元素(图5d),组织中还有尺寸细小的碳化物(图5e)。碳化物中的椭球状物为VC,主要分布在板条内部。纯TiC一般呈不规则形状,固溶Mo、V等合金元素使其形状发生变化[12]。根据对图4b的相分析和相关研究结果[13,14],长条状和方形析出物均为TiC,分布于贝氏体板条边界和板条内部。在时效过程中,合金元素Mo、V的扩散,使TiC以不同形状分布在基体组织中。
图5
图5
20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢时效2000 h析出相的形貌和能谱
Fig.5
Morphologies and energy spectra of precipitates in the 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel after aging for 2000 h (a) Ellipsoidal VC and its diffraction pattern; (b) Energy spectrum analysis of VC; (c) Square TiC and its diffraction pattern; (d) TiC energy spectrum analysis; (e) TiC morphology
3 讨论
3.1 第二相的强化作用
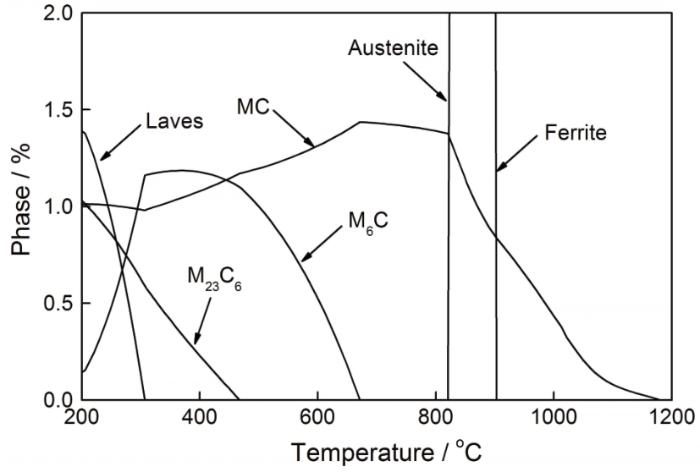
对微观组织的分析结果表明,20Cr1Mo1VTiB钢时效后仍为贝氏体组织,VC和TiC相分布在晶界、晶内及板条内。使用JmatPro软件计算出的20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢的平衡相图表明,螺栓钢的主要强化相为MC,析出峰值温度区间为700~800℃,在1200℃完全回溶(图6)。
图6
时效0~2000 h后的试样,其组织中分布着大量细小的碳化物(图7a,c,e)。在放大图中可见,时效前组织中的碳化物多为椭球状VC,长轴尺寸为5~26 nm。长条状TiC长15~31 nm,宽约3 nm,弥散分布于板条界及板条内,且能看到其对位错的阻碍作用(图7b)。在时效1000 h的组织中位错较少,椭球状VC长轴尺寸为6~23 nm,长条状TiC长10~35 nm,宽约4 nm (图7d)。在时效2000 h的组织中观察到大量方形碳化物,平均尺寸为8~25 nm,长条状和椭球状碳化物减少 (图7f)。时效时间从0 h延长到2000 h,组织中的碳化物尺寸变化不大,因为20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢中的合金元素Mo降低了碳化物成核的势垒[13]。在碳化物的粗化阶段,晶格中能量较低的Mo元素部分替代了晶格中的Ti元素,减缓了碳化物粗化的速度[15]。20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢组织中细小碳化物的弥散强化作用使其能在高温保持较高的强度。
图7
图7
时效不同时间后20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢中析出相的TEM照片
Fig.7
TEM analysis of precipitates in the 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel treated for different aging times (a)、(b) 0 h; (c)、(d) 1000 h; (e)、(f) 2000 h
3.2 20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢的力学性能
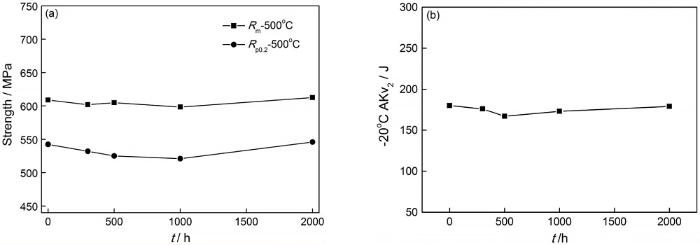
图8
图8
时效时间对20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢力学性能的影响
Fig.8
Effect of aging time on mechanical properties in the 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel (a) Tensile strength at 500℃; (b) impact toughness at -20℃
表2 20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢力学性能的执行标准
Table 2
| Mechanical Property | Rm/MPa (500℃) | Rp0.2/MPa (500℃) | - 2 0 ℃ ) Akv2/J ( |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental value | 605.5 | 537.3 | 168 |
| Required value | ≥543 | ≥507 | ≥70 |
4 结论
(1) 在20Cr1Mo1VTiB钢的时效过程中贝氏体组织形成包体。随着时效时间的延长包体尺寸减小,由时效前的13 μm减小到时效2000 h后的9 μm。
(2) 20Cr1Mo1VTiB钢时效前的组织为板条贝氏体,板条宽度细小且边界清晰,平均尺寸约为191 nm;时效1000 h后板条的边界发生软化,时效2000 h后板条的宽度明显增大,其平均尺寸约为420 nm。
(3) 20Cr1Mo1VTiB钢长时间时效后的主要强化相为VC和TiC,时效2000 h后碳化物没有明显长大,其弥散强化和位错强化使该钢具有较高且稳定的强韧性。
参考文献
Effect of long-term aging on the microstructure and mechanical properties of T23 steel weld metal without post-weld heat treatment
[J].
Effect of heat treatment process on microstructure and properties of 20Cr1Mo1VTiB bolt steel
[J].
热处理工艺对20Cr1Mo1VTiB螺栓钢组织及性能的影响
[J].
Influence of long-term ageing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of T24 steel
[J].
Influence of long-term service on microstructure, mechanical properties, and service life of HCM12A steel
[J].
Effect of long-term aging on microstructural stabilization and mechanical properties of 20Cr32-Ni1Nb steel
[J].
Precipitation hardening of high-strength low-alloy steels by nanometer-sized carbides
[J].
Effects of vanadium on microstructure and mechanical properties of a wrought nickel-based superalloy
[J].
V元素对铁镍基变形高温合金GH4061组织和性能的影响
[J].
High temperature creep characteristics of in-situ micro-/nano-meter TiC dispersion strengthened 304 stainless steel
[J].
原位微米/纳米TiC颗粒弥散强化304不锈钢的高温蠕变特性
[J].
Relationship between mechanical behavior and microstructure for an ultra-high strength maraging steel
[J].
超高强度马氏体时效钢的力学行为与微观组织演化的关系
[J].
Effect of microstructure on the strength of 25CrMo48V martensitic steel tempered at different temperature and time
[J].
Effect of long-term aging on microstructure and local behavior in the heat-affected zone of a Ni-Cr-Mo-V steel welded joint
[J].
Quantitative analysis on hydrogen trapping of TiC particles in steel
[J].
Stability of (Ti, M)C (M=Nb, V, Mo and W) carbide in steels using first-principles calculations
[J].
TiC precipitation induced effect on microstructure and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel
[J].
Modelling coarsening behaviour of TiC precipitates in high strength, low alloy steels
[J].
Effects of interphase TiC precipitates on tensile properties and dislocation structures in a dual phase steel
[J].